www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Dell™ Dimension™ E520
Gebruikershandleiding
Model DCSM
FlexBay voor optioneel
diskettestation of
mediakaartlezer
lampje van vaste schijf
microfoonaansluiting
hoofdtelefoonconnector
Lampje van cd-
of dvd-station
Eject-knop cd- of dvd-station
controlelampjes
USB 2.0-connectoren (2)
vergrendeling
behuizing
Servicelabel
activiteitslampje
aan-/uit-knop
netkabelconnector
USB 2.0-connectoren (6)
optionele VGA-videoconnector
(geïntegreerd)
netwerkadapter
geluidsconnectoren (geïntegreerd) (6)
kaartsleuven voor PCI Express x16
(1), PCI (2), PCI Express x1 (1)
PCI Express grafische kaart

Opmerkingen, kennisgevingen en waarschuwingen
OPMERKING: Een OPMERKING geeft belangrijke informatie weer voor optimaal gebruik van de computer.
KENNISGEVING: Een KENNISGEVING wijst op mogelijke schade aan hardware of verlies van gegevens en geeft aan
hoe u het probleem kunt voorkomen.
VOORZICHTIG: een WAARSCHUWING duidt het risico van schade aan eigendommen, lichamelijk letsel of overlijden aan.
Als u een Dell™-computer uit de n-serie hebt aangeschaft, zijn de verwijzingen naar de Microsoft
®
Windows
®
-
besturingssystemen in dit document niet van toepassing.
Afkortingen en acroniemen
Zie voor een volledige lijst van afkortingen en acronymen de "Verklarende woordenlijst" op pagina 153.
____________________
Informatie in deze tekst kan worden gewijzigd zonder voorafgaande kennisgeving.
© 2006 Dell Inc. All rights reserved.
Het is ten strengste verboden om de inhoud zonder schriftelijke toestemming van Dell Inc. op enigerlei wijze te reproduceren.
Handelsmerken in deze tekst: Dell, het DELL-logo, Inspiron, Dell Precision, Dimension, OptiPlex, Latitude, PowerEdge, PowerVault,
PowerApp, DellNet, Dell TravelLite, Strike Zone, en PowerConnect zijn handelsmerken van Dell Inc.; Bluetooth is een geregistreerd
handelsmerk van Bluetooth SIG, Inc. dat door Dell in licentie wordt gebruikt; Intel en Pentium zijn geregistreerde handelsmerken van de Intel
Corporation; Microsoft, Windows, en Outlook zijn geregistreerde handelsmerken van de Microsoft Corporation; ENERGY STAR is een
geregistreerd handelsmerk van de Amerikaanse Environmental Protection Agency.
Overige handelsmerken en handelsnamen worden in deze tekst gebruikt om te verwijzen of naar de eenheden van de merken en namen of naar
hun producten. Dell Inc. verwerpt elk particulier belang voor handelsmerken en handelsnamen anders dan haar eigen belang.
Model DCSM
Juli 2006 P/N PH522 Rev. A00

Inhoud 3
Inhoud
Informatie vinden . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1 Uw computer installeren en gebruiken . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Een printer installeren . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Printerkabel
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Een printer aansluiten
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Verbinding maken met het internet
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Uw internetverbinding instellen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Cd's en dvd's afspelen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Het volume aanpassen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Het beeld aanpassen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Cd's en dvd's kopiëren
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Hoe kan ik een cd of dvd kopiëren
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Lege cd's en dvd's gebruiken
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Nuttige tips
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Een mediakaartlezer gebruiken (optioneel)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Twee monitoren aansluiten
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Twee monitors met VGA-connectoren aansluiten
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Eén monitor aansluiten met een VGA-connector
en één monitor aansluiten met en DVI-connector
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Een TV aansluiten
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Beeldscherminstellingen wijzigen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Een thuis- en bedrijfsnetwerk instellen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Aansluiten op een netwerkadapter
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
De wizard Netwerk instellen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Power Management (Energiebeheer)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Stand-bymodus
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Slaapstand
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Eigenschappen voor energiebeheer
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26

4 Inhoud
Hyper-Threading . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Over RAID-configuraties
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Controleren of RAID werkt
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
RAID-level 1
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
RAID-problemen oplossen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Herstellen na het uitvallen van meerdere vaste schijfstation
met behulp van het hulpprogramma Intel
®
RAID Option ROM. . . . . . . 30
Herstellen van een uitval van één enkele vaste schijf
met behulp van de Intel Matrix Storage Manager
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Uw computer instellen op de modus RAID-Enabled (RAID ingeschakeld)
. 31
Dell™ DataSafe (Optioneel)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
2 Problemen oplossen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Tips voor het oplossen van problemen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Problemen met de batterij
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Problemen met een station
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Problemen met het cd- en dvd-station
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Problemen met de vaste schijf
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
E-mail-, modem- en internetproblemen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Foutberichten
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Problemen met het toetsenbord
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Lockups en problemen met de software
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
De computer start niet op
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
De computer reageert niet
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Een programma reageert niet meer
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Een programma loopt regelmatig vast
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Een programma werd ontworpen voor een eerdere versie
van het Microsoft
®
Windows
®
besturingsysteem . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Er verschijnt een blauw scherm
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Andere softwareproblemen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Problemen met een mediakaartlezer
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Geheugenproblemen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Problemen met de muis
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41

Inhoud 5
Netwerkproblemen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Problemen met de voeding
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Problemen met de printer
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Problemen met de scanner
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Problemen met het geluid en de luidsprekers
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Geen geluid uit de luidsprekers
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Geen geluid uit de hoofdtelefoon
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Problemen met video en de monitor
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Als het scherm leeg is
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Als het scherm moeilijk te lezen is
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
3 Hulpmiddelen voor het oplossen van problemen. . . . . . . . 49
Controlelampjes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Dell Diagnostics
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Hoofdmenu van Dell Diagnostics
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Stuurprogramma’s
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Wat is een stuurprogramma?
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Stuurprogramma's controleren
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Een stuurprogramma opnieuw installeren
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Software- en hardwareconflicten oplossen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Uw besturingssysteem herstellen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Systeemherstel van MicrosoftWindows XP
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Dell PC Restore van Symantec gebruiken
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Plaats de cd voor het besturingssysteem.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
4 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Voordat u begint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Aanbevolen hulpmiddelen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Uw computer uitschakelen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Voordat u aan de computer gaat werken
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Vooraanzicht van de computer
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65

6 Inhoud
Achteraanzicht van de computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Connectoren op het achterpaneel
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
De computerbehuizing verwijderen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
De binnenkant van uw computer
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Systeemkaartcomponenten
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Geheugen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Overzicht van DDR2-geheugen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Geheugen aanspreken bij 4-GB-configuraties
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Geheugen installeren
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Geheugen verwijderen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Kaarten
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
PCI-kaarten
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
PCI Express-kaarten
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Stationspaneel
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Stationpaneel verwijderen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Inzetstuk stationpaneel verwijderen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Inzetstuk stationspaneel terugplaatsen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Stationspaneel terugplaatsen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Stations
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Stationskabels aansluiten
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Interfaceconnectoren voor station
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Stationskabels aansluiten en loskoppelen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Harde schijf
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Een vaste schijf verwijderen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Een harde schijf installeren
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Tweede vast schijf toevoegen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Diskettestation
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Een diskettestation verwijderen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Een diskettestation installeren
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Mediakaartlezer
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Een mediakaartlezer verwijderen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Een mediakaartlezer installeren
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103

Inhoud 7
cd/dvd-station . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Een cd/dvd-station verwijderen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Een cd/dvd-station installeren
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Batterij
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
De batterij vervangen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
De computerbehuizing terugplaatsen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
5 Bijlage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Specificaties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
System Setup
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Overzicht
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
System Setup openen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
System Setup-opties
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Bootsequence (Opstartvolgorde)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Vergeten wachtwoorden wissen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
CMOS-instellingen wissen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Uw computer reinigen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Computer, toetsenbord en monitor
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Muis
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Diskettestation
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Cd's en dvd's
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Technische ondersteuningsbeleid van Dell (alleen voor de V.S.)
. . . . . . 129
Definitie van door Dell geïnstalleerde software en randapparatuur
. . . 129
Definitie van software en randapparatuur van derden
. . . . . . . . . . 129
FCC-kennisgeving (alleen V.S.)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
FCC Klasse B
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Contact met Dell
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Verklarende woordenlijst . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Index
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165

8 Inhoud

Informatie vinden 9
Informatie vinden
OPMERKING: Sommige functies of media zijn optioneel en worden niet bij de computer geleverd. Sommige functies
of media zijn in bepaalde landen niet beschikbaar.
OPMERKING: Soms wordt er extra informatie bij de computer geleverd.
Waar bent u naar op zoek? Hier kunt u het vinden
• Informatie omtrent garantie
• Voorwaarden (alleen VS)
• Veiligheidsinstructies
• Informatie omtrent wet- en regelgeving
• Informatie omtrent ergonomie
• Licentieovereenkomst voor eindgebruikers
Dell™ Productinformatiehandleiding
• De computer installeren
Installatiediagram

10 Informatie vinden
• Servicelabel en Express Service Code
• Microsoft Windows-licentielabel
Servicelabel en Microsoft
®
Windows
®
-licentie
Deze labels bevinden zich op de computer.
•Gebruik de gegevens op
het servicelabel wanneer
u naar
support.dell.com
gaat of contact opneemt
met de technische
ondersteuning.
•Voer de Express Service
Code in om uw
telefoontje naar de
ondersteuning aan de
juiste persoon te
richten.
• Solutions — Troubleshooting hints and tips, articles
from technicians, and online courses, frequently
asked questions
• Community — Online discussion with other Dell
customers
• Upgrades — Upgrade information for components,
such as memory, the hard drive, and the operating
system
• Customer Care — Contact information, service call
and order status, warranty, and repair information
• Service and support — Service call status and support
history, service contract, online discussions with
technical support
• Reference — Computer documentation, details on my
computer configuration, product specifications, and
white papers
• Downloads — Certified drivers, patches, and software
updates
Dell Support Website — support.dell.com
OPMERKING: Selecteer uw land om de voor u van
toepassing zijnde support-website te bekijken.
OPMERKING: Zakelijke, overheids- en onderwijsklanten
kunnen ook gebruik maken van de aangepaste Dell Premier
Support-website op premier.support.dell.com.
Waar bent u naar op zoek? Hier kunt u het vinden

Informatie vinden 11
• Desktop System Software (DSS)— If you reinstall
the operating system for your computer, you should
also reinstall the DSS utility. DSS bevat belangrijke
updates voor het besturingssysteem en ondersteuning
voor Dell™ 3.5-inch USB-diskettes, Intel
®
-processors,
optische stations en USB-apparaten. DSS is nodig
voor een juiste werking van de Dell-computer. De
software spoort automatisch de computer en
besturingssysteem op en installeert de juiste updates
voor de configuratie.
U downloadt
DSS
als volgt:
1
Ga naar
support.dell.com
en klik op
Downloads
.
2
Voer uw sevicelabel of productmodel in.
3
Klik in de keuzelijst
Download Category
(Download-
categorie) op
All
(Alles).
4
Selecteer het besturingssysteem en de taal van het
besturingssysteem voor uw computer en klik op
Submit
(Verzenden)
.
5
Blader onder
Select a Device
(Selecteer een apparaat)
naar
System and Configuration Utilities
(Hulpprogramma’s voor systeem en configuratie) en klik
op
Dell Desktop System Software
.
• Met Windows XP werken
• Met programma's en bestanden werken
• Het bureaublad aanpassen
Help en ondersteuning van Windows
1
Klik op
Start
→
Help en ondersteuning
.
2
Geef met een of meer woorden een beschrijving van het
probleem en klik vervolgens op het pijlpictogram.
3
Klik op het onderwerp dat uw probleem beschrijft.
4
Volg de instructies op het scherm.
Waar bent u naar op zoek? Hier kunt u het vinden

12 Informatie vinden

Uw computer installeren en gebruiken 13
Uw computer installeren en gebruiken
Een printer installeren
KENNISGEVING: Zorg dat de installatie van het besturingssysteem is voltooid voordat u een printer op de
computer aansluit.
Raadpleeg de bij de printer geleverde documentatie voor de volgende informatie over de installatie:
• Bijgewerkte stuurprogramma's verkrijgen en installeren.
• De printer op de computer aansluiten.
• Papier laden en de toner of inktcassette installeren.
Zie de gebruikershandleiding van de printer of neem contact op met de fabrikant van de printer voor
technische ondersteuning.
Printerkabel
De printer wordt met een USB-kabel op de computer aangesloten. Sommige printers worden zonder
printerkabel geleverd. Ga dus bij de aankoop van een kabel na of deze compatibel is met de printer.
Als u de printerkabel en de computer tegelijkertijd koopt, vindt u de kabel bij levering in de
computerdoos.
Een printer aansluiten
OPMERKING: USB-apparaten kunnen worden aangesloten terwijl de computer is ingeschakeld.
1
Als u de installatie van het besturingssysteem nog niet hebt voltooid, doet u dit alsnog.
2
Sluit de USB-printerkabel aan op de USB-connectoren van de computer en de printer.
De USB-connectoren passen slechts op één manier.

14 Uw computer installeren en gebruiken
3
Schakel de printer in en vervolgens de computer. Als het venster
Wizard Hardware toevoegen
verschijnt,
klikt u op
Annuleren
.
4
Indien nodig installeert u het printerstuurprogramma. Raadpleeg de documentatie bij de printer werd
geleverd.
Verbinding maken met het internet
OPMERKING: Internetaanbieders en hun aanbod zijn per land verschillend.
Als u verbinding wilt maken met het internet, hebt u een modem of netwerkverbinding nodig en een
internetaanbieder (ISP). Uw internetaanbieder biedt een of meer van de volgende opties voor
internetverbinding.
• Inbelverbindingen die internettoegang via een telefoonlijn bieden. Inbelverbindingen zijn aanzienlijk
trager dan DSL- en kabelmodemverbindingen.
• DSL-verbindingen die internettoegang met hoge snelheid via een bestaande telefoonlijn bieden. Met
een DSL-verbinding kunt u bellen en internetten tegelijk.
• Kabelmodemverbindingen die internettoegang met hoge snelheid bieden via een plaatselijke kabel-tv-lijn.
Als u een inbelverbinding gebruikt, moet u voor het instellen van de internetverbinding een telefoonlijn
aansluiten op de modemconnector op de computer en op de telefoonaansluiting. Gebruikt u een DSL- of
kabelmodemverbinding, neem dan contact op met uw internetaanbieder voor installatie-instructies.
1 USB-connector op de computer 2 USB-printerkabel 3 USB-connector op de printer
2
1
3

Uw computer installeren en gebruiken 15
Uw internetverbinding instellen
U stelt als volgt een internetverbinding in met een snelkoppeling naar de internetaanbieder:
1
Sla eventuele geopende bestanden op en sluit deze en sluit eventuele geopende programma's af.
2
Dubbelklik op het pictogram
van de internetaanbieder op het bureaublad van Microsoft
®
Windows
®
.
3
Volg de instructies op het scherm om het instellen te voltooien.
Doe het volgende als er geen pictogram van de internetaanbieder op het bureaublad staat of als u een
verbinding via een andere aanbieder wilt instellen:
1
Sla eventuele geopende bestanden op en sluit deze en sluit eventuele geopende programma's af.
2
Klik op de knop
Start
en vervolgens op
Internet Explorer
.
Het venster
Wizard Nieuwe verbinding
verschijnt.
3
Klik op
Verbinding met het Internet maken
.
4
Klik in het volgende venster op de juiste optie:
• Als u geen internetaanbieder hebt en er een wilt selecteren, klikt u op
Ik wil zelf een Internet-
provider in een lijst selecteren
.
• Als u al installatie-informatie van uw internetaanbieder hebt gekregen, maar nog geen installatie-cd,
klikt u op
Ik wil handmatig een verbinding instellen
.
• Hebt u wel een cd, dan klikt u op
Ik heb een cd-rom met software van een Internet-provider
.
5
Klik op
Volgende
.
Als
Ik wil handmatig een verbinding instellen
hebt gekozen, gaat u naar stap 6. Anders volgt u de
instructies op het scherm op om het instellen te voltooien.
OPMERKING: Neem contact op met uw internetaanbieder als u niet weet welke verbindingstype u moet
selecteren.
6
Klik op de juiste optie onder
Op welke manier wilt u contact met het Internet maken?
en vervolgens
op
Volgende
.
7
Gebruik de installatie-informatie gekregen van de internetaanbieder om de installatie te voltooien.
Zie "E-mail-, modem- en internetproblemen" op pagina 35 als u problemen hebt bij het maken van een
verbinding met het internet. Als u nu geen verbinding kunt maken, maar dit eerder wel is gelukt,
functioneert het netwerk mogelijk niet. Neem contact op met uw internetaanbieder of probeer het later
nog eens.

16 Uw computer installeren en gebruiken
Cd's en dvd's afspelen
KENNISGEVING: Oefen geen druk uit op de cd- of dvd-lade wanneer u deze opent of sluit. Zorg dat de lade gesloten
is wanneer u het station niet gebruikt.
KENNISGEVING: Verplaats de computer niet tijdens het afspelen van cd's of dvd's.
1
Druk op de eject-knop op de voorkant van het station.
2
Plaats de schijf met het label omhoog in het midden van de lade.
3
Druk op de eject-knop of duw de lade zachtjes naar binnen.
Zie de meegeleverde cd-software om cd's te formatteren voor het opslaan van gegevens, het maken van
muziek-cd's of het kopiëren van cd's.
OPMERKING: Ga na of u aan alle auteursrechten voldoet wanneer u cd's maakt.
Een cd-speler bevat de volgende basisknoppen:
Afspelen
Terugspoelen binnen het huidige nummer
Pauze
Vooruitspoelen binnen het huidige nummer
Stoppen
Naar het vorige nummer
Uitwerpen
Naar het volgende nummer

Uw computer installeren en gebruiken 17
Een dvd-speler bevat de volgende basisknoppen:
Klik voor meer informatie over het afspelen van cd's of dvd's op Help op de cd- of dvd-speler (indien
beschikbaar).
Het volume aanpassen
OPMERKING: Wanneer de speakers zijn gedempt, hoort u niet dat er een cd of dvd wordt afgespeeld.
1
Klik op
Start
, wijs
Alle programma's
→
Bureau-accessoires
→
Entertainment
aan en klik op
Volumeregeling
.
2
Klik in het venster
Volumeregeling
op de balk in de kolom
Volumeregeling
en schuif deze omhoog of
omlaag om het volume te verhogen of te verlagen.
Klik voor meer informatie over volumeregelingsopties op Help in het venster Volumeregeling.
Het beeld aanpassen
Als er een foutbericht verschijnt dat de huidige resolutie en kleurdiepte te veel geheugen in beslag nemen
en dat de dvd hierdoor niet kan worden afgespeeld, moet u de beeldschermeigenschappen aanpassen.
1
Klik op de knop
Start
en klik op
Configuratiescherm
.
2
Klik onder
Kies een categorie
op
Vormgeving en thema's
.
3
Klik onder
Kies een taak...
op
De schermresolutie wijzigen
.
4
Klik in het venster
Eigenschappen voor Beeldscherm
op de balk in
Beeldschermresolutie
en verschuif
deze om de instelling te wijzigen in
800 bij 600 pixels
.
5
Selecteer in het vervolgkeuzemenu onder
Kleurkwaliteit
de optie
Gemiddeld (16 bits)
.
6
Klik op
OK
.
Stoppen
Het huidige hoofdstuk opnieuw beginnen
Afspelen
Vooruitspoelen
Pauze
Achteruitspoelen
Eén frame vooruit in de pauzemodus
Naar de volgende titel of het volgende hoofdstuk
De huidige titel of het huidige hoofdstuk doorlopend
afspelen
Naar de vorige titel of het vorige hoofdstuk
Uitwerpen

18 Uw computer installeren en gebruiken
Cd's en dvd's kopiëren
OPMERKING: Ga na of u aan alle auteursrechten voldoet wanneer u cd's of dvd's maakt.
Dit hoofdstuk is alleen van toepassing op computers met een cd-rw-, dvd+/-rw- of cd-rw/dvd (combi) -station.
OPMERKING: De typen cd- of dvd-stations die door Dell worden aangeboden, verschillen per land.
In de onderstaande instructies wordt uitgelegd hoe u een kopie van een CD of een DVD maakt. U kunt
Sonic DigitalMedia ook voor andere dingen gebruiken, zoals het maken van muziek-cd's van audiobestanden
die op de computer zijn opgeslagen, of van reservekopieën van belangrijke gegevens. Voor hulp opent u
Sonic DigitalMedia en klikt u op het vraagteken rechts boven in het scherm.
Hoe kan ik een cd of dvd kopiëren
OPMERKING: Cd-rw/dvd-combostations kunnen niet naar dvd-media schrijven. Als u opnameproblemen hebt met
een cd-rw/dvd-combostation, controleert u op beschikbare softwarepatches op de ondersteuningswebsite van
Sonic op www.sonic.com.
De stations voor beschrijfbare dvd's die in Dell™-computers zijn geïnstalleerd, kunnen dvd+/-r-, dvd+/-
rw- en dvd+r dl (dubbele laag)-media lezen en ernaar schrijven, maar kunnen niet naar dvdram- of dvd-r
dl-media schrijven en deze waarschijnlijk ook niet lezen.
OPMERKING: De meeste commerciële dvd's zijn auteursrechtelijk beschermd en kunnen niet met Sonic
DigitalMedia worden gekopieerd.
1
Klik op
Start
→
Programma’s
→
Sonic
→
DigitalMedia Projects
→
Copy
→
Disc Copy
.
2
U kopieert de cd of dvd als volgt:
•
Als u maar één cd/dvd-station hebt
, gaat u na of de instellingen correct zijn en klikt u op
Disc Copy
.
De computer leest de bron-cd of -dvd en kopieert de gegevens naar een tijdelijke map op de vaste
schijf van de computer.
Plaats een lege cd of dvd in het station wanneer hierom wordt gevraagd, en klik op
OK
.
•
Als u twee cd/dvd-stations hebt
, selecteert u het station waarin u de bron-cd of -dvd hebt geplaatst
en klikt u op
Disc
Copy
. De computer kopieert de gegevens van de bron-cd of -dvd naar de lege cd
of dvd.
Nadat u de bron-cd of -dvd hebt gekopieerd, wordt de cd of dvd die u hebt gemaakt, automatisch
uitgeworpen.

Uw computer installeren en gebruiken 19
Lege cd's en dvd's gebruiken
Cd-rw-stations kunnen naar alleen naar cd-opnamemedia schrijven (inclusief snelle cd-rw-media),
terwijl -dvd-beschrijfbare stations naar zowel cd- als dvd-opnamemedia kunnen schrijven.
Gebruik lege cd-r's om muziek op te nemen of gegevensbestanden permanent op te slaan. Wanneer u
een cd-r hebt gemaakt, kunt u niet opnieuw naar die cd-r schrijven (zie de Sonic-documentatie voor
meer informatie). Gebruik lege cd-rw’s als u gegevens wilt kunnen wissen, opnieuw schrijven of bijwerken.
U kunt lege dvd+/-r's gebruiken om grote hoeveelheden gegevens op te slaan. Wanneer u een dvd+/-r-
schijf hebt gemaakt, kunt u mogelijk niet meer naar die schijf schrijven als de schijf tijdens de laatste fase
van het aanmaakproces is voltooid of afgesloten. Gebruik lege dvd+/-rw's als u de gegevens op de schijf
later wilt wissen, overschrijven of bijwerken.
Cd-beschrijfbare stations
Dvd-beschrijfbare stations
Nuttige tips
• Gebruik Microsoft
®
Windows
®
Explorer om bestanden alleen naar een cd-r of cd-rw te slepen als u
Sonic DigitalMedia hebt gestart en een DigitalMedia -project hebt geopend.
• Gebruik cd-r's om muziek-cd's te branden die u in normale stereoapparatuur wilt afspelen. Cd-rw's
kunnen op de meeste stereoapparatuur, thuis of in de auto, niet worden afgespeeld.
• U kunt geen audio-dvd’s maken met Sonic DigitalMedia.
• MP3-bestanden kunnen alleen op MP3-spelers worden afgespeeld of op computers met MP3-software.
• Commercieel beschikbare dvd-spelers die voor televisies worden gebruikt, ondersteunen niet alle
beschikbare dvd-indelingen. Zie de bij de dvd-speler geleverde documentatie of neem contact op met
de fabrikant voor een lijst met indelingen die door de dvd-speler worden ondersteund.
Mediatype Lezen Schrijven Beschrijfbaar
Cd-rJaJaNee
Cd-rw Ja Ja Ja
Mediatype Lezen Schrijven Beschrijfbaar
Cd-rJaJaNee
Cd-rw Ja Ja Ja
Dvd+r Ja Ja Nee
Dvd-r Ja Ja Nee
Dvd+rw Ja Ja Ja
Dvd-rw Ja Ja Ja
Dvd+r+dl Ja Ja Nee

20 Uw computer installeren en gebruiken
• Gebruik nooit de maximale capaciteit van een lege cd-r of cd-rw. Kopieer bijvoorbeeld nooit een bestand
van 650 MB naar een lege cd van 650 MB. The CD-RW drive needs 1–2 MB of the blank space to finalize
the recording.
• Gebruik een lege cd-rw om het opnemen op cd te oefenen, totdat u vertrouwd bent met de cd-
opnametechnieken. Als u een fout maakt, kunt u de gegevens op de cd-rw wissen en opnieuw proberen.
U kunt lege cd-rw's ook gebruiken om muziekbestandprojecten te testen voordat u ze voorgoed op een
lege cd-r opneemt.
• Zie de Sonic-website op
www.sonic.com
voor extra informatie.
Een mediakaartlezer gebruiken (optioneel)
Met de mediakaartlezer stuurt u gegevens direct naar de computer.
De mediakaartlezer ondersteunt de volgende geheugentypen:
• xD-Picture-kaart
• SmartMedia (SMC)
• CompactFlash Type I en II (CF I/II)
• MicroDrive-kaart
• SecureDigital-kaart (SD)
• MultiMediaCard (MMC)
• Memory Stick (MS/MS Pro)
Zie "Een mediakaartlezer installeren" op pagina 103 voor meer informatie over het gebruik van de
mediakaartlezer.

Uw computer installeren en gebruiken 21
U gebruikt de mediakaartlezer als volgt:
1
Ga na hoe het medium of de kaart moet worden geplaatst.
2
Schuif het medium of de kaart in de juiste sleuf totdat deze volledig in de connector is geplaatst.
Als u weerstand voelt, mag u het medium of de kaart niet forceren. Controleer of de kaart juist is
geplaatst en probeer het opnieuw.
1 xD-Picture-kaart en
SmartMedia (SMC)
2 CompactFlash Type-I en II
(CF I/II) en MicroDrive-kaart
3 Memory Stick (MS/MS Pro)
4 SecureDigital-kaart (SD)/
MultiMediaCard (MMC)
1
3
4
2

22 Uw computer installeren en gebruiken
Twee monitoren aansluiten
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
KENNISGEVING: Wanneer u twee monitors aansluit die beschikken over VGA-connectoren, moet u beschikken
over de optionele DVI-adapter. Wanneer u twee platte monitoren aansluit, moet ten minste een ervan beschikken
over een VGA-connector. Wanneer u een TV aansluit, kunt u daarnaast slechts één monitor (VGA of DVI) aansluiten.
Wanneer u een grafische kaart hebt gekocht die twee monitors ondersteunt, volgt u deze instructies voor
het aansluiten en inschakelen van uw twee monitors In deze instructies vindt u hoe u naar keuze twee
monitors (elk met een VGA-connector), één monitor met een VGA-connector en één monitor met en
DVI-connector of een TV kunt aansluiten.
Twee monitors met VGA-connectoren aansluiten
1
Volg de procedures in "Voordat u begint" op pagina 63.
OPMERKING: Als uw computer beschikt over geïntegreerde audio, kunt u geen van beide monitors aansluiten op
de geïntegreerde videoconnector. Als een geïntegreerde videoconnector wordt afgedekt door een huls, verwijdert
u deze huls niet om de monitor aan te sluiten; de monitor zal niet werken.
2
Sluit een van de monitors aan op de VGA-connector (blauw) op de achterzijde van de computer.
3
Sluit de andere monitor aan op de optionele DVI-adapter en sluit de DVI-adapter aan op de DVI-
connector (wit) op de achterzijde van de computer.

Uw computer installeren en gebruiken 23
Eén monitor aansluiten met een VGA-connector en één monitor aansluiten met en DVI-connector
1
Volg de procedures in "Voordat u begint" op pagina 63.
2
Sluit de VGA-connector op de monitor aan op de VGA-connector (blauw) op de achterzijde van
de computer.
3
Sluit de DVI-connector op de andere monitor aan op de DVI-connector (wit) op de achterzijde van
de computer.
Een TV aansluiten
OPMERKING: U moet een S-videokabel aanschaffen om een TV op uw computer te kunnen aansluiten. Deze is
verkrijgbaar in de meeste zaken voor consumentenelektronica. Deze wordt niet bij uw computer geleverd.
1
Volg de procedures in "Voordat u begint" op pagina 63.
2
Sluit het ene uiteinde van de S-videokabel aan op de optionele TV-OUT-connector op de achterzijde
van de computer.
3
Sluit het andere uiteinde van de S-videokabel aan op de S-video-ingang op uw TV.
4
Sluit de VGA- of DVI-monitor aan.
1 optionele DVDI-adapter 2 DVI-connector (wit) 3 TV-OUT-connector
4 VGA-connector (blauw)
*Niet op alle computers aanwezig.
4
2*
1
3*

24 Uw computer installeren en gebruiken
Beeldscherminstellingen wijzigen
1
Nadat u uw monitors of een TV hebt aangesloten, schakelt u de computer in.
Het Microsoft
®
Windows
®
-bureaublad wordt weergegeven op de primaire monitor.
2
Schakel de clone-modus of de dubbel-bureaubladmodus in in de beeldscherminstellingen.
• In de clone-modus tonen beide monitors het zelfde beeld.
• In de dubbele-bureaubladmodus kunt u objecten van het ene scherm naar het andere slepen,
waardoor u dus feitelijk de beschikbare hoeveelheid werkruimte verdubbelt.
For information on changing the display settings for your graphics card, see the user’s guide in the Help
and Support Center (click the
Start
button, click
Help and Support
, click
User and system guides
, click
Device guides
, and then click the guide for your graphics card).
Een thuis- en bedrijfsnetwerk instellen
Aansluiten op een netwerkadapter
KENNISGEVING: Sluit de netwerkkabel aan op de connector voor de netwerkadapter van de computer. Sluit de
netwerkkabel niet aan op de modemconnector van de computer. Pas op dat u een netwerkkabel niet in de
telefoonaansluiting steekt.
1
Sluit de netwerkkabel aan op de connector voor de netwerkadapter op achterkant van de computer.
Zorg dat de kabel vastklikt en trek er zachtjes aan om te controleren of deze goed vastzit.
2
Sluit het andere uiteinde van de netwerkkabel aan op een netwerkapparaat.
1 connector voor netadapter 2 Netwerkapparaat 3 Netwerkadapterconnector op
de computer
4 netwerkkabel
2
3
4
1

Uw computer installeren en gebruiken 25
De wizard Netwerk instellen
Het besturingssysteem Microsoft
®
Windows
®
XP biedt een wizard Netwerk instellen om u te helpen bij
het delen van bestanden, printers of een internetverbinding tussen computers thuis of van een klein bedrijf.
1
Klik op de knop
Start
, wijs naar
Alle programma's
→
Bureau-accessoires
→
Communicatie
, en klik op
Wizard Netwerk instellen
.
2
Klik in het welkomstscherm op
Volgende
.
3
Klik op
Controlelijst voor het instellen van een netwerk
.
OPMERKING: Wanneer u de verbindingsmethode Deze computer maakt rechtstreeks verbinding met het Internet
kiest, wordt de geïntegreerde firewall ingeschakeld die bij het Windows XP Service Pack is geleverd.
4
Voltooi de controlelijst en de vereiste voorbereidingen.
5
Keer terug naar het venster Wizard Netwerk instellen en volg de instructies op het scherm.
Power Management (Energiebeheer)
Met de energiebeheerfuncties van Microsoft
®
Windows
®
XP kunt u de hoeveelheid elektriciteit die de
computer gebruikt, reduceren wanneer deze is ingeschakeld maar niet wordt gebruikt. Dit is mogelijk
door de energie te beperken tot de monitor of de vaste schijf, of de stand-bymodus of slaapstand te
gebruiken. Wanneer de computer wordt uitgeschakeld vanaf een energiebesparingsmodus, wordt het
Windows-bureaublad teruggezet in de status van voor deze modus.
OPMERKING: Windows XP Professional bevat beveiligings- en netwerkfuncties die niet beschikbaar zijn in
Windows XP Home Edition. Wanneer een computer met Windows XP Professional is aangesloten op een netwerk,
verschijnen er in bepaalde vensters verschillende opties voor beveiliging en netwerken.
Stand-bymodus
Met de stand-bymodus wordt energie bespaard doordat het beeldscherm en de vaste schijf na een time-
out worden uitgeschakeld. Wanneer de computer uit de stand-bymodus komt, wordt deze teruggezet in
de status van voor de stand-bymodus.
U stelt de computer als volgt in om na een bepaalde inactieve periode automatisch in de stand-bymodus
te gaan:
1
Klik op de knop
Start
en klik op
Configuratiescherm
.
2
Klik onder
Kies een categorie
op
Prestaties en onderhoud
.
3
Klik onder
of kies een pictogram...
op
Energiebeheer
.
Wanneer u direct naar de stand-bymodus wilt gaan zonder een inactieve periode af te wachten, klikt u op
de knop Start, daarna op Afsluiten en vervolgens op Stand-by.
U schakelt de stand-bymodus uit door op een toets op het toetsenbord te drukken of de muis te bewegen.
KENNISGEVING: Als de computer uitvalt in de stand-bymodus, kunnen er gegevens verloren gaan.

26 Uw computer installeren en gebruiken
Slaapstand
Met de slaapstand bespaart u energie doordat systeemgegevens naar een gereserveerd gebied op de vaste
schijf worden gekopieerd en de computer wordt uitgeschakeld. Wanneer de computer wordt uitgeschakeld
vanaf de slaapstand, wordt het bureaublad teruggezet in de status
van voor deze modus.
U activeert de slaapstand als volgt:
1
Klik op de knop
Start
en klik op
Configuratiescherm
.
2
Klik onder
Kies een categorie
op
Prestaties en onderhoud
.
3
Klik onder
of kies een pictogram...
op
Energiebeheer
.
4
Definieer de slaapstand-instellingen op het tabblad
Energiebeheerschema's
,
Geavanceerd
en
Slaapstand
.
U schakelt de slaapstand uit door op de aan/uit-knop te drukken. Het kan even duren voordat de slaapstand
is uitgeschakeld. U kunt de slaapstand niet uitschakelen door op een toets op het toetsenbord te drukken
of de muis te bewegen, omdat deze niet werken in de slaapstand.
Voor de slaapstand wordt een speciaal bestand op de vaste schijf vereist met voldoende schijfruimte om
de inhoud van het computergeheugen op te slaan. Daarom maakt Dell een slaapstandbestand met de
juiste grootte voordat de computer wordt afgeleverd. If the computer’s hard drive becomes corrupted,
Windows XP recreates the hibernate file automatically.
Eigenschappen voor energiebeheer
Definieer de stand-bymodusinstellingen, slaapstandinstellingen en andere energie-instellingen in het
venster Eigenschappen voor energiebeheer.
U opent als volgt het venster Eigenschappen voor energiebeheer :
1
Klik op de knop
Start
en klik op
Configuratiescherm
.
2
Klik onder
Kies een categorie
op
Prestaties en onderhoud
.
3
Klik onder
of kies een pictogram...
op
Energiebeheer
.
4
Definieer de energie-instellingen op het tabblad
Energiebeheerschema's
,
Geavanceerd
en
Slaapstand
.
Het tabblad Energiebeheerschema's
Elke standaard energie-insteling wordt een schema genoemd. Als u een van de standaard Windows-
schema's wilt selecteren die op de computer zijn geïnstalleerd, kiest u een schema uit de vervolgkeuzelijst
Energiebeheerschema's. De instellingen voor elk schema verschijnen in de velden onder de schemanaam.
Elk schema heeft andere instellingen voor het inschakelen van de stand-bymodus of de slaapstand en
voor het uitschakelen van de monitor en de vaste schijf.
De vervolgkeuzelijst Energiebeheerschema's geeft de volgende schema's weer:
•
Always On
(default) — If you want to use your computer with no power conservation.
•
Home/Office Desk
— If you use your computer as a home or office computer and you require minimal
power conservation.
•
Presentation
— If you want your computer to run without interruption (using no power conservation).

Uw computer installeren en gebruiken 27
•
Minimal Power Management
— If you want your computer to run with minimal power conservation.
•
Max Battery
— If your computer is a portable computer and you run your computer from batteries for
extended periods of time.
Als u de standaardinstellingen voor een schema wilt wijzigen, klikt u op de vervolgkeuzelijst in het veld
Beeldscherm uitschakelen, Vaste schijven uitschakelen, Systeem op stand-by of Systeem in slaapstand
en selecteert u een time-out in de weergegeven lijst. Wanneer u de time-out voor een schema wijzigt,
wijzigt u de standaardinstellingen voor dat schema permanent, tenzij u op Opslaan als klikt en een nieuwe
naam voor het gewijzigde schema invoert.
KENNISGEVING: Als u de time-out van de vaste schijf (harde schijf) korter instelt dan die van het beeldscherm,
lijkt het alsof de computer is vastgelopen. U schakelt de modi uit door op een toets op het toetsenbord te drukken
of de muis te bewegen. U voorkomt dit door de time-out van het beeldscherm altijd korter in te stellen dan die van
de vaste schijf.
Het tabblad Geavanceerd
Met het tabblad Geavanceerd kunt u het volgende doen:
• Plaats het energiebeheerpictogram op de Windows-taakbalk voor snelle toegang.
• Stel de computer zo in dat u het Windows-wachtwoord moet invoeren om de stand-bymodus
of de slaapstand uit te schakelen.
• Stel de aan/uit-knop zodanig in dat de stand-bymodus wordt geactiveerd, de slaapstand wordt geactiveerd
of de computer wordt uitgeschakeld.
U doet dit door op een optie te klikken in de overeenkomstige vervolgkeuzelijst en vervolgens op OK
te klikken.
Het tabblad Slaapstand
Met het tabblad Slaapstand kunt u de slaapstand inschakelen. Als u de slaapstandinstellingen wilt
gebruiken die u gedefinieerd hebt op het tabblad Energiebeheerschema's, schakelt u het selectievakje
Slaapstand inschakelen op het tabblad Slaapstand in.
Doe het volgende voor meer informatie over energiebeheeropties:
1
Klik op de knop
Start
en vervolgens op
Help en ondersteuning
.
2
Klik in het venster
Help en ondersteuning
op
Prestaties en onderhoud
.
3
Klik in het venster
Prestaties en onderhoud
op
Energie besparen op de computer
.

28 Uw computer installeren en gebruiken
Hyper-Threading
Hyperthreading is een Intel
®
-technologie die de algemene computerprestaties kan verbeteren door één
fysieke processor te laten functioneren als twee logische processors die bepaalde taken tegelijk kunnen
uitvoeren. Het is raadzaam om Microsoft
®
Windows
®
XP Service Pack 1 (SP1) of later te gebruiken,
omdat Windows XP is afgestemd om de hyperthreading-technologie optimaal te benutten. Hoewel er veel
programma's zijn die veel met de hyperthreading-technologie kunnen, zijn ze niet allemaal afgestemd op
hyperthreading en vereisen een update van de softwarefabrikant. Neem contact op met de softwarefabrikant
voor updates en informatie over het gebruik van hyperthreading samen met uw software.
Bepaal als volgt of uw computer gebruik maakt van hyperthreading-technologie:
1
Klik op de knop
Start
, klik op
Deze computer
en vervolgens op
Eigenschappen
.
2
Klik op de tab
Hardware
en klik vervolgens op
Apparaatbeheer
.
3
Klik in het venster
Apparaatbeheer
op de plus (+) naast
Processors
. Als Hyper-Threading is ingeschakeld,
wordt de processor twee keer weergegeven.
U kunt Hyper-Threading in- of uitschakelen in de systeeminstellingen. Zie voor meer informatie over het
openen van de systeeminstellingen "System Setup" op pagina 117. Raadpleeg voor meer informatie over
Hyper-Threading de Knowledge Base op de website van Dell Support op support.dell.com.
Over RAID-configuraties
Dit gedeelte biedt een overzicht van de RAID-configuratie die u eventueel hebt geselecteerd toen u uw
computer kocht. Van alle RAID-configuraties die er voor verschillende doeleinden beschikbaar zijn in de
computerindustrie, biedt Dell op uw RAID-level 1 aan op uw computer. Een RAID-level 1-configuratie
wordt aanbevolen voor gebruikers die een hogere mate van gegevensintegriteit wensen.
De Intel Raid-controller op uw computer kan alleen een RAID-levelconfiguratie maken op basis van twee
fysiek afzonderlijke station. Deze stations dienen even groot te zijn o te voorkomen dat een eventuele
grotere niet-toegewezen (en dus onbruikbare ruimte bevat).
OPMERKING: Als u een Dell-computer hebt gekocht met RAID, is uw computer geconfigureerd met twee vaste
schijfstations van dezelfde grootte.

Uw computer installeren en gebruiken 29
Controleren of RAID werkt
Uw computer geeft bij het opstarten informatie weer over uw RAID-configuratie, nog voordat het
besturingsysteem wordt geladen. Als er geen RAID is geconfigureerd, wordt de melding none defined
(niets gedefinieerd) weergegeven onder RAID Volumes, gevolgd door een lijst van fysieke
stations die zijn geïnstalleerd op uw systeem. Wanneer er een RAID-volume wordt gevonden, kunt u in
het veld Status kijken in welke toestand uw RAID_configuratie zich bevindt. Het veld Status bevat
informatie over de volgende toestanden:
•
Normal
— Your RAID configuration is functioning properly.
•
Degraded
— One of your hard drives has failed. De computer kan nog wel worden gestart, maar RAID
werkt niet meer en er worden geen gegevens naar het andere station gekopieerd.
•
Rebuild
— Following a degraded condition, the computer has detected the replacement/connection of
a secondary hard drive and will automatically restore the RAID configuration the next time the operating
system loads.
RAID-level 1
RAID-level 1 maakt gebruik van een opslagtechniek gebaseerd gegevensredundantie die bekend staat als
"mirroring." When data is written to the primary drive, the data is then duplicated—or mirrored—on the
other drive. Een RAID-level 1-configuratie offert een snelle toegang tot gegevens op aan de voordelen van
redundantie.
Wanneer een schijfstoring optreedt, wordt lees- en schrijfbewerkingen automatisch omgeleid naar het
overgebleven station. Vervolgens kan opnieuw een vervangend station worden opgebouwd met de gegevens
van het overgebleven station. Als gevolg van het feit dat gegevens op beide schijven worden gedupliceerd,
hebben twee 120-GB Raid-level 1 stations dus samen een maximumcapaciteit van 120 GB voor gegevensopslag.
vaste schijf 1
segment 1
segment 2
segment 3
vaste schijf 2
segment 4
segment 5
segment 6
segment 1 gedupliceerd
segment 2 gedupliceerd
segment 3 gedupliceerd
segment 4 gedupliceerd
segment 5 gedupliceerd
segment 6 gedupliceerd
seriële ATA RAID
geconfigureerd
voor RAID-level 1

30 Uw computer installeren en gebruiken
RAID-problemen oplossen
U kunt kiezen uit twee methoden om problemen met RAID-vaste-schijfvolumes op te lossen. Bij de ene
methode gebruikt u het Intel RAID Option ROM-hulpprogramma en voert u de bewerking uit voordat u
het besturingsysteem op de vast schijf installeert. Bij de tweede methode maakt u gebruik van de Intel
Matrix Storage Manager, of het Intel Matrix Storage Console, en deze methode wordt altijd toegepast
nadat het besturingssysteem en de Intel Matrix Storage Console zijn geïnstalleerd. Voor beide methoden
is het vereist dat u de computer instelt op de modus RAID-enabled (RAID ingeschakeld) (zie "Uw computer
instellen op de modus RAID-Enabled (RAID ingeschakeld)" op pagina 31) alvorens u begint.
Herstellen na het uitvallen van meerdere vaste schijfstation met behulp van het hulpprogramma
Intel
®
RAID Option ROM.
OPMERKING: Met de volgende stappen worden geen gegevens teruggezet die verloren zijn gegaan bij het
uitvallen van de vaste schijf. Dit programma kan pas worden uitgevoerd nadat de defecte vaste schijven zijn
vervangen (zie "Harde schijf" op pagina 92).
Hoewel u een RAID-configuratie kunt opbouwen uit vaste schijven van elke gewenste grootte, is het aan
te bevelen in elk geval twee even grote schijven te kiezen wanneer u het hulpprogramma Intel RAID
Option ROM gebruikt. In een RAID-level 1-configuratie is de totale omvang van de totale configuratie
namelijk altijd gelijk aan de kleinste van de twee schijven die u hebt gebruikt.
1
Stel uw computer in op de modus RAID-enabled (RAID ingeschakeld) (zie "Uw computer instellen op
de modus RAID-Enabled (RAID ingeschakeld)" op pagina 31).
2
Druk op <Ctrl><i> wanneer u wordt het hulpprogramma Intel RAID Option ROM te openen.
3
Gebruik de pijlen omhoog en omlaag om de optie
Create RAID Volume
(RAID-volumes maken) te
selecteren en druk op <Enter>.
4
Voer een naam voor het RAID-volume in of neem de standaardnaam over en druk op <Enter>.
5
Selecteer
RAID1
(Mirror) en druk op <Enter>.
6
Selecteer de gewenste capaciteit voor het volume en druk op <Enter>. De standaardwaarde is de
maximale beschikbare grootte.
7
Druk op <Enter> om het volume aan te maken.
8
Druk op <y> om te bevestigen dat u een RAID volume wilt maken.
9
Controleer of de juiste volumeconfiguratie wordt weergegeven in het hoofdscherm van het
hulpprogramma Intel RAID Option ROM.
10
Gebruik de pijlen omhoog en omlaag om de optie
Exit
(Afsluiten) te selecteren en druk op <Enter>.
11
Installeer het besturingssysteem met de geleverde media (zie "Uw besturingssysteem herstellen" op
pagina 57).

Uw computer installeren en gebruiken 31
Herstellen van een uitval van één enkele vaste schijf met behulp van de Intel Matrix Storage
Manager
OPMERKING: De volgende stappen kunnen pas worden uitgevoerd nadat de defecte vaste schijven zijn vervangen
(zie "Harde schijf" op pagina 92).
1
Klik op
Start
en kies voor
Programma’s
→
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager
→
Intel Matrix Storage
Console
om de Intel Storage Utility te starten.
2
Klik op de knop
Restore RAID 1 data protection
(RAID 1-gegevensbeveiliging herstellen).
3
Klik op de knop
Rebuild RAID volume now
(RAID-volume nu opnieuw opbouwen).
4
Klik op
Yes
(Ja) om het opnieuw opbouwen van het RAID-volume op de nieuwe vaste schijf te starten.
OPMERKING: U kunt uw computer gewoon gebruiken terwijl het RAID-level 1-volume wordt opgebouwd.
Uw computer instellen op de modus RAID-Enabled (RAID ingeschakeld)
1
Open System Setup (zie "System Setup" op pagina 117).
2
Gebruik de pijlen omhoog en omlaag om de optie
Drives
(Stations) te selecteren en druk op <Enter>.
3
Gebruik de pijlen omhoog en omlaag om de optie
SATA Operation
(SATA-bewerking) te selecteren en
druk op <Enter>.
4
Druk op de pijltoetsen links of rechts om
RAID On
(RAID aan) te selecteren, druk op <Enter> en
vervolgens op <Esc>.
OPMERKING: Raadpleeg voor meer informatie over RAID-opties "System Setup-opties" op pagina 118.
5
Druk op de pijltjestoetsen links en rechts om
Save/Exit
(Opslaan/Afsluiten) te selecteren en druk op
<Enter> om de systeemsetup af te sluiten en het opstarten te hervatten.
Dell™ DataSafe (Optioneel)
Dell DataSafe is een oplossing die u helpt uw gegevens te beschermen tegen verlies als gevolg van
systeemcrashes, vaste-schijffouten, beschadigde software, virussen en andere calamiteiten. Dankzij de
gebruikte Intel-technologie beschikt uw computer al bij aflevering over een krachtige gegevensbescherming.
Met Dell DataSafe wordt er op uw systeem automatisch een deel geselecteerd waar regelmatig kopieën
van de gegevens op de harde schijf worden opgeslagen.
Dell DataSafe helpt u niet alleen uw waardevolle gegevens zoals foto’s, muziek, video’s en andere bestanden
op te slaan en te beschermen, het helpt ook uw computer en uw gegevens te herstellen wanneer de
computer uitvalt. De bijgeleverde software stelt u in staat het systeem terug te brengen in een gezonde
toestand nadat er een probleem was opgetreden, eenvoudig verwijderde bestanden of een hele vast schijf
te herstellen, en de Intel Matrix Storage Console (RAID) maakt het mogelijk dat uw computer blijft
functioneren wanneer er één vaste schijf uitvalt.

32 Uw computer installeren en gebruiken

Problemen oplossen 33
Problemen oplossen
Tips voor het oplossen van problemen
Gebruik de volgende tips voor het oplossen van problemen met uw computer:
• Als u een onderdeel hebt verwijderd voordat het probleem zich voordeed, controleert u de
installatieprocedures en zorgt u dat het onderdeel correct is geïnstalleerd.
• Als een randapparaat niet werkt, controleert u of het apparaat goed is aangesloten.
• Als er een foutbericht op het scherm verschijnt, noteert u de exacte tekst. Aan de hand van dit
bericht kan een technische ondersteuningsmedewerker het probleem mogelijk achterhalen en
oplossen.
• If an error message occurs in a program, see the program’s documentation.
Problemen met de batterij
VOORZICHTIG: Wanneer u een nieuwe batterij niet goed plaatst, kan deze exploderen. Vervang de batterij
alleen door hetzelfde of een gelijkwaardig type, dat wordt aanbevolen door de fabrikant. Verwijder de
gebruikte batterijen overeenkomstig de instructies van de fabrikant.
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
VERVANG DE BATTERIJ. Als u de tijd en datum meerdere malen opnieuw hebt moeten instellen nadat
u de computer inschakelt of als er een onjuiste tijd of datum wordt weergegeven tijdens het opstarten,
vervangt u de batterij (zie "De batterij vervangen" op pagina 109). Als de batterij nog steeds niet goed
functioneert, neemt u contact op met Dell (zie "Contact met Dell" op pagina 130).

34 Problemen oplossen
Problemen met een station
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
Problemen met het cd- en dvd-station
OPMERKING: Door de hoge snelheid in het cd- of dvd-station ontstaan er vibraties waardoor u geluiden hoort. Dit
is normaal en duidt niet op een defect aan het station of de cd of dvd.
OPMERKING: Vanwege de verschillende regio's wereldwijd en de verschillende indelingen kunnen niet alle dvd's
in alle dvd-stations worden afgespeeld.
ZORG DAT HET STATION DOOR MICROSOFT
®
WINDOWS
®
WORDT HERKEND. Klik op de knop Starten
klik op Mijn Computer. Als het diskette-, cd- of dvd-station niet wordt weergegeven in de lijst, voert u
een volledige scan uit met uw antivirussoftware om de computer op virussen te controleren en deze
eventueel te verwijderen. Virussen kunnen ervoor zorgen dat een bepaald station niet door Windows
wordt herkend.
TEST HET STATION.
• Plaats een andere diskette, cd of dvd in het betreffende station om te controleren of de originele
diskette, cd of dvd is beschadigd.
• Plaats de opstartbare media en start de computer opnieuw op.
REINIG HET STATION OF DE DISKETTE. Zie "Uw computer reinigen" op pagina 127.
CONTROLEER DE KABELCONNECTOREN.
VOER DE PROBLEEMOPLOSSER VOOR HARDWARE UIT. Zie "Software- en hardwareconflicten oplossen"
op pagina 57.
VOER DELL DIAGNOSTICS UIT. Zie "Dell Diagnostics" op pagina 53.
PAS HET VOLUMENIVEAU IN WINDOWS AAN.
• Klik op het luidsprekerpictogram in de rechterbenedenhoek van het scherm.
• Zorg dat het volume is ingeschakeld door de schuifregelaar omhoog te slepen.
• Zorg dat het geluid niet is gedempt door op de selectievakjes te klikken die zijn ingeschakeld.
SCHAKEL DE LUIDSPREKER EN SUBWOOFER IN. Zie "Problemen met het geluid en de luidsprekers" op
pagina 46.

Problemen oplossen 35
Problemen met het schrijven naar een cd/dvd-rw-station
Problemen met de vaste schijf
E-mail-, modem- en internetproblemen
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
OPMERKING: Sluit de modem alleen aan op een analoge telefoonconnector. De modem werkt niet als deze is
aangesloten op een digitaal telefoonnetwerk.
SLUIT ANDERE PROGRAMMA'S. Het cd/dvd-rw-station moet een constante stroom aan gegevens
ontvangen tijdens het schrijven. Als de stroom wordt onderbroken, treedt er een fout op. Sluit alle
programma's voordat u gegevens naar een cd/dvd-rw schrijft.
SCHAKEL DE STANDBY-MODUS IN WINDOWS UIT VOORDAT U GEGEVENS NAAR EEN CD/DVD-RW SCHRIJFT.
Zoek in de Help van Windows op het trefwoord stand-by.
VOER SCHIJF CONTROLEREN UIT.
1
Klik op de knop
Start
en klik op
Mijn Computer
.
2
Klik met de rechtermuisknop op
Lokaal station (C:)
.
3
Klik op
Eigenschappen
.
4
Klik op de tab
Extra
.
5
Klik in het gedeelte
Foutcontrole
op
Nu controleren
.
6
Klik op
Beschadigde sectoren zoeken en repareren
.
7
Klik op
Starten
.
CONTROLEER DE BEVEILIGINGSINSTELLINGEN IN MICROSOFT OUTLOOK
®
EXPRESS. Als u uw
e-mailbijlagen niet kunt openen:
1
Klik in Outlook Express achtereenvolgens op
Extra
,
Opties
en
Beveiliging
.
2
Klik op
Opslaan of openen van bijlagen die mogelijk een virus bevatten niet toestaan
om het vinkje te
verwijderen.

36 Problemen oplossen
CONTROLEER DE VERBINDING VAN DE TELEFOONLIJN.
C
ONTROLEER DE TELEFOONCONNECTOR.
S
LUIT DE MODEM RECHTSTREEKS AAN OP DE TELEFOONCONNECTOR AAN DE MUUR.
G
EBRUIK EEN ANDERE TELEFOONLIJN.
• Controleer of de telefoonlijn is aangesloten op de modem. (De connector wordt aangeduid met een
groen label of connectorpictogram.)
• Zorg dat u een klik hoort als u de plug van de telefoonlijn in de modem steekt.
• Koppel de telefoonlijn los van de modem en sluit deze aan op een telefoon. Luister of u een kiestoon
hoort.
• Als de lijn wordt gedeeld met andere telefoonapparaten, zoals een antwoordapparaat, een faxapparaat,
stroomstootbeveiliging of splitter, moet u deze omzeilen en de telefoon gebruiken om de modem
rechtstreeks aan te sluiten op telefoonconnector aan de muur. Als u een lijn van meer dan 3 m (10 ft)
gebruikt, probeert u een kortere lijn.
VOER MODEM HELPER UIT. Klik op de knop Start wijs Alle programma's aan en klik op Modem
Helper. Volg de instructies op het scherm om het probleem met de modem te achterhalen en op te
lossen. (Modem Helper is niet beschikbaar op alle computers.)
CONTROLEER OF DE MODEM COMMUNICEERT MET WINDOWS.
1
Klik op de knop
Start
en klik op
Configuratiescherm
.
2
Klik op
Printers en andere hardware
.
3
Klik op
Telefoon- en modemopties
.
4
Klik op de tab
Modems
.
5
Klik op de COM-poort voor uw modem.
6
Klik op
Eigenschappen
, klik op de tab
Diagnostische gegevens
en klik op
Instellingen opvragen
om te
controleren of de modem met Windows communiceert.
Als u op alle opdrachten respons krijgt, werkt de modem naar behoren.
ZORG DAT U VERBINDING HEBT MET INTERNET. Zorg dat u een abonnement hebt bij een
internetprovider. Open het e-mailprogramma Outlook Express en klik op Bestand. Als u voor de optie
Off line werken een vinkje ziet staan, klikt u op de optie om het vinkje te verwijderen en verbinding te
maken met internet. Voor hulp neemt u contact op met uw internetaanbieder.

Problemen oplossen 37
Foutberichten
Als het bericht niet wordt vermeld, raadpleegt u de documentatie bij het besturingssysteem of het
programma dat werd uitgevoerd toen het bericht verscheen.
A FILENAME CANNOT CONTAIN ANY OF THE FOLLOWING CHARACTERS: \ / : * ? “ < > |. Gebruik
deze tekens niet in bestandsnamen.
A REQUIRED .DLL FILE WAS NOT FOUND. Er ontbreekt een essentieel bestand voor het programma dat
u probeert te openen. Het programma verwijderen en opnieuw installeren:
1
Klik op de knop
Start
, klik op
Configuratiescherm
en klik vervolgens op
Software
.
2
Klik op het programma dat u wilt verwijderen.
3
Klik op het pictogram
Wijzigen/Verwijderen
.
4
Raadpleeg de documentatie bij het programma voor installatie-instructies.
WAARSCHUWING! Controleer bij elke type computer behalve het kleinste type of alle kabels goed zijn
bevestigd aan het I/O-paneel en het moederbord en start uw computer opnieuw op. Als het probleem
nu niet verholpen is of wanneer u over een extreem compacte computer beschikt, neemt u contact op
met Dell (zie "Contact met Dell" op pagina 130)..
drive letter :\ IS NOT ACCESSIBLE. THE DEVICE IS NOT READY. Het station kan de diskette niet
lezen. Plaats een diskette in het station en probeer het nogmaals.
INSERT BOOTABLE MEDIA. Plaats een opstartdiskette of -cd in het station.
NON-SYSTEM DISK ERROR. Verwijder de diskette uit het station en start de computer opnieuw op.
NOT ENOUGH MEMORY OR RESOURCES. CLOSE SOME PROGRAMS AND TRY AGAIN. Sluit alle vensters
en open het programma dat u wilt gebruiken. In bepaalde gevallen moet u de computer mogelijk
opnieuw opstarten om de computerbronnen te herstellen. In dat geval voert u eerst het programma uit
dat u wilt gebruiken.
OPERATING SYSTEM NOT FOUND. Neem contact op met Dell (zie "Contact met Dell" op pagina 130).

38 Problemen oplossen
Problemen met het toetsenbord
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
Lockups en problemen met de software
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
De computer start niet op
De computer reageert niet
KENNISGEVING: U loopt het risico dat er gegevens verloren gaan als u het besturingssysteem niet correct kunt
afsluiten.
CONTROLEER DE KABEL VAN HET TOETSENBORD.
• Zorg dat de kabel van het toetsenbord goed is aangesloten op de computer.
• Sluit de computer af (zie "Uw computer uitschakelen" op pagina 63), sluit de kabel van het toetsenbord
opnieuw aan zoals wordt weergegeven in de schematische weergave voor uw computer, en start de
computer opnieuw op.
• Controleer de kabelconnector op omgebogen of afgebroken pinnen of beschadigde of gedraaide kabels.
Trek de gebogen pinnen recht.
• Verwijder de verlengkabels voor het toetsenbord en sluit het toetsenbord rechtstreeks aan op de computer.
TEST HET TOETSENBORD. Sluit een goed werkend toetsenbord aan op de computer om te kijken of u het
toetsenbord kunt gebruiken.
VOER DE PROBLEEMOPLOSSER VOOR HARDWARE UIT. Zie "Software- en hardwareconflicten oplossen"
op pagina 57.
CONTROLEER DE CONTROLELAMPJES. Zie "Controlelampjes" op pagina 49.
ZORG DAT HET NETSNOER GOED IS AANGESLOTEN OP DE COMPUTER EN HET STOPCONTACT.
SLUIT DE COMPUTER AF. Als de computer niet reageert wanneer u op een toets op het toetsenbord
drukt of de muis beweegt, houdt u de aan/uit-knop minimaal 8 tot 10 seconden ingedrukt totdat de
computer wordt uitgeschakeld. Vervolgens start u de computer opnieuw op.

Problemen oplossen 39
Een programma reageert niet meer
Een programma loopt regelmatig vast
OPMERKING: Doorgaans bevat de documentatie, diskette of cd die bij de software is geleverd Software ook
installatie-instructies.
Een programma werd ontworpen voor een eerdere versie van het Microsoft
®
Windows
®
besturingsysteem
Er verschijnt een blauw scherm
SLUIT HET PROGRAMMA.
1
Druk de toetsen <Ctrl><Shift><Esc> tegelijk in.
2
Klik op
Toepassingen
.
3
Klik op het programma dat niet meer reageert.
4
Klik op
Taak beëindigen
.
CONTROLEER DE DOCUMENTATIE BIJ DE SOFTWARE. Indien noodzakelijk verwijdert u het programma
en installeert u het opnieuw.
VOER DE WIZARD PROGRAMMACOMPATIBILITEIT UIT.
Met de wizard Programmacompatibiliteit wordt een programma zodanig geconfigureerd dat deze wordt
uitgevoerd in een omgeving die vergelijkbaar is met een andere omgeving dan die van het
besturingssysteem Windows XP.
1
Klik op de knop
Start
, wijs achtereenvolgens
Alle programma's
→
Bureau-accessoires
aan en klik op
Wizard Programmacompatibiliteit
.
2
Klik in het welkomstvenster op
Volgende
.
3
Volg de instructies op het scherm.
SLUIT DE COMPUTER AF. Als de computer niet reageert wanneer u op een toets op het toetsenbord
drukt of de muis beweegt, houdt u de aan/uit-knop minimaal 8 tot 10 seconden ingedrukt totdat de
computer wordt uitgeschakeld. Vervolgens start u de computer opnieuw op.

40 Problemen oplossen
Andere softwareproblemen
Problemen met een mediakaartlezer
RAADPLEEG DE DOCUMENTATIE BIJ DE SOFTWARE OF NEEM CONTACT OP MET DE FABRIKANT VAN DE
SOFTWARE VOOR INFORMATIE OVER HET OPLOSSEN VAN PROBLEMEN.
• Controleer of het programma compatibel is met het besturingssysteem dat op uw computer is
geïnstalleerd.
• Controleer of uw computer aan de minimale hardwarevereisten voldoet voor het uitvoeren van de
software. Raadpleeg de documentatie bij de software voor meer informatie.
• Zorg dat het programma is geïnstalleerd en goed is geconfigureerd.
• Controleer of de apparaatstuurprogramma's niet conflicteren met het programma.
• Indien noodzakelijk verwijdert u het programma en installeert u het opnieuw.
MAAK METEEN RESERVEKOPIEËN VAN UW BESTANDEN.
GEBRUIK EEN VIRUSSCANNER OM DE VASTE SCHIJF, DISKETTES OF CD'S TE SCANNEN.
SLA ALLE GEOPENDE BESTANDEN OP, SLUIT DE BESTANDEN VERVOLGENS EN SLUIT UW COMPUTER
AF VIA HET MENU START MENU.
ER IS GEEN STATIONSLETTER TOEGEWEZEN.
Wanneer Microsoft Windows XP een mediakaartlezer herkent, wordt er automatisch een stationsletter
toegewezen als het volgende logische station na alle andere fysieke stations in het systeem. Als het
volgende logische station na de fysieke stations wordt toegewezen aan een netwerkstation, wordt er in
Windows XP niet automatisch een stationsletter aan de mediakaartlezer toegewezen.
Handmatig een station voor de mediakaartlezer toewijzen:
1
Klik met de rechtermuisknop op
Deze computer
en selecteer
Beheren
.
2
Selecteer de optie
Schijfbeheer
.
3
Klik in het rechterdeelvenster met de rechtermuisknop op de stationsletter die moet worden gewijzigd.
4
Selecteer
Stationsletter en paden wijzigen
.
5
Selecteer in de vervolgkeuzelijst een nieuwe stationsletter die moet worden toegewezen aan de
mediakaartlezer.
6
Klik op
OK
om uw selectie te bevestigen.
OPMERKING: De mediakaartlezer verschijnt alleen als toegewezen station wanneer hij met de computer
verbonden is. Elk van de vier sleuven van de mediakaartlezer is toegewezen aan een station, zelfs wanneer
er geen media zijn geplaatst. Als u probeert toegang te krijgen tot de mediakaartlezer wanneer er geen
media zijn geplaatst, wordt u gevraagd media te plaatsen.

Problemen oplossen 41
Geheugenproblemen
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
Problemen met de muis
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
FLEXBAY-APPARAAT IS UITGESCHAKELD.
Het BIOS bevat een optie waarmee u een FlexBay kunt uitschakelen. Deze is echter alleen beschikbaar
als er een FlexBay-apparaat is geïnstalleerd. Als u het FlexBay-apparaat fysiek is geïnstalleerd, maar niet
wordt uitgevoerd, controleert u in het BIOS of het apparaat is ingeschakeld.
ALS HET BERICHT ONTVANGT DAT ER ONVOLDOENDE GEHEUGEN BESCHIKBAAR IS.
• Sla alle geopende bestanden op en sluit ze. Sluit vervolgens alle programma's die u niet gebruikt om te
kijken of het probleem hiermee is opgelost.
• Raadpleeg de documentatie bij de software voor de minimale geheugenvereisten. Indien noodzakelijk
installeert u extra geheugen (zie "Geheugen installeren" op pagina 74).
• Plaats de geheugenmodules terug (zie "Geheugen installeren" op pagina 74) om ervoor te zorgen dat uw
computer goed communiceert met het geheugen.
• Voer Dell Diagnostics uit (zie "Dell Diagnostics" op pagina 53).
ALS U ANDERE GEHEUGENPROBLEMEN ONDERVINDT.
• Plaats de geheugenmodules terug (zie "Geheugen installeren" op pagina 74) om ervoor te zorgen dat uw
computer goed communiceert met het geheugen.
• Zorg dat u de installatie-instructies voor het geheugen volgt (zie "Geheugen installeren" op pagina 74).
• Uw computer ondersteunt DDR2-geheugen. Zie voor meer informatie over het type geheugen dat uw
computer ondersteunt, de sectie "Geheugen" op pagina 113.
• Voer Dell Diagnostics uit (zie "Dell Diagnostics" op pagina 53).
REINIG DE MUIS. Zie "Muis" op pagina 128 voor instructies voor het reinigen van de muis.
CONTROLEER DE KABEL VAN DE MUIS.
1
Verwijder de verlengkabel, indien u hier gebruik van maakt, en sluit de muis rechtstreeks aan op de
computer.
2
Sluit de muiskabel aan zoals wordt weergegeven in de schematische weergave
voor uw computer.

42 Problemen oplossen
Netwerkproblemen
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
START DE COMPUTER OPNIEUW OP.
1
Druk tegelijk op <Ctrl><Esc> om het menu
Start
weer te geven.
2
Ty p
u
, druk op de pijltoetsen op het toetsenbord om
Uitschakelen
of
Turn Off
te selecteren en druk
vervolgens op <Enter>.
3
Zodra de computer is uitgeschakeld, sluit u de muiskabel opnieuw aan zoals wordt afgebeeld in de
schematische weergave voor uw computer.
4
Start the computer op
TEST DE MUIS. Sluit een goed werkende muis aan op de computer om te kijken of u de muis kunt
gebruiken.
CONTROLEER DE MUISINSTELLINGEN.
1
Klik achtereenvolgens op de knop
Start
,
Configuratiescherm
en
Printers en andere hardware
.
2
Klik op
Muis
.
3
Pas de instellingen aan.
INSTALEER HET STUURPROGRAMMA VOOR DE MUIS OPNIEUW. Zie "Een stuurprogramma opnieuw
installeren" op pagina 56.
VOER DE PROBLEEMOPLOSSER VOOR HARDWARE UIT. Zie "Software- en hardwareconflicten oplossen"
op pagina 57.
CONTROLEER DE CONNECTOR VAN DE NETWERKKABEL. Zorg dat de netwerkkabel goed is aangesloten
op zowel de netwerkconnector aan de achterzijde van de computer als op de netwerkpoort of het
apparaat.
CONTROLEER DE NETWERKLAMPJES AAN DE ACHTERZIJDE VAN DE COMPUTER. Als het lampje voor
de integriteit van de verbinding uit is, vindt er geen communicatie met het netwerk plaats. Vervang de
netwerkkabel. Zie voor een beschrijving van de netwerklampjes de sectie "Schakelaars en lampjes" op
pagina 115.
START DE COMPUTER OPNIEUW OP EN MELD U OPNIEUW AAN BIJ HET NETWERK.

Problemen oplossen 43
Problemen met de voeding
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
CONTROLEER UW NETWERKINSTELLINGEN. Neem contact op met uw netwerkbeheerder of de persoon
die uw netwerk heeft ingesteld om te controleren of uw netwerkinstellingen juist zijn en dat het netwerk
functioneert.
VOER DE PROBLEEMOPLOSSER VOOR HARDWARE UIT. Zie "Software- en hardwareconflicten oplossen"
op pagina 57.
ALS HET AAN/UIT-LAMPJE GROEN IS EN DE COMPUTER NIET REAGEERT. Zie "Controlelampjes" op
pagina 49.
ALS HET AAN/UIT-LAMPJE GROEN IS EN KNIPPERT. De computer bevindt zich in de stand-bymodus.
Druk op een toets op het toetsenbord, beweeg de muis of druk op de aan/uit-knop om de computer te
activeren.
ALS HET AAN/UIT-LAMPJE UIT IS. De computer is uitgeschakeld of krijgt geen stroom.
• Sluit het netsnoer opnieuw aan, zowel op de connector aan de achterzijde van de computer als op het
stopcontact.
• Als de computer is aangesloten op een stekkerdoos, controleert u of de stekker van de stekkerdoos in een
stopcontact zit en de stekkerdoos is ingeschakeld. Gebruik geen stroomonderbrekers, stekkerdozen en
verlengkabels, zodat u kunt controleren of de computer correct wordt ingeschakeld.
• Controleer of het stopcontact goed werkt door deze te testen met een apparaat, bijvoorbeeld een lamp.
• Controleer of het netsnoer en het voorpaneel goed zijn aangesloten op het moederbord (zie
"Systeemkaartcomponenten" op pagina 72).
ALS HET AAN/UIT-LAMPJE CONSTANT ORANJE IS. Mogelijk is er een apparaat dat niet goed
functioneert of niet goed is geïnstalleerd.
• Controleer of het 12-voltssnoer (12V) goed is aangesloten op het moederbord (zie "Systeemkaartcomponenten"
op pagina 72).
• Verwijder de geheugenmodules en installeer ze vervolgens opnieuw (zie "Geheugen installeren" op
pagina 74).
• Verwijder alle kaarten en installeer ze vervolgens opnieuw (zie "Kaarten" op pagina 77).
• Verwijder en herinstalleer de grafische kaart, indien van toepassing (zie "PCI Express-kaarten" op
pagina 81).

44 Problemen oplossen
Problemen met de printer
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
OPMERKING: If you need technical assistance for your printer, contact the printer’s manufacturer.
ALS HET AAN/UIT-LAMPJE ORANJE IS EN KNIPPERT. De computer krijgt wel stroom, maar er is een
intern probleem met de voeding.
• Controleer of de stroomselectieschakelaar zodanig is ingesteld dat deze overeenkomt met de
wisselstroom die van toepassing is voor uw locatie (indien van toepassing). Zie "Achteraanzicht van de
computer" op pagina 67.
• Controleer of het 12-voltssnoer (12V) goed is aangesloten op het moederbord (zie
"Systeemkaartcomponenten" op pagina 72).
SLUIT INTERFERENTIE UIT. Enkele mogelijke oorzaken van interferentie zijn:
• Verlengkabels voor het netsnoer, de kabel van het toetsenbord of de muis
• Er zijn te veel apparaten aangesloten op één stekkerdoos
• Er zijn meerdere stekkerdozen aangesloten op hetzelfde stopcontact.
RAADPLEEG DE DOCUMENTATIE BIJ DE PRINTER. Raadpleeg de documentatie bij de printer voor meer
informatie over de instellingen en het oplossen van problemen.
CONTROLEER OF DE PRINTER IS INGESCHAKELD.
CONTROLEER DE CONNECTOREN VAN DE PRINTERKABELS.
• Raadpleeg de documentatie bij de printer voor meer informatie over de kabelconnectoren.
• Zorg dat de printerkabels goed zijn aangesloten op de printer en de computer (zie "Een printer installeren"
op pagina 13).
TEST HET STOPCONTACT. Controleer of het stopcontact goed werkt door deze te testen met een
apparaat, bijvoorbeeld een lamp.

Problemen oplossen 45
Problemen met de scanner
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
OPMERKING: If you need technical assistance for your scanner, contact the scanner’s manufacturer.
CONTROLEER OF DE PRINTER DOOR WINDOWS WORDT HERKEND.
1
Klik achtereenvolgens op de knop
Start
,
Configuratiescherm
en
Printers en andere hardware
.
2
Klik op
Reeds geïnstalleerde printers en faxprinters weergeven
.
Als de printer hier niet wordt vermeld, klikt u met de rechtermuisknop op het printerpictogram.
3
Klik op
Eigenschappen
en klik vervolgens op de tab
Poorten
. Controleer of de optie
Print to the
following port(s) (Afdrukken op de volgende poorten) is ingesteld op:
USB
.
INSTALLEER DE PRINTERSTUURPROGRAMMA'S OPNIEUW. Raadpleeg de documentatie bij de printer
voor instructies.
RAADPLEEG DE DOCUMENTATIE BIJ DE SCANNER. Raadpleeg de documentatie bij de scanner voor
meer informatie over de instellingen en het oplossen van problemen.
DE SCANNER ONTGRENDELEN. Controleer of de scanner is ontgrendeld als deze over een
vergrendelknop of -tab beschikt.
START DE COMPUTER OPNIEUW OP EN PROBEER DE SCANNER NOGMAALS.
CONTROLEER DE KABELCONNECTOREN.
• Raadpleeg de documentatie bij de scanner voor meer informatie over de kabelconnectoren.
• Zorg dat de scannerkabels goed zijn aangesloten op de printer en de computer.
CONTROLEER OF DE SCANNER DOOR WINDOWS WORDT HERKEND .
1
Klik achtereenvolgens op knop
Start
,
Configuratiescherm
en
Printers en andere hardware
.
2
Klik op
Scanners en camera's
.
Als uw scanner voorkomt op de lijst, wordt deze door Windows herkend.
INSTALLEER DE SCANNERSTUURPROGRAMMA'S OPNIEUW. Raadpleeg de documentatie bij de scanner
voor instructies.

46 Problemen oplossen
Problemen met het geluid en de luidsprekers
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
Geen geluid uit de luidsprekers
OPMERKING: De volume-instellingen van bepaalde MP3-spelers overschrijven de volume-instellingen van
Windows. Als u MP3-bestanden afspeelt, controleer dan of u het volume van de speler niet hebt uitgeschakeld of
gereduceerd.
CONTROLEER DE CONNECTOR VAN DE LUIDSPREKERKABELS. Controleer of de luidsprekers zijn
aangesloten zoals wordt weergegeven in de schematische weergave die bij de luidsprekers is geleverd. Als
u een geluidskaart hebt gekocht, controleer dan of de luidsprekers zijn aangesloten op de kaart.
CONTROLEER OF DE SUBWOOFER EN DE LUIDSPREKERS ZIJN INGESCHAKELD. Raadpleeg de
schematische weergave die bij de luidsprekers is geleverd. Als uw luidsprekers volumeregelaars hebben,
past u het volume, de basinstellingen en de instellingen voor de hoge tonen aan om vervorming te
voorkomen.
PAS HET VOLUMENIVEAU IN WINDOWS AAN. Klik of dubbelklik op het luidsprekerpictogram in de
rechterbenedenhoek van het scherm. Zorg dat het volume is ingeschakeld en dat het geluid niet wordt
gedempt.
KOPPEL DE HOOFDTELEFOON LOS VAN DE HOOFDTELEFOONCONNECTOR. Sound from the speakers is
automatically disabled when headphones are connected to the computer’s front-panel headphone
connector.
TEST HET STOPCONTACT. Controleer of het stopcontact goed werkt door deze te testen met een
apparaat, bijvoorbeeld een lamp.
ELIMINEER MOGELIJKE INTERFERENTIE. Schakel ventilatoren, fluorescerende lampen of
halogeenlampen in de buurt van de luidsprekers uit om te controleren op interferentie.
INSTALLEER DE STUURPROGRAMMA'S VOOR GELUID OPNIEUW. Zie "Handmatig een stuurprogramma
installeren" op pagina 56.
VOER DE PROBLEEMOPLOSSER VOOR HARDWARE UIT. Zie "Software- en hardwareconflicten oplossen"
op pagina 57.

Problemen oplossen 47
Geen geluid uit de hoofdtelefoon
Problemen met video en de monitor
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
OPMERKING: Raadpleeg de documentatie bij de monitor voor de procedures voor het oplossen van problemen.
Als het scherm leeg is
CONTROLEER DE KABELCONNECTOREN VAN DE HOOFDTELEFOON. Zorg dat de hoofdtelefoonkabel
goed is aangesloten op de hoofdtelefoonconnector (zie "Vooraanzicht van de computer" op pagina 65).
PAS HET VOLUMENIVEAU IN WINDOWS AAN. Klik of dubbelklik op het luidsprekerpictogram in de
rechterbenedenhoek van het scherm. Zorg dat het volume is ingeschakeld en dat het geluid niet wordt
gedempt.
CONTROLEER DE KABELCONNECTOREN VAN DE MONITOR.
• Controleer of de grafische kabel is aangesloten zoals wordt weergegeven in de schematische weergave
voor uw computer.
• Als u een grafische verlengkabel gebruikt en het probleem is opgelost wanneer u de kabel verwijdert, is
de kabel defect.
• Ruil het netsnoer van de computer en de monitor om te bepalen of het netsnoer defect is.
• Controleer de connector op verbogen of gebroken pinnen. (Het is normaal voor een monitorkabel dat er
enkele pinnen ontbreken.)
CONTROLEER HET AAN/UIT-LAMPJE. Als het aan/uit-lampje uit is, drukt u stevig op de knop om ervoor
te zorgen dat de monitor is ingeschakeld. Als het aan/uit-lampje brandt of knippert, krijgt de monitor
stroom. Als het aan/uit-lampje knippert, drukt u op een toets op het toetsenbord of beweegt u de muis.
TEST HET STOPCONTACT. Controleer of het stopcontact goed werkt door deze te testen met een
apparaat, bijvoorbeeld een lamp.
CONTROLEER DE CONTROLELAMPJES. Zie "Controlelampjes" op pagina 49.

48 Problemen oplossen
Als het scherm moeilijk te lezen is
CONTROLEER DE MONITORINSTELLINGEN. Raadpleeg de documentatie bij de monitor voor instructies
voor het aanpassen van het contrast, de helderheid en het demagnetiseren (degaussing) van de monitor
en het uitvoeren van de zelftest.
PLAATS DE SUBWOOFER UIT DE BUURT VAN DE MONITOR. Als uw luidsprekersysteem een subwoofer
bevat, zorg dan dat de subwoofer op minimaal 60 cm (2 ft) van de monitor plaatst.
PLAATS DE MONITOR NIET NABIJ EXTERNE ENERGIEBRONNEN. Ventilatoren, fluorescerende lampen,
halogeenlampen en andere elektrische apparaten kunnen trillingen op het scherm veroorzaken. Schakel
de apparaten in de buurt van de monitor uit om te controleren op interferentie.
DRAAI DE MONITOR OM SCHITTERING VAN ZONLICHT EN MOGELIJKE INTERFERENTIE TE VOORKOMEN.
PAS DE WEERGAVE-INSTELLINGEN VAN WINDOWS AAN.
1
Klik achtereenvolgens op
Start
,
Configuratiescherm
en
Vormgeving en thema's
.
2
Klik op
Beeldscherm
en vervolgens op de tab
Instellingen
.
3
Probeer verschillende instellingen voor de
Schermresolutie
en
Kleurkwaliteit.

Hulpmiddelen voor het oplossen van problemen 49
Hulpmiddelen voor het oplossen
van problemen
Controlelampjes
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
Om u te helpen bij het oplossen van een probleem beschikt uw computer over vier lampjes
genummers "1," "2," "3," en "4" op het voorpaneel (zie "Vooraanzicht van de computer" op pagina 65).
Wanneer de computer normaal kan worden opgestart, knipperen de lampjes. Als de computer niet
goed functioneert, kunt u aan de kleuren van de lampjes het probleem achterhalen.
Lichtpatroon Omschrijving probleem Mogelijke oplossing
De computer is normaal
uitgeschakeld, normaal ingeschakeld
nadat de computer er in geslaagd
is het besturingsysteem op te
starten, of er is mogelijk een
pre-BIOS-fout opgetreden.
Steek de stekker van de computer in een
werkend stopcontact en druk op de aan-/uit-
knop. Zie ook "Problemen met de voeding"
op pagina 43.
Er is mogelijk een processorfout
opgetreden.
Neem contact op met Dell (zie "Contact
met Dell" op pagina 130).

50 Hulpmiddelen voor het oplossen van problemen
Er zijn geheugenmodules
gevonden maar er is een
geheugenfout opgetreden.
• Als er twee geheugenmodules zijn
geïnstalleerd, verwijder dan beide modules,
installeer één module opnieuw (zie
"Geheugen installeren" op pagina 74) en
start de computer opnieuw op. Als de
computer normaal opstart, kunt u een
extra module installeren. Ga hiermee door
totdat u een defecte module hebt
gevonden of alle modules zonder
problemen opnieuw hebt geïnstalleerd.
• Installeer, indien beschikbaar, een goed
werkend geheugen van hetzelfde type in de
computer (zie "Geheugen installeren" op
pagina 74).
• Als het probleem aanhoudt, neemt u
contact op met Dell (zie
"Contact met
Dell" op pagina 130
).
Er is mogelijk een probleem met
de grafische kaart.
• Als de computer beschikt over een
grafische kaart, neemt u deze uit,
installeert u deze opnieuw (zie "PCI
Express-kaarten" op pagina 81) en start u
vervolgens de computer opnieuw op.
• Als het probleem blijft bestaan installeert u
een grafische kaart waarvan u zeker weet
dat hij werkt en start u de computer
opnieuw op.
• Als het probleem blijft bestaan of de
computer beschikt over geïntegreerde
grafische voorzieningen, neemt u contact
op met Dell (zie
"Contact met Dell" op
pagina 130
).
Er is mogelijk een probleem met
het diskettestation of de vaste
schijf.
Sluit alle stroom- en datakabels opnieuw aan
en start de computer opnieuw op.
Er is mogelijk een fout in de USB-
connector opgetreden.
Installeer alle USB-apparaten opnieuw,
controleer kabelaansluitingen en start de
computer opnieuw op.
Lichtpatroon (vervolg) Omschrijving probleem Mogelijke oplossing

Hulpmiddelen voor het oplossen van problemen 51
Er zijn geen geheugenmodules
gevonden.
• Als er twee geheugenmodules zijn
geïnstalleerd, verwijder dan beide modules,
installeer één module opnieuw (zie
"Geheugen installeren" op pagina 74) en
start de computer opnieuw op. Als de
computer normaal opstart, kunt u een
extra module installeren. Ga hiermee door
totdat u een defecte module hebt gevonden
of alle modules zonder problemen opnieuw
hebt geïnstalleerd.
• Installeer, indien beschikbaar, een goed
werkend geheugen van hetzelfde type in de
computer (zie "Geheugen installeren" op
pagina 74).
• Als het probleem aanhoudt, neemt u
contact op met Dell (zie
"Contact met
Dell" op pagina 130
).
Er zijn geheugenmodules
gevonden, maar er is sprake van
een configuratie- of
compatibiliteitsfout in het
geheugen.
• Zorg dat u geen speciale
geheugenmodule/geheugenconnector
hoeft te plaatsen (zie "Overzicht van
DDR2-geheugen" op pagina 73).
• Controleer of de geheugenmodules die u
installeert, compatibel zijn met uw
computer (zie "Overzicht van DDR2-
geheugen" op pagina 73).
• Als het probleem aanhoudt, neemt u
contact op met Dell (zie
"Contact met
Dell" op pagina 130
).
Lichtpatroon (vervolg) Omschrijving probleem Mogelijke oplossing

52 Hulpmiddelen voor het oplossen van problemen
Er is mogelijk een fout in de
uitbreidingskaart opgetreden.
1
Controleer of er sprake is van een conflict
door een kaart (niet de grafische kaart) te
verwijderen en de computer opnieuw op te
starten. Zie "Kaarten" op pagina 77.
2
Als het probleem aanhoudt, installeert u
opnieuw de kaart die u hebt verwijderd,
verwijdert u een andere kaart en start u de
computer opnieuw op.
3
Herhaal deze stappen voor elke kaart. Als
de computer normaal opstart, controleert u
of de laatste kaart die u uit de computer
hebt verwijderd, voor bronconflicten zorgt
(zie "Software- en hardwareconflicten
oplossen" op pagina 57).
4
Als het probleem aanhoudt, neemt u
contact op met Dell (zie "Contact met
Dell" op pagina 130).
Er is een andere fout opgetreden.
• Controleer of de kabels van de vaste schijf,
het CD-station en het DVD-station juist
zijn aangesloten op het moederbord
(zie"Stations" op pagina 90).
• Als er op uw scherm een foutmelding
wordt afgebeeld die aangeeft dat er een
probleem is met een apparaat (zoals met
het diskettestation of de vaste schijf),
controleert u het apparaat om er zeker van
te zijn dat het goed functioneert.
• Het besturingssysteem probeert te starten
vanaf een apparaat (zoals een diskettestation
of een vaste schijf); controleer de
systeemsetup om er zeker van te zijn dat de
opstartvolgorde correct is voor de apparaten
die geïnstalleerd zijn op uw computer (zie
"System Setup" op pagina 117).
• Als het probleem aanhoudt, neemt u
contact op met Dell (zie
"Contact met
Dell" op pagina 130
).
Alle vier de lampjes knipperen als
de computer zich in een normale
werkstoestand bevindt na POST.
Geen.
Lichtpatroon (vervolg) Omschrijving probleem Mogelijke oplossing

Hulpmiddelen voor het oplossen van problemen 53
Dell Diagnostics
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
Als u problemen ondervindt met uw computer, controleert u de punten in "Problemen oplossen" op
pagina 33 en voert u Dell Diagnostics (Dell-diagnostiek) uit voordat u contact opneemt met Dell voor
technische ondersteuning.
KENNISGEVING: Dell Diagnostics werkt alleen op Dell™-computers.
1
Zet de computer aan of start deze opnieuw op.
2
Wanneer het logo DELL™ verschijnt, drukt u meteen op <F12>.
Vervolgens sluit u de computer af (zie "Uw computer uitschakelen" op pagina 63) en probeert u het
opnieuw.
3
Selecteer in de lijst met opstartapparaten
Boot to Utility Partition
(Opstarten vanaf partitie van
hulpprogramma) en druk op <Enter>.
4
Wanneer het
hoofdmenu
van het Dell-diagnoseprogramma wordt weergegeven, selecteert u de test die
u wilt uitvoeren.
Hoofdmenu van Dell Diagnostics
1
2
Als tijdens het uitvoeren van een test een probleem wordt aangetroffen, wordt een bericht weergegeven
met de foutcode en een beschrijving van het probleem. Noteer de foutcode en de beschrijving van het
probleem en volg de instructies op het scherm.
Neem contact op met Dell, als u de foutconditie niet kunt herstellen (zie "Contact met Dell" op
pagina 130).
Optie Functie
Snelle test Hiermee wordt een snelle test uitgevoerd van apparaten.
Deze test neemt doorgaans 10 tot 20 minuten in beslag. Er is
geen interactie vereist. Als u eerst de Express Test (snelle test)
uitvoert, vergroot u de kans om het probleem snel op te sporen.
Uitgebreide test Hiermee wordt een grondige controle van apparaten uitgevoerd.
Deze test neemt doorgaans een uur of langer in beslag. U
moet af en toe vragen beantwoorden.
Aangepaste test Hiermee kunt u een bepaald apparaat testen. U kunt de uit te
voeren tests aanpassen.
Symptomenstructuur Hier vindt u de meest voorkomende symptomen. U kunt hier
een test kiezen op basis van de symptomen van het
aangetroffen probleem.

54 Hulpmiddelen voor het oplossen van problemen
OPMERKING: Boven in elk testscherm ziet u het servicelabel van de computer. Als u contact opneemt met Dell,
vraagt de technische ondersteuning naar het servicelabel.
3
Wanneer u een test uitvoert van de optie
Custom Test
(Aangepaste test) of
Symptom Tree
(Symptomenstructuur), kunt u voor meer informatie over de test op een van de tabbladen klikken
die
in de volgende tabel worden beschreven.
4
Sluit het testscherm om terug te keren naar het
hoofdmenu
. Als u Dell Diagnostics wilt afsluiten en de
computer opnieuw wilt opstarten, sluit u het
hoofdmenu
.
Tabblad Functie
Results (Resultaten) Hier worden de resultaten van de test weergegeven, samen met
eventuele foutcondities die zijn aangetroffen.
Errors (Fouten) Hier worden aangetroffen foutcondities, foutcodes en
probleembeschrijvingen weergegeven.
Help Hier wordt de test beschreven en worden eventuele vereisten voor
het uitvoeren van de test vermeld.
Configuration
(Configuratie)
Hier wordt de hardwareconfiguratie beschreven voor het
geselecteerde apparaat.
Het Dell-diagnoseprogramma verkrijgt de configuratiegegevens
voor alle apparaten via de systeeminstellingen, het geheugen en
verschillende interne tests. Deze gegevens worden weergegeven in
het linkerdeelvenster van het scherm. Mogelijk worden in het
apparaatoverzicht niet de namen van alle onderdelen weergegeven
die zijn geïnstalleerd in of aangesloten op de computer.
Parameters Hiermee kunt u de test aanpassen door de testinstellingen te
wijzigen.

Hulpmiddelen voor het oplossen van problemen 55
Stuurprogramma’s
Wat is een stuurprogramma?
Een stuurprogramma is een programma waarmee een apparaat, zoals een printer, muis of toetsenbord,
wordt bestuurd. Voor alle apparaten is een stuurprogramma nodig.
Een stuurprogramma fungeert als een vertaler voor het apparaat en de andere programma's die
gebruikmaken van het apparaat. Elk apparaat beschikt over een eigen reeks speciale opdrachten die
alleen door het bijbehorende stuurprogramma worden herkend.
Dell ships your computer to you with required drivers already installed—no further installation or
configuration is needed.
Veel stuurprogramma's, bijvoorbeeld het stuurprogramma voor het toetsenbord, worden geleverd met het
besturingssysteem Microsoft
®
Windows
®
. In de volgende gevallen moet u mogelijk stuurprogramma's
installeren:
• U voert een upgrade voor uw besturingssysteem uit
• U installeert uw besturingssysteem opnieuw.
• U sluit een nieuw apparaat aan of u installeert een nieuw apparaat.
Stuurprogramma's controleren
Als u problemen met een apparaat ondervindt, controleert u of het stuurprogramma de bron van het
probleem is en werkt u het stuurprogramma indien noodzakelijk bij.
Windows XP
1
Klik op de knop
Start
en klik op
Configuratiescherm
.
2
Klik onder
Kies een categorie
op
Prestaties en onderhoud
.
3
Klik op
Systeem
.
4
Klik in het venster
Systeemeigenschappen
op de tab
Hardware
.
5
Klik op
Apparaatbeheer
.
6
Controleer of er een apparaat in de lijst voorkomt met een uitroepteken (een gele cirkel met een [
!
]) op
het pictogram voor het apparaat.
Als u een uitroepteken naast de naam van het apparaat ziet staan, moet u het stuurprogramma mogelijk
opnieuw installeren of een nieuw stuurprogramma installeren.

56 Hulpmiddelen voor het oplossen van problemen
Een stuurprogramma opnieuw installeren
KENNISGEVING: Op de ondersteuningssite van Dell op support.dell.com kunt u goedgekeurde
stuurprogramma's voor een computer van Dell™ downloaden. Als u stuurprogramma's installeert die afkomstig zijn
van een andere bron, loopt u het risico dat uw computer niet meer goed functioneert.
De functie Vorig stuurprogramma in Windows XP gebruiken
Als u problemen ondervindt op uw computer nadat u een stuurprogramma hebt bijgewerkt of geïnstalleerd,
gebruikt u de functie Vorig stuurprogramma in Windows XP om het stuurprogramma te vervangen door
de vorige geïnstalleerde versie van het stuurprogramma.
1
Klik op de knop
Start
en klik op
Configuratiescherm
.
2
Klik onder
Kies een categorie
op
Prestaties en onderhoud
.
3
Klik op
Systeem
.
4
Klik in het venster
Systeemeigenschappen
op de tab
Hardware
.
5
Klik op
Apparaatbeheer
.
6
Klik met de rechtermuisknop op het apparaat waarvoor u een nieuw stuurprogramma hebt geïnstalleerd
en klik op
Eigenschappen
.
7
Klik op de tab
Stuurprogramma
.
8
Klik op
Vorig stuurprogramma
.
Als u het probleem niet kunt verhelpen met Vorig stuurprogramma, kunt u met Systeemherstel de staat
herstellen waarin uw computer verkeerde voordat u het nieuwe stuurprogramma installeerde (zie
"Systeemherstel van MicrosoftWindows XP" op pagina 57).
Handmatig een stuurprogramma installeren
1
Nadat u de benodigde stuurprogrammabestanden naar uw vaste schijf hebt gekopieerd, klikt u op de
knop
Start
en klikt u met de rechtermuisknop op
Deze computer
.
2
Klik op
Eigenschappen
.
3
Klik op de tab
Hardware
en klik vervolgens op
Apparaatbeheer
.
4
Dubbelklik op het type apparaat waarvoor u het stuurprogramma wilt installeren.
5
Dubbelklik op de naam apparaat waarvoor u het stuurprogramma wilt installeren.
6
Klik op de tab
Stuurprogramma
en klik vervolgens op
Stuurprogramma bijwerken
.
7
Klik op
Ik wil zelf kiezen (geavanceerd)
en klik vervolgens op
Volgende
.
8
Klik op
Bladeren
en blader naar de locatie waarnaar u de stuurprogrammabestanden de vorige keer
hebt uitgepakt.
9
Wanneer de naam van het juiste stuurprogramma verschijnt, klikt u op
Volgende
.
10
Klik op
Voltooien
en start de computer opnieuw op.

Hulpmiddelen voor het oplossen van problemen 57
Software- en hardwareconflicten oplossen
Als een apparaat tijdens de installatie van het besturingssysteem niet wordt gevonden, of wel wordt gevonden
maar onjuist wordt geconfigureerd, kunt u het conflict oplossen met de Probleemoplosser voor hardware.
Conflicten oplossen met de Probleemoplosser voor hardware:
1
Klik op de knop
Start
en vervolgens op
Help en ondersteuning
.
2
Ty p
probleemoplosser hardware
in het veld
Zoeken
en klik op de pijl om de zoekbewerking te
starten.
3
Klik op
Probleemoplosser voor hardware
in de lijst
Zoekresultaten
.
4
Klik in de lijst
Probleemoplosser voor hardware
op
Er is een hardwareconflict op de computer
en klik
op
Volgende
.
Uw besturingssysteem herstellen
U kunt uw besturingssysteem op de volgende manieren herstellen:
• Met Systeemherstel van Microsoft
®
Windows
®
XP kunt u de computer terugzetten in een eerdere
status zonder dat gegevensbestanden verloren gaan. Gebruik het Systeemherstel als de eerste oplossing
om uw besturingsysteem te herstellen en gegevensbestanden te bewaren.
• Met Dell PC Restore van Symantec kunt u de vaste schijf terugzetten naar de status op het moment
dat u de computer kocht. Met Dell PC Restore worden alle gegevens op de vaste schijf definitief
verwijderd. Ook worden alle toepassingen verwijderd die u hebt geïnstalleerd nadat u de computer
hebt ontvangen. Gebruik PC Restore alleen als Systeemherstel de problemen met uw
besturingssysteem niet kon verhelpen.
• Gebruik de cd
alleen
als Systeemherstel de problemen met uw besturingssysteem niet kon verhelpen.
Systeemherstel van MicrosoftWindows XP
Met Systeemherstel biedt het besturingssysteem Microsoft Windows XP u de mogelijkheid om de computer
terug te zetten in een eerdere status (zonder dat er gegevensbestanden verloren gaan) als de computer
door wijzigingen in de hardware, software of andere systeeminstellingen niet meer naar behoren werkt.
Zie Help en ondersteuning van Windows voor informatie over het gebruik van Systeemherstel. Raadpleeg
voor Windows Help en ondersteuning "Informatie vinden" op pagina 9.
KENNISGEVING: Maak regelmatig reservekopieën van uw gegevensbestanden. Systeemherstel kan uw
gegevensbestanden niet controleren of herstellen.
OPMERKING: De procedures in dit document zijn geschreven voor de standaardweergave van Windows. Het
is dus mogelijk dat wanneer u de klassieke weergave inschakelt, deze procedures niet werken op uw computer
van Dell™.

58 Hulpmiddelen voor het oplossen van problemen
Een herstelpunt maken
1
Klik op de knop
Start
en vervolgens op
Help en ondersteuning
.
2
Klik op de taak voor
Systeemherstel
.
3
Volg de instructies op het scherm.
De computer terugzetten in een eerdere status
Als er zich problemen voordoen nadat u een apparaatstuurprogramma hebt geïnstalleerd, gebruikt u de
functie Vorig stuurprogramma (zie "De functie Vorig stuurprogramma in Windows XP gebruiken" op
pagina 56) om het probleem op te lossen. Als u het probleem hiermee niet kunt oplossen, gebruikt u
Systeemherstel.
KENNISGEVING: Voordat u de computer in een eerdere status terugzet, moet u alle geopende bestanden opslaan
en sluiten en alle actieve programma's afsluiten. Het is pas mogelijk om bestanden of programma's te bewerken,
openen of verwijderen nadat de herstelbewerking is voltooid.
1
Klik op de knop
Start
, wijs achtereenvolgens
Alle programma's
→
Bureau-accessoires
→
Systeemwerkset
aan en klik op
Systeemherstel
.
2
Controleer of
Een eerdere status van deze computer herstellen
is geselecteerd en klik op
Volgende
.
3
Klik op de datum waarnaar u de computer wilt terugzetten.
Het scherm
Selecteer een herstelpunt
laat een kalender zien met herstelpunten die u kunt selecteren.
De datums met beschikbare herstelpunten zijn vetgedrukt.
4
Selecteer een herstelpunt en klik op
Volgende
.
Als een datum slechts één herstelpunt bevat, wordt dat herstelpunt automatisch geselecteerd. Zijn er
twee of meer herstelpunten beschikbaar, klik dan op het herstelpunt van uw voorkeur.
5
Klik op
Volgende
.
Als Systeemherstel klaar is met het verzamelen van gegevens, verschijnt het scherm
Herstellen voltooid
en start de computer opnieuw op.
6
Nadat de computer opnieuw is opgestart, klikt u op
OK
.
Om het herstelpunt te wijzigen, kunt u bovenstaande stappen met een ander herstelpunt herhalen of de
herstelbewerking ongedaan maken.

Hulpmiddelen voor het oplossen van problemen 59
De laatste herstelbewerking ongedaan maken
KENNISGEVING: Voordat u de laatste herstelbewerking ongedaan maakt, moet u alle geopende bestanden
opslaan en sluiten en alle actieve programma's afsluiten. Het is pas mogelijk om bestanden of programma's te
bewerken, openen of verwijderen nadat de herstelbewerking is voltooid.
1
Klik op de knop
Start
en wijs achtereenvolgens
Alle programma's
→
Bureau-accessoires
→
Systeemwerkset
aan en klik op
Systeemherstel
.
2
Klik op
De laatste herstelbewerking ongedaan maken
en klik op
Volgende
.
Systeemherstel inschakelen
Als u Windows XP opnieuw installeert met minder dan 200 MB vrije ruimte op de vaste schijf, wordt
Systeemherstel automatisch uitgeschakeld. Ga als volgt te werk om te controleren of Systeemherstel is
ingeschakeld:
1
Klik op de knop
Start
en klik op
Configuratiescherm
.
2
Klik op
Prestaties en onderhoud
.
3
Klik op
Systeem
.
4
Klik op het tabblad
Systeemherstel
.
5
Controleer of het selectievakje
Systeemherstel uitschakelen
is uitgeschakeld.
Dell PC Restore van Symantec gebruiken
KENNISGEVING: Met Dell PC Restore worden alle gegevens op de vaste schijf definitief verwijderd. Ook worden
alle toepassingen of stuurprogramma's verwijderd die u hebt geïnstalleerd nadat u de computer hebt ontvangen.
Indien mogelijk maakt u een reservekopie van de gegevens voordat u PC Restore gebruikt. Gebruik PC Restore
alleen als Systeemherstel de problemen met uw besturingssysteem niet kon verhelpen.
OPMERKING: Dell PC Restore van Symantec is niet in alle landen en op alle computers beschikbaar.
Gebruik Dell PC Restore van Symantec alleen als laatste methode om uw besturingssysteem te herstellen.
Met Dell PC Restore kunt u de vaste schijf terugzetten naar de status op het moment dat u de computer
kocht. Any programs or files added since you received your computer—including data files—are permanently
deleted from the hard drive. Gegegevensbestanden zijn onder andere documenten, spreadsheets, e-
mailberichten, digitale foto's, muziekbestanden, enzovoort. Indien mogelijk maakt u een reservekopie
van alle gegevens voordat u PC Restore gebruikt.
PC Restore gebruiken:
1
Schakel de computer in.
Tijdens het opstarten verschijnt er een blauwe balk met het opschrift
www.dell.com
bovenin het scherm.
2
Druk zodra u deze balk ziet op <Ctrl><F11>.
Als u niet op tijd op <Ctrl><F11> drukt, wacht u tot de computer is opgestart en start u de computer
vervolgens opnieuw op.
KENNISGEVING: Als u niet wilt doorgaan met PC Restore, klikt u bij de volgende stap op Reboot (opnieuw opstarten).

60 Hulpmiddelen voor het oplossen van problemen
3
Klik in het volgend scherm dat verschijnt op
Restore
(herstellen)
4
Klik in het volgende scherm op
Confirm
(bevestigen)
The restore process takes approximately 6–10 minutes to complete.
5
Wanneer hiernaar wordt gevraagd, klikt u op
Finish
(voltooien) om de computer opnieuw op te starten.
OPMERKING: Sluit de computer niet handmatig af. Klik op Finish (voltooien) en wacht totdat de computer
helemaal opnieuw is opgestart.
6
Wanneer u hiernaar wordt gevraagd, klikt u op
Yes
(ja).
De computer start opnieuw op. Omdat de computer is teruggezet naar de oorspronkelijke status,
verschijnen weer dezelfde schermen als toen u de computer voor de eerste keer inschakelde, zoals het
scherm met de gebruiksrechtovereenkomst.
7
Klik op
Volgende
.
Het scherm
Systeemherstel
verschijnt en de computer start opnieuw op.
8
Nadat de computer opnieuw is opgestart, klikt u op
OK
.
Dell PC Restore verwijderen
KENNISGEVING: Als u het hulpprogramma Dell PC Restore van de vaste schijf verwijdert, wordt het
hulpprogramma PC Restore definitief van uw computer verwijderd. After you have removed Dell PC Restore, you
will not be able to use it to restore your computer’s operating system.
Met Dell PC Restore kunt u de vaste schijf terugzetten naar de oorspronkelijke status; de status op het
moment dat u de computer kocht. We raden u aan PC Restore niet van uw computer te verwijderen, ook
niet om extra schijfruimte te winnen. If you remove PC Restore from the hard drive, you cannot ever
recall it, and you will never be able to use PC Restore to return your computer’s operating system to its
original state.
PC Restore verwijderen:
1
Meld u aan bij de computer als lokale beheerder.
2
Ga in Windows Verkenner naar
c:\dell\utilities\DSR
.
3
Dubbelklik op de bestandsnaam
DSRIRRemv2.exe
.
OPMERKING: Als u zich niet aanmeldt als lokale beheerder, verschijnt er een bericht dat u zich moet
aanmelden als lokale beheerder. Klik op Quit (sluiten) om u vervolgens aan te melden als lokale beheerder.
OPMERKING: If the partition for PC Restore does not exist on your computer’s hard drive, a message appears
stating that the partition was not found. Klik op Quit (sluiten); er is geen partitie die u kunt verwijderen.
4
Klik op
OK
om de PC Restore-partitie op de vaste schijf te verwijderen.
5
Klik op
Ja
wanneer het bevestigingsbericht verschijnt.
De PC Restore-partitie is verwijderd en de beschikbare schijfruimte wordt toegevoegd aan de toegewezen
schijfruimte op de vaste schijf.

Hulpmiddelen voor het oplossen van problemen 61
6
Klik in Windows Verkenner met de rechtermuisknop op
Lokaal station (C:)
, klik op
Eigenschappen
en controleer de waarde bij
Beschikbaar
om te controleren of de extra schijfruimte beschikbaar is
7
Klik op
Finish
(voltooien) om het venster
PC Restore Removal
te sluiten.
8
Start de computer opnieuw op.
Plaats de cd voor het besturingssysteem.
Voordat u begint
Als u overweegt om het besturingssysteem Windows XP opnieuw te installeren om een probleem met een
recent geïnstalleerd stuurprogramma te verhelpen, probeer dan eerst de functie Vorig stuurprogramma
van Windows XP (zie "De functie Vorig stuurprogramma in Windows XP gebruiken" op pagina 56). Als u
het probleem niet kunt verhelpen met Vorig stuurprogramma, zet u het besturingssysteem via Systeemherstel
terug in de status waarin het was voordat u het nieuwe stuurprogramma installeerde (zie "Systeemherstel
van MicrosoftWindows XP" op pagina 57).
KENNISGEVING: Maak voordat u met de installatie begint reservekopieën van al uw gegevensbestanden op de
primaire vaste schijf. Bij normale configuraties is de primaire vaste schijf de eerste schijf die de computer detecteert.
Om Windows XP opnieuw te installeren, hebt u het volgende nodig:
• De cd Dell™
Besturingssysteem
•Dell ResourceCD
OPMERKING: De cd ResourceCD bevat stuurprogramma's die tijdens de montage van de computer geïnstalleerd
werden. Gebruik de ResourceCD om eventuele vereiste stuurprogramma’s te laden.
Windows XP opnieuw installeren
Het installatieproces kan één tot twee uur in beslag nemen. Nadat u het besturingssysteem opnieuw hebt
geïnstalleerd, moet u ook de apparaatstuurprogramma's, anti-virusprogramma's en andere software
opnieuw installeren.
KENNISGEVING: De cd Besturingssysteem biedt opties voor het opnieuw installeren van Windows XP. De opties
kunnen bestanden overschrijven en op uw vaste schijf geïnstalleerde programma's beschadigen. Ga dus pas over
tot het opnieuw installeren van Windows XP als een medewerker van de technische ondersteuning van Dell u dat
aangeeft.
1
Voordat u begint, moet u alle geopende bestanden opslaan en sluiten, en alle actieve programma's
afsluiten.
2
Plaats de cd
Besturingssysteem
. Klik op
Afsluiten
als het bericht
Windows XP installeren
verschijnt.
3
Start de computer opnieuw op.
4
Druk op <F12> zodra het DELL™-logo verschijnt.
Als het logo van het besturingssysteem verschijnt, wacht u totdat u het bureaublad van Windows ziet.
Sluit vervolgens de computer af en probeer opnieuw.
5
Volg de instructies op het scherm om het instellen te voltooien.

62 Hulpmiddelen voor het oplossen van problemen

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 63
Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
Voordat u begint
Dit hoofdstuk bevat procedures voor het verwijderen en installeren van de componenten in uw
computer. Tenzij anders vermeld, wordt voor elke procedure uitgegaan van de volgende condities:
• U hebt de stappen in "Uw computer uitschakelen" op pagina 63 en "Voordat u aan de computer
gaat werken" op pagina 64 uitgevoerd.
• U hebt de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids
van Dell™ gelezen.
• A component can be replaced or—if purchased separately—installed by performing the removal
procedure in reverse order.
Aanbevolen hulpmiddelen
Bij de procedures in dit document hebt u mogelijk de volgende hulpmiddelen nodig:
• Kleine sleufkopschroevendraaier
• Kruiskopschroevendraaier
• Diskette of cd met het updateprogramma voor Flash-BIOS
Uw computer uitschakelen
KENNISGEVING: Om gegevensverlies te voorkomen, dient u alle openstaande bestanden op te slaan en te
sluiten en alle programma's af te sluiten, voordat u uw computer uitschakelt.
1
Het besturingssysteem afsluiten:
a
Sla openstaande bestanden op en sluit ze, sluit alle programma's af, klik op
Start
en vervolgens
op
Computer uitschakelen
.
b
Klik op
Uitschakelen
in het venster
Computer uitschakelen
.
De computer schakelt uit zodra het afsluitproces van het besturingssysteem is voltooid.
2
Zorg ervoor dat de computer en alle aangesloten apparaten zijn uitgeschakeld. Houd de aan/uit-
knop 4 seconden ingedrukt, indien uw computer en aangesloten apparaten niet automatisch
worden uitgeschakeld wanneer u het besturingssysteem afsluit.

64 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
Voordat u aan de computer gaat werken
Neem de volgende veiligheidsrichtlijnen in acht om uw computer te beschermen tegen mogelijke schade
en voor uw persoonlijke veiligheid.
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
VOORZICHTIG: Ga voorzichtig om met componenten en kaarten. Raak de componenten of de contacten op een
kaart niet aan. Houd een kaart vast aan de uiteinden of aan de metalen montagebeugel. Houd een component,
zoals een processor, vast aan de uiteinden, niet aan de pinnen.
KENNISGEVING: Laat alleen een gekwalificeerd onderhoudstechnicus reparaties aan uw computer uitvoeren.
Schade als gevolg van door Dell niet geautoriseerde dienstverlening valt niet onder de garantie.
KENNISGEVING: Trek aan de connector of de kabelontlastingslus, wanneer u een kabel loskoppelt. Trek niet aan
de kabel zelf. Sommige kabels hebben een connector met vergrendelingsklemmen. Druk deze in voordat u de kabel
loskoppelt. Houd connectoren recht terwijl u ze loskoppelt om buiging van connectorpinnen te voorkomen. Zorg
ervoor dat u beide connectoren recht en op één lijn houdt, wanneer u een kabel aansluit.
KENNISGEVING: Voer de volgende stappen uit voordat u aan de computer gaat werken, om schade aan het
apparaat te voorkomen.
1
Schakel uw computer uit (zie "Uw computer uitschakelen" op pagina 63).
KENNISGEVING: Als u een netwerkkabel loskoppelt, dient u deze eerst uit uw computer te verwijderen en
vervolgens uit het netwerkapparaat.
2
Koppel telefoon- of telecommunicatielijnen los van de computer.
3
Haal de stekkers van uw computer en alle aangesloten apparaten uit het stopcontact en druk
vervolgens op de aan/uit-knop om de systeemkaart te aarden.
VOORZICHTIG: Om u te beschermen tegen elektrische schokken, dient u voordat u de computerbehuizing
verwijdert altijd eerst de stekker uit het stopcontact te halen.
4
Verwijder de kap van de computer (zie "De computerbehuizing verwijderen" op pagina 69).
KENNISGEVING: Aard uzelf door een ongeverfd metalen oppervlak, zoals het metaal aan de achterzijde van uw
computer, aan te raken, voordat u iets binnen in uw computer aanraakt. Raak tijdens het werken aan uw computer
af en toe een ongeverfd metalen oppervlak aan om eventuele statische elektriciteit, die schadelijk kan zijn voor
interne componenten, te ontladen.

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 65
Vooraanzicht van de computer
1 vergrendeling behuizing Gebruik deze vergrendeling om de behuizing te verwijderen.
Zie "De computerbehuizing verwijderen" op pagina 69.
2 locatie van het Servicelabel Gebruik het servicelabel om de computer te identificeren
wanneer u de Dell Support-website bezoekt of contact
opneemt met de technische ondersteuning.
3 Ejectknop cd- of dvd-station Druk op deze knop om een schijf uit het cd- of dvd-station te
werpen.
4 Lampje van cd- of dvd-station Het lampje brandt wanneer de computer gegevens leest van
het cd- of dvd-station.
5 FlexBay-station Kan optioneel een diskettestation of mediakaartlezer bevatten.
Zie "Een mediakaartlezer gebruiken (optioneel)" op pagina 20.
voor meer informatie over het gebruik van de mediakaartlezer.
2
1
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12

66 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
6 microfoonconnector Gebruik de microfoonconnector om een computermicrofoon
op uw computer aan te sluiten voor spraak of muziek in een
geluids- of telefonie programma.
Op computers met een geluidskaart bevindt deze connector
zich op de kaart.
7 hoofdtelefoonconnector Gebruik de hoofdtelefoonconnector om hoofdtelefoons en de
meeste typen speakers aan te sluiten.
8 controlelampjes (4) Gebruik de lampjes om een computerprobleem op te lossen op
basis van de diagnostische code. Zie "Controlelampjes" op
pagina 49 voor meer informatie.
9 lampje van vaste schijf Het lampje van de vaste schijf brandt wanneer de computer
gegevens leest van of schrijft naar de vaste schijf. Het lampje
brandt soms ook wanneer een apparaat als een cd-speler is
ingeschakeld.
10 aan/uit-knop,
aan/uit-lampje
Druk op de aan-/uit-knop om de computer in te schakelen. Het
lampje in het midden van de knop geeft aan of de computer is
ingeschakeld. Voor meer informatie zie "Schakelaars en
lampjes" op pagina 115.
KENNISGEVING: Gebruik de aan/uit-knop niet om de
computer uit te schakelen, anders kunnen er gegevens
verloren gaan. Schakel in plaats hiervan het
besturingssysteem uit.
11 USB 2.0-connectoren (2) Gebruik de voorste USB-connectoren voor apparaten die u af
en toe aansluit, zoals joysticks of camera's, of voor opstartbare
USB-apparaten (zie "System Setup-opties" op pagina 118 voor
meer informatie over het opstarten vanaf een USB-apparaat).
Het is raadzaam om de USB-connectoren aan de achterzijde te
gebruiken voor apparaten die normaal gesproken altijd
aangesloten zijn, zoals printers en toetsenborden.
12 ventilatieopeningen Controleer of de ventilatieopeningen niet zijn geblokkeerd om
zeker te zijn van voldoende koeling.
KENNISGEVING: Zorg dat er tussen de ventilatieopeningen
en objecten in de buurt ervan een ruimte zit van minimaal
twee inches.
KENNISGEVING: Zorg dat de ruimte om de luchtopeningen
schoon en stofvrij is zodat dat de computer voldoende
geventileerd wordt. Gebruik slechts een droge doek om de
ruimte rondom de ventilatieopening te reinigen; zo voorkomt u
waterschade aan de computer.

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 67
Achteraanzicht van de computer
1 stroomselectieschakelaar (niet op
alle computers beschikbaar)
Zie de veiligheidsinstructies in de Productinformatiegids voor meer
informatie.
2 netkabelconnector Sluit de stroomkabel aan.
3 connectoren op het achterpaneel Steek USB-, audio- en andere apparaten in de juiste connectoren.
Voor meer informatie zie "Connectoren op het achterpaneel" op
pagina 68.
4 kaartsleuven Toegang tot connectoren voor geïnstalleerde PCI en PCI Express-
kaarten.
1
3
4
2

68 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
Connectoren op het achterpaneel
12
8
7
34
5
6
1011 9
1 lampje integriteit
verbinding
• Green — A good connection exists between a 10-Mbps network and the
computer.
• Orange — A good connection exists between a 100-Mbps network and the
computer.
• Off — The computer is not detecting a physical connection to the network.
2 connector voor
netadapter
Wanneer u de computer op een netwerk of breedbandapparaat wilt aansluiten,
verbindt u het ene uiteinde van een netwerkkabel met een netwerkpoort of met
uw netwerk of breedbandapparaat. Sluit het andere uiteinde van de netwerkkabel
aan op de connector voor de netwerkadapter op de achterzijde van de computer.
Als u een klik hoort, is de netwerkkabel goed bevestigd.
OPMERKING: Sluit geen telefoonkabel aan op de netwerkconnector.
Gebruik voor computers met een netwerkconnectorkaart de connector op de kaart.
U wordt aangeraden om Category 5-bedrading en -ingangen voor uw netwerk te
gebruiken. Als u toch gebruikmaakt van Category 3-bedrading, moet u de
netwerksnelheid verhogen tot 10 Mbps om een betrouwbare werking te garanderen.
3 activiteitsindicator
netwerk
Er knippert een geel lampje wanneer de computer gegevens van het netwerk ontvangt
of ernaar verzendt. Bij veel verkeer kan het lijken alsof dit lampje continu brandt.
4 surround-sound-
connector
Gebruik de zwarte connector voor surround-sound om meerkanaalsluidsprekers
aan te sluiten.
5 lijningang Gebruik de blauwe lijningang om een opname-/afspeelapparaat aan te sluiten,
zoals een cassette-, cd- of videospeler.
Op computers met een geluidskaart bevindt deze connector zich op de kaart.

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 69
De computerbehuizing verwijderen
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
VOORZICHTIG: Om u te beschermen tegen elektrische schokken, dient u voordat u de computerbehuizing
verwijdert altijd eerst de stekker uit het stopcontact te halen.
1
Volg de procedures in "Voordat u begint" op pagina 63.
KENNISGEVING: Ensure that sufficient space exists to support the removed cover—at least 30 cm (1 ft) of desk
top space.
KENNISGEVING: Werk op een vlakke, beschermde ondergrond om krassen op de computer of het werkblad te
voorkomen.
2
Leg uw computer op zijn zijde met de computerbehuizing naar boven.
3
Trek de grendel van het deksel naar achteren die zich op het bovenpaneel bevindt.
6 lijnuitgang Gebruik de groene line-out-connector (beschikbaar op computers met
geïntegreerd geluid) om een hoofdtelefoon en de meeste luidsprekers met
geïntegreerde versterking aan te sluiten.
Op computers met een geluidskaart bevindt deze connector zich op de kaart.
7 microfoon Gebruik de roze connector om een computermicrofoon op uw computer
aan te sluiten voor spraak of muziek in een geluids- of telefonieprogramma.
Op computers met een geluidskaart bevindt deze connector zich op de kaart.
8 connector voor
zijspeakers surround
sound
Gebruik de zilverkleurige connector voor verbeterde audio op computers
met 7.1-speakers.
Op computers met een geluidskaart bevindt deze connector zich op de kaart.
9 midden/subwoofer-
connector
Gebruik de gele connector voor een luidspreker voor het Low Frequency Effects
(LFE) –kanaal.
10 optionele VGA-
videoconnector
Als uw monitor beschikt over een VGA-connector, steekt u deze in de VGA-
connector op de computer.
11 USB 2.0-connectoren (6) Gebruik de USB-connectoren aan de achterzijde voor apparaten die normaal
gesproken altijd aangesloten zijn, zoals printers en toetsenborden.
Het is raadzaam om de voorste USB-connectoren te gebruiken voor apparaten die
u af en toe aansluit, zoals joysticks of camera's, of voor startbare USB-apparaten.

70 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
4
Zoek de drie schanier punten in de onderrand van de computer.
5
Pak beide zijden van het deksel van de computer beet en wip deze op met behulp van de scharnieren
als hefboom.
6
Maak het deksel los van de scharnierpunten zet dit weg op een veilige plaats.
1 vergrendeling behuizing 2 computerdeksel 3 achterkant computer
4 onderste schanieren
2
1
3
4

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 71
De binnenkant van uw computer
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
1 diskettestation 2 Cd- of dvd-station 3 voeding
4 moederbord 5 vaste schijf
5
3
4
*1
2
*Niet op alle computers aanwezig.

72 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
Systeemkaartcomponenten
processorconnector (CPU)
geheugenmodule
connectoren (2, 4)
voedingsconnec
tor (12V)
geheugenmodulec
onnectoren (1, 3)
Voedingsconnect
or (POWER12V)
Jumper CMOS
wissen
(CLRCMOS)
SATA-connector
(SATA1)
Connector
voorpaneel
(FRNTPANEL)
SATA-connector
(SATA0)
optionele
videoconnector (VGA)
line-in-, line-out-,
microfoone-, zij-
surround-, midden-
en LFE-connectoren
Connector
processorventilator
(CPUFAN)
diskettestationconne
ctor (FLOPPY)
PCI Express x1-
connector (SLOT2)
PCI Express x16-
connector (SLOT1)
netwerkconnector (NIC) en
USB-connectoren (2) (USB2)
USB-connectoren (4) (USBBACK)
batterijhouder
(BATTERY)
PCI-connectoren
(SLOT4)
Connector Media Card
Reader (USBINT)
Connector
luchttemperatuursensor
(THRM)
wachtwoordjumper (CLRPSWD)
SATA-connector
(SATA4)
SATA-connector
(SATA5)
PCI-connector
(SLOT3)

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 73
Geheugen
U kunt de hoeveelheid werkgeheugen van uw computer vergroten door geheugenmodules te installeren
op het moederbord.
Uw computer ondersteunt DDR2-geheugen. Zie "Geheugen" op pagina 113 voor aanvullende informatie
over het door uw computer ondersteunde type geheugen.
Overzicht van DDR2-geheugen
DDR2-geheugenmodules moeten worden geïnstalleerd in paren van overeenkomstige geheugengrootte, -snelheid
en -technologie. Als de DDR2-geheugenmodules niet in overeenkomstige paren worden geïnstalleerd,
functioneert de computer nog wel, maar dalen de prestaties enigszins. See the label on the module to
determine the module’s capacity.
OPMERKING: Installeer DDR2-geheugenmodules altijd in de volgorde die wordt aangegeven op de systeemkaart.
De aanbevolen geheugenconfiguraties zijn:
– Een overeenkomstig paar van geheugenmodules geïnstalleerd in DIMM-connectoren 1 en 2
of
– Een overeenkomstig paar geheugenmodules geïnstalleerd in DIMM-connectoren 1 en 2 en nog
een overeenkomstig paar geïnstalleerd in connectoren 3 en 4.
KENNISGEVING: Installeer geen ECC- of buffergeheugenmodules. Alleen ongebufferd, niet-ECC geheugen wordt
ondersteund.
• Wanneer u gemengde paren van DDR2 533-MHz en DDR2 667-MHz-geheugen installeert,
functioneren de modules op de snelheid van de minst snelle module.
• Let op dat u een enkele geheugenmodule in DIMM-connector 1 (de connector die zich het dichtst bij
de processor bevindt) installeert, voordat u een module in de andere connector installeert.

74 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
KENNISGEVING: Wanneer u de originele geheugenmodules uit de computer verwijdert tijdens een opwaardering
van uw geheugen, houd deze dan gescheiden van nieuwe modules die u hebt, zelfs als u die nieuwe modules van
Dell hebt gekocht. Combineer een originele geheugenmodule, indien mogelijk, niet met een nieuwe geheugenmodule.
Anders start uw computer mogelijk niet goed op. U dient uw oorspronkelijke geheugenmodules in paren aan te
sluiten met de DIMM-connectoren 1 en 2 of DIMM-connectoren 3 en 4.
OPMERKING: Geheugen dat via Dell is gekocht valt onder de garantie van uw computer.
Geheugen aanspreken bij 4-GB-configuraties
Uw computer biedt ondersteuning voor maximaal 4 GB geheugen wanneer u gebruik maakt van vier 1-GB
DIMM’s. Huidige 32--bit besturingssystemen, zoals Microsoft
®
Windows
®
XP, kunnen maximaal 4 GB
adresruimte gebruiken; de hoeveelheid geheugen die beschikbaar is voor het besturingssysteem is echter
geringer dan wat er werd geïnstalleerd. Bepaalde onderdelen van de computer gebruiken adresruimte
binnen dit 4-GB grote bereik. Alle geheugenruimte die is gereserveerd voor deze onderdelen kan niet
worden gebruikt door het computergeheugen.
Geheugen installeren
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
KENNISGEVING: To prevent static damage to components inside your computer, discharge static electricity from
your body before you touch any of your computer’s electronic components. Dit kunt u doen door een ongeverfd
metalen oppervlak van het computerchassis aan te raken.
1 Kanaal A: overeenkomstig paar
geheugenmodules in connectoren DIMM_1
en DIMM_2 (witte bevestigingsclips)
2 Kanaal B: overeenkomstig paar
geheugenmodules in connectoren
DIMM_3 en DIMM_4 (zwarte
bevestigingsclips)
1
2

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 75
1
Volg de procedures in "Voordat u begint" op pagina 63.
2
Leg de computer op zijn zijkant zodat het moederbord zich onderin de computer bevindt.
3
Druk de borgklemmen aan de uiteinden van de geheugenmoduleconnector naar buiten.
4
Lijn de inkeping aan de onderkant van de module uit met de horizontale streep in de connector.
1 geheugenconnector
dichtst bij processor
2 borgklemmen (2) 3 connector
1 uitsparingen (2) 2 geheugenmodule 3 inkeping
4 horizontale streep
2
3
1
3
2
1
4

76 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
KENNISGEVING: Druk de geheugenmodule met gelijke druk aan de uiteinden recht naar beneden in de connector
om schade aan de module te voorkomen.
5
Druk de module in de connector totdat de module op zijn plaats klikt.
Wanneer u de module juist plaatst, klikken de borgklemmen in de uitsparingen aan de uiteinden van
de module.
6
Plaats de computerbehuizing terug.
KENNISGEVING: Als u een netwerkkabel wilt aansluiten, sluit u de kabel eerst aan op de netwerkaansluiting of
het netwerkapparaat en sluit u de kabel vervolgens aan op de computer.
7
Sluit uw computer en apparaten aan op het lichtnet en zet ze vervolgens aan.
8
Klik met de rechtermuisknop op het pictogram
Deze computer
en vervolgens op
Eigenschappen
.
9
Klik op het tabblad
Algemeen
.
10
Controleer de hoeveelheid weergegeven geheugen (RAM), om te verifiëren of het geheugen juist is
geïnstalleerd.
Geheugen verwijderen
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
KENNISGEVING: To prevent static damage to components inside your computer, discharge static electricity from
your body before you touch any of your computer’s electronic components. Dit kunt u doen door een ongeverfd
metalen oppervlak van het computerchassis aan te raken.
1
Volg de procedures in "Voordat u begint" op pagina 63.
2
Druk de borgklemmen aan de uiteinden van de geheugenmoduleconnector naar buiten.
3
Pak de module vast en trek hem omhoog.
Indien de module moeilijk te verwijderen is, beweegt u de module voorzichtig heen en weer terwijl u hem
omhoog trekt.

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 77
Kaarten
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
KENNISGEVING: To prevent static damage to components inside your computer, discharge static electricity from
your body before you touch any of your computer’s electronic components. Dit kunt u doen door een ongeverfd
metalen oppervlak van het computerchassis aan te raken.
Uw Dell™ computer bevat de volgende sleuven voor PCI- en PCI Express-kaarten:
• Twee PCI-kaartsleuven
• Eén PCI Express x16-kaartsleuf
• Eén PCI Express x1-kaartsleuf
PCI-kaarten
Uw computer biedt ondersteuning voor twee PCI-kaarten.
Volg de procedures in de volgende sectie, wanneer u een kaart installeert of vervangt. Zie "Een PCI-kaart
verwijderen" op pagina 81, wanneer u een PCI-kaart verwijdert en niet vervangt.
Verwijder het huidige station voor de kaart van het besturingssysteem, indien u een kaart vervangt
Zie "Een PCI Express-kaart installeren" op pagina 82, wanneer u een PCI Express-kaart installeert of
vervangt.

78 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
Een PCI-kaart installeren
1
Volg de procedures in "Voordat u begint" op pagina 63.
2
Druk voorzichtig tegen het ontgrendellipje aan de binnenzijde van het kaartslotpaneel om het paneel
te openen. Omdat het paneel vastzit, blijft deze geopend.
3
Indien u een nieuwe kaart installeert, verwijdert u eerst de beugels om een kaartsleuf te openen. Ga dan
verder met stap 5.
4
Wanneer u een geïnstalleerde kaart vervangt, dient u de huidige kaart te verwijderen.
Koppel, indien nodig, op de kaart aangesloten kabels los. Pak de kaart vast bij de bovenste hoeken en
trek hem voorzichtig uit de connector.
5
Maak de kaart klaar voor installatie.
Zie de documentatie die met de kaart is meegeleverd voor informatie over de configuratie van de kaart,
interne aansluitingen, of andere aanpassingen voor uw computer.
VOORZICHTIG: Sommige netwerkadapters starten de computer automatisch op wanneer ze zijn verbonden met
een netwerk. Haal de stekker van de computer uit het stopcontact, voordat u een kaart installeert, om u te
beschermen tegen elektrische schokken.
6
Plaats de kaart in de connector en druk deze stevig aan. Controleer of de kaart volledig in de sleuf valt.
1 ontgrendellipje 2 kaartslotpaneel
2
1

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 79
7
Controleer, voordat u het kaartslotpaneel sluit, of:
• de bovenkant van alle kaarten en beugels zich op één lijn bevinden met de uitlijningsstreep;
• de inkeping boven in de kaart of beugel om de uitlijningsgeleider past.
1 uitlijningsstreep 2 volledig geplaatste kaart 3 niet volledig geplaatste kaart
4 uitlijningsgeleider 5 beugel binnen de sleuf 6 beugel buiten de sleuf
2
3
6
5
4
1

80 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
8
Sluit het kaartslotpaneel door het vast te klikken.
KENNISGEVING: Geleid geen kabels van kaarten over of achter de kaarten. Kabels die over de kaarten zijn geleid
kunnen er voor zorgen dat de computerbehuizing niet goed sluit of dat er schade aan de apparatuur ontstaat.
9
Sluit kabels aan die verbonden moeten zijn met de kaart.
See the documentation for the card for information about the card’s cable connections.
KENNISGEVING: Als u een netwerkkabel wilt aansluiten, sluit u de kabel eerst aan op de netwerkaansluiting of
het netwerkapparaat en sluit u de kabel vervolgens aan op de computer.
10
Plaats de computerbehuizing terug, sluit de computer en apparaten opnieuw op het lichtnet aan en zet
ze vervolgens aan.
11
Indien u een geluidskaart hebt geïnstalleerd:
a
Ga naar systeeminstellingen (zie "System Setup" op pagina 117), selecteer
Audiocontroller
en
wijzig vervolgens de instellingen naar
Off
.
b
Connect external audio devices to the sound card’s connectors. Sluit geen externe apparaten aan
op de microfoon-, speaker/hoofdtelefoon- of line-in-connectoren op het achterpaneel.
1 uitlijningsgeleider 2 uitlijningsstreep 3 ontgrendellipje
4 kaartslotpaneel
1
2
4
3

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 81
12
Volg onderstaande instructies, wanneer u een netwerkadapter hebt geïnstalleerd en de geïntegreerde
netwerkadapter wilt uitschakelen:
a
"System Setup" op pagina 117
b
Connect the network cable to the add-in network adapter’s connectors. Sluit de netwerkkabel niet
aan op de geïntegreerde connector op het achterpaneel.
13
Installeer de benodigde stuurprogramma's voor de kaart zoals beschreven in de kaartdocumentatie.
Een PCI-kaart verwijderen
1
Volg de procedures in "Voordat u begint" op pagina 63.
2
Druk voorzichtig tegen het ontgrendellipje aan de binnenzijde van het kaartslotpaneel om het paneel
te openen. Omdat het paneel vastzit, blijft deze geopend.
3
Plaats een beugel in de lege kaartsleufopening als u de kaart permanent verwijdert.
OPMERKING: Het plaatsen van beugels voor lege kaartsleufopeningen is nodig in verband met het FCC-certificaat
van de computer. De beugels houden ook stof en vuil tegen.
4
Sluit het kaartslotpaneel door het vast te klikken.
KENNISGEVING: Als u een netwerkkabel wilt aansluiten, sluit u de kabel eerst aan op de netwerkaansluiting of
het netwerkapparaat en sluit u de kabel vervolgens aan op de computer.
5
Plaats de computerbehuizing terug, sluit de computer en apparaten opnieuw op het lichtnet aan en zet
ze vervolgens aan.
6
Remove the card’s driver from the operating system.
7
Indien u een geluidskaart hebt verwijderd:
a
Ga naar systeeminstellingen (zie "System Setup" op pagina 117), selecteer
Audiocontroller
en wijzig
vervolgens de instellingen naar
On
.
b
Sluit externe audioapparaten aan op de audioconnectoren op het achterpaneel van de computer.
8
Indien u een ingebouwde netwerkconnector hebt verwijderd:
a
Ga naar systeeminstellingen (zie "System Setup" op pagina 117), selecteer
Integrated NIC
en wijzig
vervolgens de instellingen naar
On
.
b
Sluit de netwerkkabel aan op de geïntegreerde connector op het achterpaneel van de computer.
PCI Express-kaarten
Uw computer biedt ondersteuning voor één PCI Express x16-kaart en één PCI Express x1-kaart. Volg de
procedures in de volgende sectie, wanneer u een PCI Express-kaart installeert of vervangt. Zie "Een PCI
Express-kaart verwijderen" op pagina 86, wanneer u een kaart verwijdert en niet vervangt. Zie "Een PCI-
kaart installeren" op pagina 78, wanneer u een PCI-kaart installeert of vervangt.
Verwijder het huidige station voor de kaart van het besturingssysteem, indien u een kaart vervangt.

82 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
Een PCI Express-kaart installeren
1
Volg de procedures in "Voordat u begint" op pagina 63.
2
Druk voorzichtig tegen het ontgrendellipje aan de binnenzijde van het kaartslotpaneel om het paneel
te openen. Omdat het paneel vastzit, blijft het open staan (zie "Een PCI-kaart installeren" op pagina 78
voor een illustratie van het kaartslotpaneel).
3
Als uw computer een kaartslotmechanisme bevat, gaat u als volgt te werk om de x16-kaart van bovenaf
vast te zetten.
a
Kantel het mechanisme omhoog en druk het aan de zijden zachtjes in om het mechanisme los te
maken van de twee lipjes die het op zijn plaats houden.
b
Leg het kaartslotmechanisme op een veilige plaats weg.
4
Indien u een nieuwe kaart installeert, verwijdert u eerst de beugels om een kaartsleuf te openen. Ga
dan verder met stap 5.
5
Wanneer u een geïnstalleerde kaart vervangt, dient u de huidige kaart te verwijderen.
Koppel, indien nodig, op de kaart aangesloten kabels los. Als uw kaart een slotmechanisme bevat,
verwijdert u de bovenzijde van het slotmechanisme door op het lipje te drukken en aan de bovenkant
te trekken. Trek voorzichtig aan het lipje, pak de kaart vast bij de bovenste hoeken en trek hem
voorzichtig uit de connector.
1 kaartslotpaneel 2 kaartslotmechanisme 3 ontgrendellipjes (2)
1
3
2

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 83
6
Maak de kaart klaar voor installatie.
Zie de documentatie die met de kaart is meegeleverd voor informatie over de configuratie van de kaart,
interne aansluitingen, of andere aanpassingen voor uw computer.
VOORZICHTIG: Sommige netwerkadapters starten de computer automatisch op wanneer ze zijn verbonden met
een netwerk. Haal de stekker van de computer uit het stopcontact, voordat u een kaart installeert, om u te
beschermen tegen elektrische schokken.
7
Wanneer u de kaart installeert in de x16-kaartconnector, plaatst u hem zo dat het slot is uitgelijnd met
het lipje en trek u voorzichtig aan het veiligheidslipje.
8
Plaats de kaart in de connector en druk deze stevig aan. Controleer of de kaart volledig in de sleuf valt.
1 PCI Express x16-kaart 2 slotlipje 3 PCI Express x1 kaart
4 PCI Express x1 kaartsleuf 5 PCI Express x16-kaartsleuf
1
5
3
4
2

84 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
9
Wanneer u een kaart vervangt die al eerder geïnstalleerd was op de computer en u het slotmechanisme
had verwijderd, kunt u dat nu opnieuw installeren.
10
Voordat u de kaart in het kaartslotmechanisme terugplaatst, moet u controleren of:
• de bovenkant van alle kaarten en beugels zich op één lijn bevinden met de uitlijningsstreep;
• de inkeping boven in de kaart of beugel om de uitlijningsgeleider past.
11
Klik het kaartslotmechanisme op zijn plaats om de x16 PCI-kaart vast te zetten.
1 uitlijningsstreep 2 volledig geplaatste kaart 3 niet volledig geplaatste kaart
4 uitlijningsgeleider 5 beugel binnen de sleuf 6 beugel buiten de sleuf
2
3
6
5
4
1

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 85
KENNISGEVING: Geleid geen kabels van kaarten over of achter de kaarten. Kabels die over de kaarten zijn geleid
kunnen er voor zorgen dat de computerbehuizing niet goed sluit of dat er schade aan de apparatuur ontstaat.
KENNISGEVING: Als u een netwerkkabel wilt aansluiten, sluit u de kabel eerst aan op de netwerkaansluiting of het
netwerkapparaat en sluit u de kabel vervolgens aan op de computer.
12
Plaats de computerbehuizing terug, sluit de computer en apparaten opnieuw op het lichtnet aan en zet
ze vervolgens aan.
13
Indien u een geluidskaart hebt geïnstalleerd:
a
Ga naar systeeminstellingen (zie "System Setup" op pagina 117), selecteer
Audiocontroller
en
wijzig vervolgens de instellingen naar
Off
.
b
Connect external audio devices to the sound card’s connectors. Sluit geen externe apparaten aan
op de microfoon-, speaker/hoofdtelefoon- of line-in-connectoren op het achterpaneel.
14
Volg onderstaande instructies, wanneer u een netwerkadapter hebt geïnstalleerd en de geïntegreerde
netwerkadapter wilt uitschakelen:
a
Ga naar de systeeminstellingen (zie "System Setup" op pagina 117), selecteer
Integrated NIC,
en
wijzig de instelling in
Off
.
b
Connect the network cable to the add-in network adapter’s connectors. Sluit de netwerkkabel niet
aan op de geïntegreerde connector op het achterpaneel.
15
Installeer de benodigde stuurprogramma's voor de kaart zoals beschreven in de kaartdocumentatie.
1 kaartslotpaneel 2 kaartslotmechanisme 3 ontgrendellipjes (2)
1
3
2

86 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
Een PCI Express-kaart verwijderen
1
Volg de procedures in "Voordat u begint" op pagina 63.
2
Druk voorzichtig tegen het ontgrendellipje aan de binnenzijde van het kaartslotpaneel om het paneel
te openen. Omdat het paneel vastzit, blijft het open staan (zie "Een PCI-kaart installeren" op pagina 78
voor een illustratie van het kaartslotpaneel).
3
Als uw computer een kaartslotmechanisme bevat, gaat u als volgt te werk om de x16-kaart van bovenaf
vast te zetten.
a
Kantel het mechanisme omhoog en druk het aan de zijden zachtjes in om het mechanisme los te
maken van de twee lipjes die het op zijn plaats houden.
b
Leg het kaartslotmechanisme op een veilige plaats weg.
4
Plaats een beugel in de lege kaartsleufopening als u de kaart permanent verwijdert.
OPMERKING: Het plaatsen van beugels voor lege kaartsleufopeningen is nodig in verband met het FCC-
certificaat van de computer. De beugels houden ook stof en vuil tegen.
5
Plaats het kaartslotmechanisme terug in de lipjes en kantel het naar beneden om het vast te zetten.
6
Sluit het kaartslotpaneel door het vast te klikken; zo zet u de kaarten vast.
KENNISGEVING: Als u een netwerkkabel wilt aansluiten, sluit u de kabel eerst aan op de netwerkaansluiting of
het netwerkapparaat en sluit u de kabel vervolgens aan op de computer.
7
Plaats de computerbehuizing terug, sluit de computer en apparaten opnieuw op het lichtnet aan en zet
ze vervolgens aan.
8
Remove the card’s driver from the operating system.
9
Indien u een geluidskaart hebt verwijderd:
a
Ga naar systeeminstellingen (zie "System Setup" op pagina 117), selecteer
Audiocontroller
en wijzig
vervolgens de instellingen naar
On
.
b
Sluit externe audioapparaten aan op de audioconnectoren op het achterpaneel van de computer.
10
Indien u een ingebouwde netwerkconnector hebt verwijderd:
a
Ga naar systeeminstellingen (zie "System Setup" op pagina 117), selecteer
Integrated NIC
en
wijzig vervolgens de instellingen naar
On
.
b
Sluit de netwerkkabel aan op de geïntegreerde connector op het achterpaneel van de computer.
11
Installeer de benodigde stuurprogramma's voor de kaart zoals beschreven in de kaartdocumentatie.
Stationspaneel
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
VOORZICHTIG: Om u te beschermen tegen elektrische schokken, dient u voordat u de computerbehuizing
verwijdert altijd eerst de stekker uit het stopcontact te halen.

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 87
Stationpaneel verwijderen
1
Volg de procedures in "Voordat u begint" op pagina 63.
2
Houd de hendel van de schuifplaat vast en trek de schuifplaat naar rechts tot deze in de open positie
klikt.
OPMERKING: De schuifplaat dient om stationspaneel vast te zetten en los te koppelen en helpt de stations op hun
plaats houden.
3
Wanneer u van binnenuit drukt en het stationspaneel naar links draait, kunt u het uit de scharnieren
aan de zijkant losmaken.
4
Leg het stationpaneel op een veilige plaats weg.
1 hendel schuifplaat 2 schuifplaat 3 stationspaneel
3
2
1

88 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
Inzetstuk stationpaneel verwijderen
1
Druk het lipje van het inzetstuk van het stationspaneel naar het midden van het stationspaneel om het
inzetstuk los te maken van het stationspaneel.
2
Draai het inzetstuk stationpanel nu naar buiten, weg van het stationspaneel, zonder het lipje los te laten.
3
Leg het inzetstuk stationpaneel op een veilige plaats weg.
Inzetstuk stationspaneel terugplaatsen
1 stationspaneel 2 inzetstuklipje stationspaneel 3 inzetstuk stationspaneel
1 middelste lipje stationspaneel 2 stationspaneel 3 inzetstuklipje stationspaneel
4 inzetstuk stationspaneel
1
3
2
1
3
2
4

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 89
1
Schuif het lipje aan de linkerzijde van het inzetstuk stationspaneel onder het middelste lipje.
2
Draai het inzetstuk stationspaneel op zijn plaats en klik het lipje van het inzetstuk stationspaneel over
het overeenkomstige lipje op het stationspaneel.
Stationspaneel terugplaatsen
1
Volg de procedures in "Voordat u begint" op pagina 63.
2
Zorg dat de lipjes van het stationspaneel zijn uitgelijnd met de scharnieren van de zijdeur.
3
Draai het stationspaneel naar de computer toe tot het op zijn plaats klikt op het voorpaneel.
1 hendel schuifplaat 2 schuifplaat 3 stationspaneel
3
2
1

90 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
Stations
Uw computer ondersteunt een combinatie van de volgende apparaten:
• Maximaal twee seriële ATA-vasteschijfstations
• Eén optioneel diskettestation of één optionele mediakaartlezer
• Maximaal twee CD- of DVD-stations
Sluit de seriële ATA CD- of DVD-stations aan op de connectoren met het label "SATA3" of "SATA4" op
het moederbord. Seriële ATA-vaste-schijfstations moeten worden aangesloten op de connectoren met
het label "SATA0" of "SATA2" op het moederbord.
1 cd/dvd-station 2 FlexBay voor optioneel
diskettestation of
mediakaartlezer
3 vaste schijf
1
2
3

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 91
Stationskabels aansluiten
When you install a drive, you connect two cables—a DC power cable and a data cable—to the back of
the drive.
Interfaceconnectoren voor station
De meeste interface-connectoren worden versleuteld voor juiste plaatsing; een inkeping of een ontbrekende
pin op de ene connector past bij een lipje of een opgevuld gaatje op de andere connector. Versleutelde
connectoren zorgen ervoor dat de pin-1 kabel terechtkomt in de pin-1-aansluiting van de connector. Het
pin-1 uiteinde van een connector op een bord of een kaart wordt meestal aangegeven door een op de
kaart of het bord geprinte zijdezeefdruk van het getal “1”.
1 stroomkabel 2 stroomtoevoerconnector
1 interfacekabel 2 interfaceconnector
1
2
Netkabelaansluiting
Seriële ATA-connector
1
2

92 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
Stationskabels aansluiten en loskoppelen
Wanneer u een seriële ATA-gegevenskabel aansluit of losmaakt, gebruikt u hiervoor het trek-lipje.
De seriële ATA-interfaceconnectoren worden versleuteld voor juiste plaatsing; een inkeping of een
ontbrekende pin op de ene connector past bij een lipje of een opgevuld gaatje op de andere connector.
Harde schijf
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
VOORZICHTIG: Om u te beschermen tegen elektrische schokken, dient u voordat u de computerbehuizing
verwijdert altijd eerst de stekker uit het stopcontact te halen.
KENNISGEVING: Plaats de schijf niet op een harde ondergrond, zodat schade wordt voorkomen. Plaats de schijf
in plaats daarvan op een zachte ondergrond, zoals schuimrubber.
KENNISGEVING: Maak een reservekopie van uw bestanden voordat u met deze procedure begint, als u een
harde schijf vervangt met gegevens die u wilt bewaren.
Controleer de documentatie van de schijf om te verifiëren dat deze geconfigureerd is voor uw computer.
Een vaste schijf verwijderen
1
Volg de procedures in "Voordat u begint" op pagina 63.
2
Maakt de stroom- en gegevenskabels los van de schijf.
KENNISGEVING: Gebruik het treklipje om de gegevenskabel van uw vaste schijf of van het moederbord
los te maken.

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 93
3
Druk de blauwe lipjes aan beide zijden van het station naar binnen en schuif het station omhoog en uit
de computer.
1 seriëlel ATA-gegevenskabel 2 stroomkabel
1 lipjes (2) 2 vaste schijf
1
2
1
2

94 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
Een harde schijf installeren
1
Pak de vervangende harde schijf uit en maak deze klaar voor installatie.
2
Controleer de documentatie van de schijf om te verifiëren dat deze geconfigureerd is voor uw computer.
OPMERKING: Als aan uw vervangende vaste schijf niet de vaste-schijfhouder is bevestigd, dient u de houder van
de oude schijf te verwijderen door deze van de schijf los te klikken. Klik de beugel op het nieuwe station.
3
Schuif het station voorzichtig op zijn plaats tot u een klik hoort of voelt dat het station stevig op zijn
plek zit.
4
Sluit de stroom- en vaste-schijfkabels aan op de schijf.
1 Station 2 vaste-schijfhouder
1
2

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 95
5
Controleer alle connectoren om er zeker van te zijn dat de kabels stevig vastzitten.
6
Plaats de computerkap weer terug (zie "De computerbehuizing terugplaatsen" op pagina 111).
KENNISGEVING: Als u een netwerkkabel wilt aansluiten, sluit u de kabel eerst aan op de netwerkpoort of het
netwerkapparaat en sluit u de kabel vervolgens aan op de computer.
7
Sluit uw computer en apparaten aan op het lichtnet en zet ze vervolgens aan.
Raadpleeg de documentatie van het station voor instructies voor het installeren van eventueel vereiste
software voor de werking van het station.
Tweede vast schijf toevoegen
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
VOORZICHTIG: Om u te beschermen tegen elektrische schokken, dient u voordat u de computerbehuizing
verwijdert altijd eerst de stekker uit het stopcontact te halen.
1 seriëlel ATA-gegevenskabel 2 stroomkabel
1
2

96 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
KENNISGEVING: Plaats de schijf niet op een harde ondergrond, zodat schade wordt voorkomen. Plaats de schijf
in plaats daarvan op een zachte ondergrond, zoals schuimrubber.
1
Controleer de documentatie van de schijf om te verifiëren dat deze geconfigureerd is voor uw computer.
2
Volg de procedures in "Voordat u begint" op pagina 63.
3
Druk de blauwe lipjes aan beide zijden van de beugel van het vasteschijfstation naar binnen en schuif
het station omhoog en uit de computer.
4
Klik de beugel op het vasteschijfstation.
5
Schuif het nieuwe (tweede) vasteschijfstation voorzichtig op zijn plek tot u een klik voelt of merkt dat
het niet verder kan.
6
Sluit de stroom- en vaste-schijfkabels aan op de schijf.
7
Controleer of het gegevenssnoer goed is aangesloten op het moederbord (zie "Systeemkaartcomponenten"
op pagina 72).
8
Controleer alle connectoren om er zeker van te zijn dat de kabels stevig vastzitten.
9
Plaats de computerkap weer terug (zie "De computerbehuizing terugplaatsen" op pagina 111).
KENNISGEVING: Als u een netwerkkabel wilt aansluiten, sluit u de kabel eerst aan op de netwerkpoort of het
netwerkapparaat en sluit u de kabel vervolgens aan op de computer.
10
Sluit uw computer en apparaten aan op het lichtnet en zet ze vervolgens aan.
Raadpleeg de documentatie van het station voor instructies voor het installeren van eventueel vereiste
software voor de werking van het station.
1 ontgrendellipjes (2) 2 tweede vaste schijf in
onderste compartiment
3 vasteschijfcompartiment
4 primaire vast schijf in
bovenste compartiment
1
2
3
4

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 97
Diskettestation
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
VOORZICHTIG: Om u te beschermen tegen elektrische schokken, dient u voordat u de computerbehuizing
verwijdert altijd eerst de stekker uit het stopcontact te halen.
OPMERKING: Als u een diskettestation toevoegt, zie "Een diskettestation installeren" op pagina 99.
Een diskettestation verwijderen
1
Volg de procedures in "Voordat u begint" op pagina 63.
2
Verwijder het stationspaneel (zie "Stationpaneel verwijderen" op pagina 87).
3
Koppel de stroom- en gegevenskabels aan de achterzijde van het diskettestation los.
OPMERKING: Wanneer u een PCI Express x16-kaart hebt geïnstalleerd, kan het voorkomen dat deze de
connectoren voor de diskettestations afdekken. Verwijder deze kaart voordat u de kabels van de diskettestations
aansluit.
1 stroomkabel 2 gegevenskabel
1
2

98 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
4
Schuif de stationsvergrendeling naar de onderkant van de computer en houd hem vast terwijl u het
diskettestation door de voorzijde van de computer schuift.
1 stationsvergrendeling 2 schuifplaat 3 diskettestation
3
2
1

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 99
Een diskettestation installeren
OPMERKING: Wanneer het nieuwe of vervangende diskettestation niet beschikt over bevestigingsschroeven,
zoekt u naar schroeven in het inzetstuk stationspaneel of gebruikt u de schroeven van het station dat u vervangt.
1
Volg de procedures in "Voordat u begint" op pagina 63.
2
Verwijder het stationspaneel (zie "Stationpaneel verwijderen" op pagina 87).
3
Schuif het station voorzichtig op zijn plaats tot u een klik hoort of voelt dat het station stevig op zijn
plek zit.
OPMERKING: Wanneer u een nieuw station installeert in plaats van er een te vervangen, verwijdert u het
inzetstuk van het stationspaneel op de plaats waar u het station wilt installeren, steekt u de schroeven die zich
achterin het stationspaneel bevinden in het station en schuift u het op zijn plaats.
4
Sluit de stroom- en gegevenskabels aan op het diskettestation.
5
Sluit het andere uiteinde van de gegevenskabel aan op de connector met het label "DSKT2" op het
moederbord (zie "Systeemkaartcomponenten" op pagina 72) en leg de kabel door de klem op de
behuizing.
1 Station 2 schroeven (4)
1
2

100 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
6
Wanneer u een nieuw diskettestation installeert in plaats van een oud te vervangen, verwijdert u het
betreffende inzetstuk van het stationpaneel (zie "Inzetstuk stationpaneel verwijderen" op pagina 88).
7
Controleer alle kabelaansluitingen en haal kabels uit de weg om blokkering van de luchtstroom tussen
de ventilator en de ventilatieopeningen te voorkomen.
8
Plaats het stationspaneel terug (zie "Stationspaneel terugplaatsen" op pagina 89).
9
Plaats de computerkap weer terug (zie "De computerbehuizing terugplaatsen" op pagina 111).
KENNISGEVING: Als u een netwerkkabel wilt aansluiten, sluit u de kabel eerst aan op de netwerkaansluiting of
het netwerkapparaat en sluit u de kabel vervolgens aan op de computer.
10
Sluit uw computer en apparaten aan op het lichtnet en zet ze vervolgens aan.
Raadpleeg de documentatie van het station voor instructies voor het installeren van eventueel vereiste
software voor de werking van het station.
11
Open de systeeminstellingen (zie "System Setup" op pagina 117) en selecteer de juiste optie voor het
Diskettestation
.
12
Controleer of uw computer correct werkt door Dell Diagnostics uit te voeren (zie "Dell Diagnostics" op
pagina 53).
1 stroomkabel 2 gegevenskabel
1
2

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 101
Mediakaartlezer
Zie "Een mediakaartlezer gebruiken (optioneel)" op pagina 20 voor meer informatie over het gebruik van
de mediakaartlezer.
Een mediakaartlezer verwijderen
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
KENNISGEVING: To prevent static damage to components inside your computer, discharge static electricity from
your body before you touch any of your computer’s electronic components. Dit kunt u doen door een ongeverfd
metalen oppervlak van het computerchassis aan te raken.
1
Volg de procedures in "Voordat u begint" op pagina 63.
2
Verwijder het stationspaneel (zie "Stationpaneel verwijderen" op pagina 87).
1 Mediakaartlezer 2 kabel
2
*1
*
Not present on all computers.

102 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
3
Koppel de FlexBay USB-kabel los van de achterkant van de mediakaartlezer en de connector op
het moederbord (zie "Systeemkaartcomponenten" op pagina 72) en haal de kabel door de klem
op de behuizing.
4
Schuif de stationsvergrendeling naar de onderkant van de computer en houd hem vast terwijl u de
mediakaartlezer door de voorzijde van de computer schuift.
5
Plaats het stationspaneel terug (zie "Stationspaneel terugplaatsen" op pagina 89).
6
Plaats de computerkap weer terug (zie "De computerbehuizing terugplaatsen" op pagina 111).
1 stationsvergrendeling 2 schuifplaat 3 Mediakaartlezer
3
2
1

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 103
Een mediakaartlezer installeren
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
KENNISGEVING: To prevent static damage to components inside your computer, discharge static electricity from
your body before you touch any of your computer’s electronic components. Dit kunt u doen door een ongeverfd
metalen oppervlak van het computerchassis aan te raken.
1
Volg de procedures in "Voordat u begint" op pagina 63.
2
Verwijder het stationspaneel (zie "Stationpaneel verwijderen" op pagina 87).
3
Neem de mediakaartlezer en de beugel uit de verpakking en controleer of alle schroeven zijn bijgevoegd.
4
Schuif de mediakaartlezer voorzichtig op zijn plaats tot u een klik hoort of voelt dat het station stevig
op zijn plek zit.
Zorg dat de mediakaartlezer geïnstalleerd is voordat de FlexBay-kabel wordt aangesloten.
1 Mediakaartlezer 2 schroeven (4)
1
2

104 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
5
Sluit de FlexBay USB-kabel aan achterop de mediakaartlezer en de connector op het moederbord (zie
"Systeemkaartcomponenten" op pagina 72).
6
Leg de FlexBay USB-kabel door de kabelklem.
7
Plaats de computerkap weer terug (zie "De computerbehuizing terugplaatsen" op pagina 111).
1 Mediakaartlezer 2 FlexBay USB-kabel
2
1

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 105
cd/dvd-station
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
VOORZICHTIG: Om u te beschermen tegen elektrische schokken, dient u voordat u de computerbehuizing
verwijdert altijd eerst de stekker uit het stopcontact te halen.
Een cd/dvd-station verwijderen
1
Volg de procedures in "Voordat u begint" op pagina 63.
2
Verwijder het stationspaneel (zie "Stationpaneel verwijderen" op pagina 87).
3
Koppel de stroom- en gegevenskabels aan de achterzijde van het station los.
4
Schuif de stationsvergrendeling naar de onderkant van de computer en houd hem vast terwijl u het
cd/dvd-station door de voorzijde van de computer schuift.
1 stroomkabel 2 gegevenskabel
1
2

106 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
1 stationsvergrendeling 2 schuifplaat 3 cd/dvd-station
3
2
1

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 107
Een cd/dvd-station installeren
1
Volg de procedures in "Voordat u begint" op pagina 63.
2
Wanneer u een nieuw cd/dvd-station installeert in plaats van een oude te vervangen, verwijdert u het
betreffende inzetstuk van het stationpaneel (zie "Inzetstuk stationpaneel verwijderen" op pagina 88).
3
Schuif het station voorzichtig op zijn plaats tot u een klik hoort of voelt dat het station stevig op zijn
plek zit.
4
Sluit de stroom- en gegevenskabels aan op de schijf.
1 cd/dvd-station 2 schroeven (3)
1
2

108 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
5
Controleer alle kabelaansluitingen en haal kabels uit de weg om blokkering van de luchtstroom tussen
de ventilator en de ventilatieopeningen te voorkomen.
6
Plaats de computerkap weer terug (zie "De computerbehuizing terugplaatsen" op pagina 111).
7
Plaats het stationspaneel terug (zie "Stationspaneel terugplaatsen" op pagina 89).
KENNISGEVING: Als u een netwerkkabel wilt aansluiten, sluit u de kabel eerst aan op de netwerkaansluiting
of het netwerkapparaat en sluit u de kabel vervolgens aan op de computer.
8
Sluit uw computer en apparaten aan op het lichtnet en zet ze vervolgens aan.
Raadpleeg de documentatie van het station voor instructies voor het installeren van eventueel vereiste
software voor de werking van het station.
9
Open de systeeminstellingen (zie "System Setup" op pagina 117) en selecteer de juiste optie voor
het
Station
.
10
Controleer of uw computer correct werkt door Dell Diagnostics uit te voeren (zie "Dell Diagnostics" op
pagina 53).
1 stroomkabel 2 gegevenskabel
1
2

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 109
Batterij
De batterij vervangen
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
KENNISGEVING: To prevent static damage to components inside your computer, discharge static electricity from
your body before you touch any of your computer’s electronic components. Dit kunt u doen door een ongeverfd
metalen oppervlak van het computerchassis aan te raken.
Een knoopcelbatterij handhaaft informatie over computerconfiguratie, datum en tijd. De batterij gaat
enkele jaren mee.
Vervang de batterij, wanneer u de tijd en datum herhaaldelijk opnieuw moet instellen als u de computer
aanzet.
VOORZICHTIG: Een nieuwe batterij kan exploderen als deze niet goed wordt geplaatst. Vervang de batterij
alleen door hetzelfde of een gelijkwaardig type, dat wordt aanbevolen door de fabrikant. Discard used batteries
according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
De batterij vervangen:
1
Leg alle schermen in systeeminstellingen vast (zie "System Setup" op pagina 117), zodat u de juiste
instellingen kunt herstellen in stap 8.
2
Volg de procedures in "Voordat u begint" op pagina 63.
3
Zoek de batterijhouder (zie "Systeemkaartcomponenten" op pagina 72).
KENNISGEVING: Als u de batterij met een stomp voorwerp uit de houder wrikt, dient u op te letten dat u de
systeemkaart niet aanraakt met dat voorwerp. Zorg ervoor dat het voorwerp tussen de batterij en de houder is
geplaatst voordat u probeert de batterij los te wrikken. Anders beschadigt u mogelijk de systeemkaart door de
houder los te wrikken of door de kopersporen te breken.
4
Verwijder de batterij door deze voorzichtig met uw vingers of met een stomp, niet-geleidend voorwerp
(zoals een plastic schroevendraaier) uit de batterijhouder te wrikken.
5
Plaats de nieuwe batterij in de houder met de "+"-zijde naar boven en klik de batterij op zijn plaats.

110 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren
6
Plaats de computerbehuizing terug (zie "De computerbehuizing terugplaatsen" op pagina 111).
KENNISGEVING: Als u een netwerkkabel wilt aansluiten, sluit u de kabel eerst aan op de netwerkaansluiting of
het netwerkapparaat en sluit u de kabel vervolgens aan op de computer.
7
Sluit uw computer en apparaten aan op het lichtnet en zet ze vervolgens aan.
8
Ga naar systeeminstellingen (zie "System Setup" op pagina 117) en herstel de instellingen die u hebt
vastgelegd in stap 1.
9
Gooi de oude batterij bij het chemisch afval. Raadpleeg de
Productinformatiegids
voor informatie over
het weggooien van batterijen.
1 ontgrendelingshendel batterij 2 batterij (positieve zijde)
2
1

Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren 111
De computerbehuizing terugplaatsen
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
1
Controleer of alle kabels zijn aangesloten en haal kabels uit de weg.
2
Controleer of er geen gereedschap of extra onderdelen in de computer achterblijven.
3
Lijn de onderkant van de behuizing uit met de lipjes aan de onderste rand van de computer.
4
Draai de behuizing naar beneden en druk deze aan om hem te sluiten, waarbij u de lipjes als draaipunt
gebruikt.
5
Controleer of de behuizing goed is geplaatst voordat u de computer rechtop zet.
KENNISGEVING: Als u een netwerkkabel wilt aansluiten, sluit u de kabel eerst aan op de netwerkaansluiting of
het netwerkapparaat en sluit u de kabel vervolgens aan op de computer.
6
Sluit uw computer en apparaten aan op het lichtnet en zet ze vervolgens aan.
1 computerdeksel 2 achterkant computer 3 onderste schanieren
1
2
3

112 Onderdelen verwijderen en installeren

Bijlage 113
Bijlage
Specificaties
Processor
Processortype Intel
®
Pentium
®
4 met Hyper-Threading-technologie
OPMERKING: Niet alle Pentium 4-processors ondersteunen Hyper-
Threading-technologie.
Level 1 (L1) cache 32 KB
Level 2 (L2) cache 1 MB (afhankelijk van de configuratie van uw computer)
pipelined-burst, eight-way set associative, write-back SRAM
Geheugen
Type 533 en 667 MHz dual DDR2 niet-gebufferde SDRAM
Geheugenconnectoren vier
Geheugencapaciteit 256 MB, 512 MB of 1 GB niet-ECC
Minimumgeheugen 256 MB
Maximumgeheugen 4 GB
OPMERKING: Zie "Geheugen aanspreken bij 4-GB-configuraties" op
pagina 74 om de hoeveelheid beschikbaar geheugen voor het
besturingssysteem te controleren.
BIOS-adres F0000h
Computergegevens
Chipset 965
RAID-ondersteuning RAID 1 (Mirroring)
DMA-kanalen acht
Interrupt-niveaus 24
BIOS-chip (NVRAM) 4 MB
NIC Geïntegreerde 10/100-netwerkkaart
Systeemklok Overdrachtsnelheid van 800 of 1066 MHz

114 Bijlage
Video
Type optioneel geïntegreerde Intel 965 Graphics Media Accelerator
(GMA965)
PCI Express:
Audio
Type Sigmatel 9227
Uitbreidingsbus
Bustype PCI 2.3
PCI Express x1 en x16
Bussnelheid PCI: 33 MHz
PCI Express:
x1 slot bidirectionele snelheid - 500 MB/s
x16 slot bidirectionele snelheid -8 GB/s
PCI
connectoren
twee
connectorgrootte
120-pins
connectorgegevensbreedte
(maximum)
32 bits
PCI Express:
connector
één x1
connectorgrootte
36-pins
connectorgegevensbreedte
(maximum)
1 PCI Express lane
PCI Express:
connector
één x16
connectorgrootte
164-pins
connectorgegevensbreedte
(maximum)
16 PCI Express lanes

Bijlage 115
Vaste schijven
Extern toegankelijk:
Compartimenten een 3,5-inch stationcompartiment (FlexBay)
twee 5,25-inch stationcompartimenten
Beschikbare apparaten Serieel ATA-station (4), diskettestation, USB-geheugenapparaten,
cd/dvd-station en mediakaartlezer
Intern toegankelijk: twee compartimenten voor 1-inch high serial ATA vaste-schijfstations
Connectoren
Externe connectoren:
Video
15-polige connector
Netwerkadapter
RJ-45-connector
USB
twee USB 2.0-connectoren aan de voorzijde en zes aan de achterzijde
Audio
zes aansluitingen voor 7.1-ondersteuning
Moederbordconnectoren:
Seriële ATA
vier 7-pins connectoren
FlexBay-station
een USB 10-pins kop voor optionele mediakaartlezer (3,5-inch
compartimentapparaat)
Diskettestation
een 33-pins connector
Ventilator
een 5-pins connector
PCI 2.3
twee 120-pins connectoren
PCI Express x1
een 36-pins connector
PCI Express x16
een 164-pins connector
Schakelaars en lampjes
Aan/uit-knop drukknop
Aan/uit-lampje groen lampje — Een knipperend groen lampje geeft aan dat het
systeem zich in de slaapstand bevindt; een groen lampje duidt erop
dat het systeem is ingeschakeld.
oranje lampje — Een knipperend oranje lampje duidt op een
probleem met de stroomvoorziening in de computer. Als het
systeem niet kan worden opgestart en er een oranje lampje brandt,
duidt dit op een probleem met het moederbord (zie "Problemen
met de voeding" op pagina 43).
Lampje van de vaste schijf groen

116 Bijlage
Lampje voor de
verbindingsintegriteit (op de
geïntegreerde netwerkadapter)
groen lampje — Er is een goede verbinding tussen het netwerk en
de computer.
uit (er brandt geen lampje) — Er is geen fysieke verbinding met
het netwerk gevonden.
Activiteitslampje (op de
geïntegreerde netwerk adapter)
knipperend geel lampje
Controlelampjes vier lampjes aan de voorzijde (zie "Controlelampjes" op pagina 49).
Stand-bylampje STBYLED op het moederbord
Voeding
Gelijkstroom:
Wattage
305 W
Maximale warmteafgifte
560,5 BTU/uur
Voltage (zie de
veiligheidsinstructies in
Productinformatiegids
voor
belangrijke informatie over het
instellen van het aantal volt)
90 tot 135 V en 180 tot 265 V bij 50/60 Hz
Reservebatterij 3-V CR2032 lithium knoopcel
Fysieke specificaties
Hoogte 41,4 cm (16.3 inches)
Breedte 18,8 cm (7.4 inches)
Diepte 45,7 cm (18.0 inches)
Gewicht 12,7 kg (28.0 lb)
Omgeving
Temperatuur:
Bedrijfstemperatuur
10° tot 35°C (50° tot 95°F)
Opslag
–40° tot 65°C (–40° tot 149°F)
Relatieve vochtigheid 20% tot 80% (niet-condenserend)
Maximumvibratie:
Bedrijfstemperatuur
5 tot 350 Hz bij 0,0002 G
2
/Hz
Opslag
5 tot 500 Hz bij 0,001 tot 0,01 G
2
/Hz
Schakelaars en lampjes (vervolg)

Bijlage 117
System Setup
Overzicht
Gebruik System Setup voor de volgende taken:
• De systeemconfiguratie wijzigen nadat u hardware hebt toegevoegd, gewijzigd of verwijderd
• Het instellen of wijzigen van een door de gebruiker te selecteren optie, zoals een wachtwoord
• Het lezen van de huidige hoeveelheid geheugen of het instellen van het type vaste schijf dat is geïnstalleerd
Voordat u System Setup gebruikt, is het verstandig de scherminformatie voor System Setup te noteren
zodat u deze later ter referentie kunt gebruiken.
KENNISGEVING: Wijzig de instellingen voor dit programma alleen als u een ervaren computergebruiker bent.
Bepaalde wijzigingen kunnen ervoor zorgen dat uw computer niet meer goed werkt.
System Setup openen
1
Zet de computer aan of start deze opnieuw op.
2
Wanneer het blauwe DELL™ wordt weergegeven, wacht u totdat de F2-prompt verschijnt.
3
Zodra de F2-prompt verschijnt, drukt u meteen op <F2>.
OPMERKING: De F2-prompt duidt erop dat het toetsenbord is geïnitialiseerd. Deze prompt wordt maar even
weergegeven. Wacht dus tot deze wordt weergegeven en druk vervolgens op <F2>. Als u te vroeg op <F2> drukt,
kunt u deze functietoets niet meer gebruiken.
4
Als u te lang hebt gewacht en het Microsoft
®
Windows
®
-logo verschijnt, wacht dan tot u het bureaublad
van Windows ziet. Vervolgens sluit u de computer af (zie "Uw computer uitschakelen" op pagina 63)
en probeert u het opnieuw.
System Setup-schermen
In het System Setup-scherm ziet u de huidige of instelbare configuratiegegevens voor uw computer.
Maximumimpact:
Bedrijfstemperatuur
40 G +/- 5% met een interval van 2 msec +/- 10% (equivalent aan
50,80 cm/sec [51 cm/sec])
Opslag
105 G +/- 5% met een interval van 2 msec +/- 10% (equivalent aan
50 in/sec [127 cm/sec])
Hoogte:
Bedrijfstemperatuur
–15,2 tot 3.048 m (–50 to 10.000 ft)
Opslag
–15,2 tot 10.668 m (–50 to 35.000 ft)
Omgeving (vervolg)

118 Bijlage
System Setup-opties
OPMERKING: Mogelijk worden de items in dit gedeelte niet weergegeven of wijken de items enigszins af van de
weergave in dit gedeelte. Dit is afhankelijk van uw computer en de geïnstalleerde apparaten.
System (Systeem)
System info
(Systeeminformatie)
Hier ziet u: System name (Systeemnaam), BIOS Version number (BIOS-
versienummer), BIOS Date, Service Tag (BIOS-servicedatum), Express
Service Code (Expresservicecode), en Asset Tag.
OPMERKING: De systeemnaam zoals die is opgegeven in het BIOS verschijnt
wellicht niet exact als de computernaam of in de documentatie van de computer.

Bijlage 119
Processor Info
(Processorgegevens)
Hiermee beeldt u de volgende gegevens af voor de processor die is
geïnstalleerd in het systeem: Processor Type (Processortype), Processor Clock
Speed (Kloksnelheid processor), Processor Bus Speed (Bussnelheid
processor), Processor Cache (Processorcache) Size (Grootte), Processor ID
number (Processoridentificatienummer, of de processor geschikt is voor
Hyperthreading en of de processor beschikt over 64-bit-technologie.
Memory info
(Geheugeninfo)
Toont de hoeveelheid Installed Memory (Geïnstalleerd geheugen), Memory
Speed (Geheugensnelheid), Memory Channel Mode (Geheugenkanaalmodus)
en een beschrijving van de Memory Technology (Geheugentechnologie). Met
deze optie wordt u ook een tabel afgebeeld met daarin de grootte van het
geheugen, of het geheugen geschikt is voor ECC, of het single of dual rank is,
het type en de organisatie.
PCI Info (PCI-info) Toont de inhoud van elke PCI-sleuf.
Date/Time
(Datum/Tijd)
Bestuurt de interne systeemklok en kalender.
Bootsequence
(Opstartvolgorde)
(Diskette drive default)
(Diskettestation
standaard)
Bepaalt de volgorde waarin het systeem zoek naar opstartapparaten tijden het
starten van het systeem.
OPMERKING: Wanneer u een opstartapparaat toevoegt en de computer opnieuw
opstart, wordt deze optie ook in het menu voor systeem-setup weergegeven. Als
u van een USB-geheugenapparaat wilt opstarten, selecteert u het USB-apparaat
en verplaatst u het zo dat het het eerste apparaat in de lijst wordt.
Stations
Diskette Drive
(Diskettestation)
(Internal default) (Intern
standaard)
Schakelt diskettestations in en uit en stelt de leestoestemming voor het
interne diskettestation in.
•
Off
(Uit) — schakelt alle diskettestations uit
•
USB
— schakelt het USB-diskettestation in
•
Internal
(Intern)
—
schakelt het interne diskettestation in
•
Read Only
(Alleen lezen)
—
schakelt de interne schijfbesturing in en geeft
voor het interne diskettestation alleen-lezen-toestemming
OPMERKING: Besturingsystemen die USB ondersteunen herkennen USB-
diskettestations toch, ongeacht deze instelling.
Drives 0 through 3
(Station 0 tot en
met 1)
(On) standaard)
Hiermee schakelt u een ATA of SATA-apparaat in (zoals een vaste schijf, CD-
station of een DVD-station). On hiermee schakelt u de interface in, zodat het
apparaat kan worden gebruikt.
Hiermee beeldt u het Controller type (ATA of SATA) af, het Poort nummer
dat het station gebruikt, het Drive ID number (Stationsidentificatienummer),
de Capacity (Capaciteit) en of het station wordt bestuurd door het BIOS.

120 Bijlage
SATA-werking
(RAID Autodetect/ATA
default)(RAID automatisch
detecteren/ATA standaard)
Geeft en definieert de instellingen van de SATA-controller voor RAID. U kunt
de SATA-controller instellen op RAID Autodetect/ATA of RAID On.
Onboard Devices (Ingebouwde apparatuur)
Integrated NIC
(Geïntegreerde NIC)
(On) standaard)
De ingebouwde NIC-controller in- of uitschakelen.
Mogelijke instellingen zijn
On, Off of On w/PXE. Wanneer de On w/ PXE-instelling actief is (alleen
beschikbaar voor het toekomstige opstarten), vraagt de computer u op
<Ctrl><Alt><b> te drukken. Wanneer u op deze toetscombinatie drukt,
wordt er een menu weergegeven waarmee u een methode kunt selecteren voor
het opstarten vanaf een netwerkserver. Als er geen opstartroutine beschikbaar
is vanaf een netwerkserver, probeert de computer op te starten vanaf het
volgende apparaat uit de lijst opstartvolgorde.
Integrated Audio
Controller
(Geïntegreerde
audiocontroller)
De ingebouwde audiocontroller in- of uitschakelen.
USB for FlexBay
(USB voor FlexBay)
(On) standaard)
Hiermee schakelt u de interne USB voor FlexBay in of uit.
OPMERKING: Deze USB-optie is alleen beschikbaar wanneer een FlexBay-station
is geïnstalleerd.
Video
Primary Video
(Primaire video)
(Auto (automatisch) is
standaard)
Geeft aan welke videocontroller de primaire is indien er twee videocontrollers
aanwezig zijn in de computer. Auto (automatisch) schakelt de ingebouwde
videocontroller in. Onboard hiermee schakelt u de geïntegreerde
videocontroller in.
Video Memory Size
(Omvang
videogeheugen)
(8 MB is standaard)
Hiermee configureert u het toegewezen systeemgeheugen dat wordt gereserveerd
voor de optionele geïntegreerde videocontroller. De instellingen zijn 1MB en
8MB.
Performance (Prestaties)
Hyper-Threading
(standaard ingeschakeld
(On))
Bepaalt of de fysieke processor wordt weergegeven als één of twee logische
processoren. De prestaties van bepaalde toepassingen zullen verbeteren
wanneer er een extra logische processor is geïnstalleerd.

Bijlage 121
SpeedStep
(standaard ingeschakeld
(On))
Hiermee stelt u het BIOS in staat de ventilator van de processor en de
snelheid hiervan aan te passen op basis van de temperatuurmetingen van de
processor.
OPMERKING: SteepStep wordt niet ondersteund door alle processors, en deze
optie is alleen beschikbaar wanneer er een processor is geïnstalleerd die het wel
ondersteunt.
HDD Acoustic Mode
(Akoestiekmodus)
•
Bypass
(Overslaan)
— Uw computer test of wijzigt de huidige instellingen
voor de akoestiekmodus niet.
•
Quiet
(Stil)
— De vast schijf werkt in zijn stilste instelling.
•
Suggested
(Voorgesteld) — De vaste schijf werkt op het door de fabrikant
voorgestelde niveau.
•
Performance
(Prestaties)
—
De vaste schijf werkt op maximale snelheid.
OPMERKING: Wanneer u naar de prestatiemodus wisselt, bewegen de leeskoppen
sneller over de schijf, waardoor de schijf lawaaieriger wordt. Bij sommige
stations treedt echter geen verbetering van de gegevensoverdrachtssnelheid op.
OPMERKING: Het wijzigen van de akoestiekinstellingen is niet van invloed op
het image van uw vaste schijf.
Security (beveiliging)
Admin Password
(beheerderswachtwo
ord)
(standaard niet ingesteld
(Not Set ))
Hiermee geeft u de huidige status van de wachtwoordbeveiliging voor het
systeemsetupprogramma weer en kunt u een nieuw beheerderswachtwoord
verifiëren en toewijzen.
System Password
(systeemwachtwoord)
(standaard niet ingesteld
(Not Set ))
Hiermee geeft u de huidige status van de wachtwoordbeveiligingsfunctie voor
het systeem weer en kunt u een nieuw systeemwachtwoord toewijzen en
verifiëren.
Password Changes
(Wachtwoordwijzigi
ngen)
(Unlocked (Ontgrendeld)
standaard)
Bepaalt de interactie tussen het Systeemwachtwoord en het Beheerderswachtwoord.
•
Locked
(Vergrendeld)
—
voorkomt dat een gebruiker zonder geldig
Beheerders
wachtwoord het
Systeem
wachtwoord kan wijzigen
•
Unlocked
(Ontgrendeld) — staat een gebruiker zonder een geldig
Beheerders
wachtwoord toe het systeemwachtwoord te wijzigen
Execute Disable
(standaard ingeschakeld
(On))
Hiermee schakelt u de Execute Disable-geheugenbeveiligingstechnologie in
of uit.

122 Bijlage
Power Management (Energiebeheer)
AC Recovery
(AC-herstel)
(standaard uitgeschakeld
(Off )
Hiermee bepaalt u hoe het systeem reageert wanneer de wisselstroom wordt
hersteld na een stroomonderbreking.
•
Off
(Uit) — Het systeem blijft uitgeschakeld nadat de stroomvoorzieninig is
hersteld. U drukt op de aan/uit-knop aan de voorkant van de computer om de
computer in te schakelen.
•
On
(Aan) — De computer wordt ingeschakeld zodra de stroomvoorziening is
hersteld.
•
Last
(Laatste) — Het systeem keert terug naar de laatste toestand waarin het
zich bevond toen het werd uitgezet.
Auto Power On
(Automatisch
inschakelen)
(Off (Uit) standaard)
Hiermee wordt de computer automatisch ingeschakeld
•
Off (Uit)
— hiermee schakelt u de functie Auto Power On (Automatisch
inschakelen) uit
•
Everyday
(Elke dag) — hiermee wordt de computer elke dag ingeschakeld op
de tijd die is ingesteld bij
Auto Power Time
(Automatisch inschakelen om).
•
Weekdays
(Werkdagen) — hiermee wordt de computer elke maandag tot en
met vrijdag ingeschakeld op de tijd die is ingesteld bij
Auto Power Time
(Automatisch inschakelen om).
OPMERKING: Deze functie werkt niet wanneer u de computer uitschakelt met
behulp van een stekkerdoos of een stroomstootbeveiliging.
Auto Power Time
(Automatisch
inschakelen)
Hiermee stelt u het tijdstip in waarop de computer automatisch wordt
ingeschakeld.
De tijd wordt uitgedrukt in het standaard 12-uursformaat (uren:minuten). U
kunt het starttijdstip wijzigen door op de linker of de rechter pijltjestoets te
drukken om een cijfer te verhogen of te verlagen, of u kunt zelf getallen typen
in de velden voor datum en tijd.
Suspend Mode
(slaapstand)
(standaard S3)
Hiermee schakelt u de slaapstand voor de computer in.
•
S1 —
hiermee wordt de computer in een slaapstand gebracht waarbij hij in
een energiezuinige modus werkt
•
S3 —
zet de computer stand-by waarbij energie wordt bespaard of voor de
meeste onderdelen zelfs is uitgeschakeld; het systeemgeheugen blijft echter
actief voor beide instellingen
Maintenance (Onderhoud)
SERR DMI Message
(SERR SMI-melding)
(standaard ingeschakeld
(On))
Bestuurt het SERR DMI-meldingsmechanisme.
OPMERKING: Voor sommige grafische kaarten is het vereist dat het SERR DMI-
meldingsmechanisme is uitgeschakeld.

Bijlage 123
Load Defaults
(Standaardinstelli
ngen laden)
Hiermee herstelt u de systeeminstellingen naar de fabriekswaarden.
Event Log
(Gebeurtenislogboek)
Hiermee kunt u het Event Log (Gebeurtenissenlogboek) bekijken. Items zijn
gemarkeerd met een R voor Read (Gelezen) of een U voor Unread
(Ongelezen). Mark All Entries Read (Alle vermeldingen markeren als gelezen)
plaatst een
R voor alle items. Clear Log (Logboek wissen) wist het Event Log
(Gebeurtenissenlogboek).
POST Behavior (POST-gedrag)
Fastboot
(Snelstarten)
(On) standaard)
Als u deze optie inschakelt, wordt de opstarttijd van de computer gereduceerd
door enkele compatibiliteitsstappen over te slaan.
•
Off
(Uit)
— er worden geen stappen overgeslagen tijdens het opstarten van
de computer
•
On
(Aan) — het systeem wordt sneller opgestart
Numlock Key
(Numlock-toets)
(On) standaard)
Bepaalt de functionaliteit van de numerieke toetsen rechts op het
toetsenbord.
•
Off
(uitgeschakeld) — de toetsen van het toetsenblok rechts op het
toetsenbord fungeren als pijlen.
•
On
(ingeschakeld) — de toetsen van het toetsenblok rechts op het
toetsenbord fungeren als cijfers.
POST Hotkeys
(POST-hotkeys)
(
Setup & Boot Menu
standaard)
Hiermee bepaalt u of in het opstartscherm de toetsencombinaties voor het
openen van het Setup-programma of de Quickboot-functie moeten worden
weergegeven.
•
Setup & Boot Menu
— beide toetsen worden weergegeven
(F2=Setup en F12=Boot Menu)
•
Setup
— alleen de toets voor setup wordt weergegeven (F2=Setup)
•
Boot Menu
— alleen de toets voor
Quickboot
wordt weergegeven
(F12=Boot Menu)
•
None
(Geen) — er worden geen toetsen weergegeven
Keyboard Errors
(Toetsenbordfouten)
(
Report
(Melden)
standaard)
Wanneer dit is ingesteld op Report en er een fout wordt aangetroffen tijdens
POST, geeft het BIOS een foutmelding weer en wordt u gevraagd op <F1> te
drukken om door te gaan of op <F2> te drukken om de systeemsetup te
openen.
Wanneer dit is ingesteld op Do Not Report (Niet melden)(uitgeschakeld) en
er een fout wordt aangetroffen tijdens POST, beeldt het BIOS wel een
foutmelding af maar wordt het systeem vervolgens gewoon opgestart.

124 Bijlage
Bootsequence (Opstartvolgorde)
Met deze functie kunt u de opstartvolgorde voor apparaten wijzigen.
Opties
•
Diskette Drive
(Diskettestation)
—
De computer wordt opgestart vanaf het diskettestation. Als de
diskette in het diskettestation geen opstartdiskette is, het diskettestation geen diskette bevat of als er
geen diskettestation is geïnstalleerd op uw computer, verschijnt er een foutbericht.
•
Hard Drive
(Vaste schijf) — De computer wordt opgestart vanaf de primaire vaste schijf. Als er geen
besturingssysteem op de vaste schijf is geïnstalleerd, verschijnt er een foutbericht.
•
CD Drive
(cd-romstation) — De computer wordt opgestart vanaf het cd-romstation. Als er geen cd in
het station is geplaatst of als de cd geen besturingssysteem heeft, verschijnt er een foutbericht.
•
USB Flash Device
(USB-flashstation)
—
Steek het geheugenapparaat in een USB-poort en start de
computer opnieuw op. Wanneer in de rechterbovenhoek van het scherm
F12 = Boot Menu
verschijnt, drukt u op <F12>. Het BIOS detecteert het apparaat en voegt de USB-flashoptie toe aan
het opstartmenu.
OPMERKING: Om op te starten vanf een USB-apparaat, moet het apparaat opstartbaar zijn. Als u zeker wilt weten
of een apparaat opstartbaar is, raadpleegt u de documentatie bij het apparaat.
De opstartvolgorde voor de huidige opstartprocedure wijzigen
U kunt deze functie gebruiken om bijvoorbeeld uw computer opnieuw op te starten vanaf een USB-
apparaat, zoals een diskettestation, een geheugenstick of een cd-rw-station.
OPMERKING: Als u opstart vanaf een USB-diskettestation, moet u het diskettestation eerst instellen op OFF in de
systeem-setup (zie "System Setup" op pagina 117).
1
Als u opstart vanaf een USB-apparaat, sluit u het USB-apparaat aan op een USB-connector (zie
"Connectoren" op pagina 115).
2
Zet de computer aan of start deze opnieuw op.
3
Wanneer in de rechterbovenhoek van het scherm
F2 = Setup, F12 = Boot Menu
verschijnt,
drukt u op <F12>.
Als u te lang hebt gewacht en het logo van het besturingssysteem verschijnt, wacht dan tot u het
bureaublad van Windows ziet. Vervolgens sluit u de computer af (zie "Uw computer uitschakelen" op
pagina 63) en probeert u het opnieuw.
Het
Boot Device Menu
(menu opstartbron) verschijnt. Dit menu bevat alle beschikbare opstartbronnen.
Naast elk apparaat staat een nummer.
4
Onderaan het menu voert u het nummer in van het apparaat dat alleen voor de huidige opstartpoging
moet worden gebruikt.
Wanneer u bijvoorbeeld start vanaf een USB-geheugenstick, selecteert u
USB Flash Device
en drukt
op <Enter>.

Bijlage 125
OPMERKING: Om op te starten vanf een USB-apparaat, moet het apparaat opstartbaar zijn. Als u zeker wilt weten
of een apparaat opstartbaar is, raadpleegt u de documentatie bij het apparaat.
De opstartvolgorde voor toekomstige opstartprocedures wijzigen
1
Open System Setup (zie "System Setup openen" op pagina 117).
2
Gebruik de pijltoetsen om het menu
Boot Sequence
(Opstartvolgorde)
te markeren en druk vervolgens
op <Enter> om het menu te openen.
OPMERKING: Noteer de huidige opstartvolgorde voor het geval u deze nadien wilt herstellen.
3
Druk op de pijl-omhoog en pijl-omlaag om door de lijst met bronnen te gaan.
4
Druk op de spatiebalk om een apparaat in of uit te schakelen (ingeschakelde apparaten zijn aangevinkt).
5
Druk op plus (+) of min (–) om een geselecteerd apparaat omhoog of omlaag te verplaatsen in de lijst.

126 Bijlage
Vergeten wachtwoorden wissen
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
1
Volg de procedures in "Voordat u begint" op pagina 63.
2
Zoek de 2-pins wachtwoordjumper (CLRPSWD) op het moederbord (zie "Systeemkaartcomponenten"
op pagina 72) en verwijder de jumperplug van pin 1 en 2 om het wachtwoord te wissen.
3
Plaats de computerkap weer terug (zie "De computerbehuizing terugplaatsen" op pagina 111).
4
Sluit uw computer en monitor aan op het lichtnet en zet ze vervolgens aan.
5
Nadat het bureaublad van Microsoft
®
Windows
®
op uw computer verschijnt, sluit u de computer af
(zie "Uw computer uitschakelen" op pagina 63).
6
Schakel de monitor uit en trek de stekker uit het stopcontact.
7
Trek het netsnoer van de computer uit het stopcontact en druk op de aan/uit-knop om het moederbord
te aarden.
8
Plaats de computerkap weer terug (zie "De computerbehuizing verwijderen" op pagina 69).
9
Zoek de 2-pins wachtwoordjumper (CLRPSWD) op het moederbord (zie "Systeemkaartcomponenten"
op pagina 72) en sluit de jumperplug aan op pin 1 en 2 om de wachtwoordfunctie opnieuw in te
schakelen.
10
Plaats de computerkap weer terug (zie "De computerbehuizing terugplaatsen" op pagina 111).
KENNISGEVING: Als u een netwerkkabel wilt aansluiten, sluit u de kabel eerst aan op de netwerkaansluiting of
het netwerkapparaat en sluit u de kabel vervolgens aan op de computer.
11
Sluit uw computer en apparaten aan op het lichtnet en zet ze vervolgens aan.

Bijlage 127
CMOS-instellingen wissen
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
1
Volg de procedures in "Voordat u begint" op pagina 63.
2
De huidige CMOS-instellingen wissen:
a
Zoek zowel de 2-pins wachtwoordjumper (CLRPSWD) als de 2-pins CMOS-jumper (CLRCMOS)
op het moederbord (zie "Systeemkaartcomponenten" op pagina 72).
b
Verwijder de 2-pins wachtwoordjumper (CLRPSWD) van de pinnen.
c
Plaats de wachtwoordjumperplug op de CLRCMOS-pinnen en wacht ongeveer 5 seconden.
d
Verwijder de jumperplug van de CLRCMOS-pinnen en plaats hem terug op de wachtwoord-
(CLRPSWD) pinnen.
3
Plaats de computerkap weer terug (zie "De computerbehuizing terugplaatsen" op pagina 111).
KENNISGEVING: Als u een netwerkkabel wilt aansluiten, sluit u de kabel eerst aan op de netwerkpoort of het
netwerkapparaat en sluit u de kabel vervolgens aan op de computer.
4
Sluit uw computer en apparaten aan op het lichtnet en zet ze vervolgens aan.
Uw computer reinigen
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u begint met de procedures in dit gedeelte, moet u de veiligheidsinstructies in de
Productinformatiegids raadplegen.
Computer, toetsenbord en monitor
VOORZICHTIG: Voordat u de computer reinigt, trekt u eerst de stekker van de computer uit het stopcontact.
Maak uw computer schoon met een zachte, met water bevochtigde doek. Gebruik geen vloeibare
reinigingsmiddelen of spuitbussen. Deze bevatten mogelijk ontvlambare stoffen.
• Gebruik een stofzuiger met een zachte borstelkop om voorzichtig het stof uit de sleuven en gaten van
uw computer en uit uw toetsenbord te verwijderen.
KENNISGEVING: Veeg het scherm nooit schoon met zeepoplossingen of een alcoholoplossing. Hiermee kunt u de
anti-schitteringscoating beschadigen.
• Om het scherm van uw monitor te reinigen, gebruikt u een zachte doek dat enigszins vochtig is gemaakt
met puur water. Gebruik een speciaal beeldschermreinigingsdoekje of een geschikte oplossing voor de
antistatische laag.
• Reinig de plastic onderdelen van het toetsenbord, de computer en de monitor met een zacht
schoonmaakdoekje dat is bevochtigd met een oplossing van drie delen water en één deel afwasmiddel.
Zorg dat het doekje niet volledig is doorweekt of dat er water in uw computer of toetsenbord drupt.

128 Bijlage
Muis
Als de cursor overslaat of een afwijkend bewegingspatroon vertoont, reinigt u de muis. Een niet-optische
muis reinigen:
1
Draai het plaatje aan de onderkant van de muis tegen de klok in en verwijder de bal.
2
Reinig de bal met een schone, pluisvrije doek.
3
Blaas voorzichtig in de behuizing van het balletje om stof en pluizen los te maken.
4
Als de rollers in de balhouder vuil zijn, reinigt u de rollers met een wattenstaafje dat is bevochtigd met
isopropylalcohol.
5
Centreer de rollers in de kanalen als deze niet meer goed zijn uitgelijnd. Zorg dat er geen pluisjes van
het wattenstaafje achterblijven.
6
Plaats de bal en het plaatje terug en draai het plaatje met de klok mee totdat deze vastklikt.
Diskettestation
KENNISGEVING: Reinig de de stationskoppen niet met een wattenstaafje. De mogelijkheid bestaat dat u de
koppen verkeerd uitlijnt waardoor het station niet meer werkt.
Reinig het diskettestation met een speciale, in de winkel verkrijgbare reinigingskit. Deze kits bevatten
voorbehandelde diskettes waarmee het vuil dat zich bij normaal gebruik ophoopt, wordt verwijderd.
Cd's en dvd's
KENNISGEVING: Gebruik altijd perslucht om de lens van het cd/dvd-station te reinigen en volg de instructies die
bij het persluchtproduct worden geleverd. Raak de lens in het station nooit aan.
Als er problemen optreden bij het afspelen van uw cd's of dvd's, zoals het overslaan van de cd, reinigt u de disc.
1
Houd de cd of dvd aan de buitenste rand. U kunt ook de disc ook vasthouden aan de binnenster rand
rond het gat.
KENNISGEVING: Om te voorkomen dat het oppervlak beschadigt, moet u de disc niet met ronddraaiende
bewegingen schoonvegen.
2
Gebruik een zacht, pluisvrij doek en veeg de onderkant van de disc (de zijde zonder label) schoon met
rechte vegen van binnen naar buiten.
Voor hardnekkig vuil kunt u water of een oplossing van water en een milde zeep gebruiken. U kunt ook
commerciële producten aanschaffen voor het reinigen van de disc en ter bescherming tegen stof,
vingervlekken en krassen. Reinigingsproducten voor cd's kunt u ook gebruiken voor dvd's.

Bijlage 129
Technische ondersteuningsbeleid van Dell (alleen voor de V.S.)
Tijdens de technische ondersteuning is bij de probleemoplossingsprocedure de medewerking van de
klant vereist om de originele instellingen van Dell voor het besturingssysteem, de software en de
hardwarestuurprogramma's, alsmede de betreffende functionaliteit van de computer en de door Dell
geïnstalleerde hardware, te herstellen. Naast de ondersteuning van een technische medewerker, wordt
online technische ondersteuning geboden op support.dell.com. Extra technische ondersteuningsopties
zijn beschikbaar tegen een vergoeding.
Dell biedt beperkte technische ondersteuning voor de computer, door Dell geïnstalleerde software en
randapparaten
1
. Ondersteuning voor software en randapparatuur van derden wordt geleverd door de
betreffende fabrikant, inclusief die producten die zijn aangeschaft en/of geïnstalleerd via Dell Software
and Peripherals, Readyware en Custom Factory Integration
2
.
1
Reparatieservices worden geboden overeenkomstig de bepalingen en voorwaarden van uw beperkte garantie en de
optionele servicecontracten- die zijn afgesloten bij de aanschaf van de computer.
2
Alle standaard Dell componenten in een Custom Factory Integration-project (CFI) vallen onder de beperkte garantievoorwaarden- van
Dell. Dell heeft het vervangingsprogramma echter uitgebreid zodat ook niet-standaard, hardwareonderdelen van derden
die via CFI zijn geïntegreerd, voor de duur van de serviceovereenkomst voor de computer worden gedekt.
Definitie van door Dell geïnstalleerde software en randapparatuur
Door Dell geïnstalleerde software omvat onder andere het besturingssysteem en bepaalde software die
tijdens het productie op de computer is geïnstalleerd (Microsoft
®
Office, Norton Antivirus, enzovoort).
Door Dell geïnstalleerde randapparatuur heeft betrekking op alle interne uitbreidingskaarten,
modulecompartimenten van Dell of PC Card-accessoires. Tevens betreft het alle monitoren, toetsenborden,
muizen, luidsprekers, microfoons voor telefoonmodems, dockingstations/poortreplicators,
netwerkproducten en de bijbehorende kabels.
Definitie van software en randapparatuur van derden
Software en randapparatuur van derden heeft betrekking op alle randapparatuur, accessoires of software
die door Dell onder een andere merknaam dan die van Dell worden verkocht (printers, scanners,
camera's, games, enzovoort). Ondersteuning voor de software en randapparatuur van derden wordt
verstrekt door de fabrikant van het product.
FCC-kennisgeving (alleen V.S.)
FCC Klasse B
Deze apparatuur genereert, gebruikt, en kan radiofrequentie uitzenden en kan, indien niet geïnstalleerd
en gebruikt in overeenstemming met de instructies, interferentie veroorzaken voor de ontvangst van
radio- en tv-signalen. Deze apparatuur is getest en geschikt bevonden binnen de grenzen van Klasse B
digitale apparatuur, in overeenstemming met Deel 15 van de FCC-richtlijnen.

130 Bijlage
Dit apparaat voldoet aan de FCC-richtlijnen, deel 15. Gebruik is onderhevig aan de volgende twee
voorwaarden:
1
Dit apparaat mag geen schadelijke interferentie veroorzaken.
2
Dit apparaat dient alle ontvangen interferentie te accepteren, inclusief interferentie die een ongewenst
effect op de werking van het apparaat heeft.
KENNISGEVING: De richtlijnen van de FCC bepalen dat met wijzigingen of aanpassingen die niet expliciet zijn
goedgekeurd door Dell Inc., uw gebruiksrecht voor deze apparatuur kan komen te vervallen.
Deze grenzen worden aangehouden om redelijke bescherming tegen schadelijke interferentie te bieden
bij plaatsing in een huiselijke omgeving. Wij kunnen echter niet garanderen dat er in een bepaalde
situatie geen interferentie zal optreden. Als deze apparatuur schadelijke interferentie veroorzaakt voor
radio- of televisieontvangst (u kunt dit bepalen door de apparatuur in en uit te schakelen), raden we u
aan de interferentie als volgt te verhelpen:
• Verander de richting van de antenne.
• Verplaats het systeem ten opzichte van de receiver.
• Plaats de subwoofer uit de buurt van de receiver.
• Sluit het systeem aan op een ander stopcontact zodat het systeem en de receiver zijn aangesloten op
verschillende vertakte circuits.
Indien nodig kunt u voor advies contact opnemen met een medewerker van Dell of een ervaren radio-
/televisie-installateur.
Overeenkomstig de FCC-richtlijnen, wordt de volgende informatie verstrekt voor het apparaat of de
apparaten waarop dit document van toepassing is:
• Productnaam: Dell™ Dimension™ E520
• Modelnummer: DCSM
• Bedrijfsnaam:
Dell Inc.
Worldwide Regulatory Compliance & Environmental Affairs
One Dell Way
Round Rock, TX 78682 USA
512-338-4400
OPMERKING: Zie voor meer informatie over overheidsvoorschriften uw Productinformatiegids.
Contact met Dell
Als u elektronisch contact wilt opnemen met Dell, kunt u de volgende websites bezoeken:
• www.dell.com
•
support.dell.com
(ondersteuning)

Bijlage 131
De specifieke webadressen voor uw land vindt u in de onderstaande tabel.
OPMERKING: De gratis nummers kunnen alleen worden gebruikt in het betreffende land.
OPMERKING: In bepaalde landen is er een speciaal telefoonnummer beschikbaar voor de ondersteuning voor
Dell™XPS™ draagbare computers. Dit telefoonnummer wordt voor de deelnemende landen vermeld. Wanneer er
geen speciaal nummer beschikbaar is voor XPS-computers, kunt u contact met Dell opnemen via het vermelde
ondersteuningsnummer. U wordt dan doorgeschakeld.
Wanneer u contact met Dell moet opnemen, gebruikt u de elektronische adressen, telefoonnummers en
codes in de volgende tabel. Als u hulp nodig hebt om te bepalen welke codes u moet gebruiken, neemt u
contact op met een lokale of internationale operator.
OPMERKING: De verstrekte contactgegevens waren correct op het moment dat dit document werd gedrukt maar
kunnen inmiddels gewijzigd zijn.
Land (Plaats)
Internationale toegangscode
Landcode
Netnummer
Afdeling of servicegebied,
Website en e-mailadres
Netnummers,
lokale nummers en
gratis nummers
Amerikaanse Maagdeneilanden E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
1-877-702-4288
Anguilla Website: www.dell.com.ai
E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
gratis: 800-335-0031
Antigua en Barbuda Website: www.dell.com.ag
E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
1-800-805-5924
Argentinië (Buenos Aires)
Internationale toegangscode: 00
Landcode: 54
Netnummer: 11
Website: www.dell.com.ar
E-mail: [email protected]
E-mail voor draagbare en destkopcomputers:
E-mail voor servers en opslagproducten van EMC
®
:
Customer Care
gratis: 0-800-444-0730
Technische ondersteuning
gratis: 0-800-444-0733
Technische ondersteuningsservices
gratis: 0-800-444-0724
Verkoop
0-810-444-3355

132 Bijlage
Aruba Website: www.dell.com.aw
E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
gratis: 800-1578
Australië (Sydney)
Internationale toegangscode:
0011
Landcode: 61
Netnummer: 2
Website: support.ap.dell.com
E-mail: support.ap.dell.com/contactus
Algemene ondersteuning
13DELL-133355
Bahamas Website: www.dell.com.bs
E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
gratis: 1-866-278-6818
Barbados Website: www.dell.com/bb
E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
1-800-534-3142
België (Brussel)
Internationale toegangscode: 00
Landcode: 32
Netnummer: 2
Website: support.euro.dell.com
Technische ondersteuning voor XPS
02 481 92 96
Technische ondersteuning
voor alle andere Dell-computers
02 481 92 88
Faxnummer technische ondersteuning
02 481 92 95
Customer Care
02 713 15 65
Verkoop ondernemingen
02 481 91 00
Fax
02 481 92 99
Schakelbord
02 481 91 00
Bermuda Website: www.dell.com/bm
E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
1-877-890-0751
Bolivia Website: www.dell.com/bo
E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
gratis: 800-10-0238
Land (Plaats)
Internationale toegangscode
Landcode
Netnummer
Afdeling of servicegebied,
Website en e-mailadres
Netnummers,
lokale nummers en
gratis nummers

Bijlage 133
Brazilië
Internationale toegangscode: 00
Landcode: 55
Netnummer: 51
Website: www.dell.com/br
E-mail: [email protected]
Klantenservice, technische ondersteuning
0800 90 3355
Faxnummer technische ondersteuning
51 3481 5470
Faxnummer Customer Care
51 3481 5480
Verkoop
0800 90 3390
Britse Maagdeneilanden Algemene ondersteuning
gratis: 1-866-278-6820
Brunei
Landcode: 673
Technische ondersteuning (Penang, Maleisië)
604 633 4966
Customer Care (Penang, Maleisië)
604 633 4888
Verkooptransacties (Penang, Maleisië)
604 633 4955
Canada (North York, Ontario)
Internationale toegangscode:
011
Online orderstatus: www.dell.ca/ostatus
AutoTech (geautomatiseerde ondersteuning
voor de hardware en garantie)
gratis: 1-800-247-9362
Verkoop aan consumenten/kleine ondernemingen
gratis: 1-800-847-4096
Klantenservice (middelgrote/grote ondernemingen,
overheid)
gratis: 1-800-326-9463
Klantenservice (printers, projectors, televisies,
handhelds, digitale jukebox en draadloze apparaten)
gratis: 1-800-847-4096
Hardwaregarantie (consumenten/kleine
ondernemingen)
gratis: 1-800-906-3355
Hardwaregarantie (middelgrote/grote
ondernemingen, overheid)
gratis: 1-800-387-5757
Hardwaregarantie (printers, projectors, televisies,
handhelds, digitale jukebox en draadloze apparaten)
1-877-335-5767
Verkoop (consumenten/kleine ondernemingen)
gratis: 1-800-387-5752
Verkoop (middelgrote/grote ondernemingen,
overheid)
gratis: 1-800-387-5755
Verkoop van onderdelen en aanvullende services
18664403355
Caymaneilanden E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
1-877-262-5415
Chili (Santiago)
Landcode: 56
Netnummer: 2
Website: www.dell.com/cl
E-mail: [email protected]
Verkoop en klantenondersteuning
gratis: 1230-020-4823
Land (Plaats)
Internationale toegangscode
Landcode
Netnummer
Afdeling of servicegebied,
Website en e-mailadres
Netnummers,
lokale nummers en
gratis nummers

134 Bijlage
China (Xiamen)
Landcode: 86
Netnummer: 592
Website voor technische ondersteuning:
support.dell.com.cn
E-mailadres technische ondersteuning:
E-mailadres Customer Care:
Faxnummer technische ondersteuning
592 818 1350
Technische ondersteuning
(Dell™ Dimension™ en Inspiron)
gratis: 800 858 2968
Technische ondersteuning
(OptiPlex™, Latitude™ en Dell Precision™)
gratis: 800 858 0950
Technische ondersteuning (servers en opslag)
gratis: 800 858 0960
Technische ondersteuning (projectors,
PDA's, switches, routers, enzovoort)
gratis: 800 858 2920
Technische ondersteuning (printers)
gratis: 800 858 2311
Customer Care
gratis: 800 858 2060
Faxnummer Customer Care
592 818 1308
Consumenten en kleine ondernemingen
gratis: 800 858 2222
Afdeling voorkeuraccounts
gratis: 800 858 2557
Grootzakelijke accounts GCP
gratis: 800 858 2055
Grootzakelijke accounts Belangrijke accounts
gratis: 800 858 2628
Grootzakelijke accounts Noord
gratis: 800 858 2999
Grootzakelijke accounts Noord,
overheid en onderwijs
gratis: 800 858 2955
Grootzakelijke accounts Oost
gratis: 800 858 2020
Grootzakelijke accounts Oost,
overheid en onderwijs
gratis: 800 858 2669
Grootzakelijke accounts, wachtrijteam
gratis: 800 858 2572
Grootzakelijke accounts Zuid
gratis: 800 858 2355
Grootzakelijke accounts West
gratis: 800 858 2811
Grootzakelijk account, onderdelen
gratis: 800 858 2621
Land (Plaats)
Internationale toegangscode
Landcode
Netnummer
Afdeling of servicegebied,
Website en e-mailadres
Netnummers,
lokale nummers en
gratis nummers

Bijlage 135
Colombia Website: www.dell.com/cl
E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
01-800-915-4755
Costa Rica Website: www.dell.com/cr
E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
0800-012-0231
Denemarken (Kopenhagen)
Internationale toegangscode: 00
Landcode: 45
Website: support.euro.dell.com
Technische ondersteuning voor XPS
7010 0074
Technische ondersteuning
voor alle andere Dell-computers
7023 0182
Customer Care (Relationeel)
7023 0184
Customer Care voor consumenten/kleine
ondernemingen
3287 5505
Schakelbord (Relationeel)
3287 1200
Faxnummer schakelbord (Relationeel)
3287 1201
Schakelbord (consumenten/kleine ondernemingen)
3287 5000
Faxnummer schakelbord (consumenten/kleine
ondernemingen)
3287 5001
Dominica Website: www.dell.com/dm
E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
gratis: 1-866-278-6821
Dominicaanse Republiek Website: www.dell.com/do
E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
1-800-156-1588
Land (Plaats)
Internationale toegangscode
Landcode
Netnummer
Afdeling of servicegebied,
Website en e-mailadres
Netnummers,
lokale nummers en
gratis nummers

136 Bijlage
Duitsland (Frankfurt)
Internationale toegangscode: 00
Landcode: 49
Netnummer: 69
Website: support.euro.dell.com
E-mail: [email protected]
Technische ondersteuning voor XPS
069 9792 7222
Technische ondersteuning
voor alle andere Dell-computers
069 9792-7200
Customer Care voor consumenten/kleine
ondernemingen
0180-5-224400
Customer Care wereldwijd
069 9792-7320
Customer Care voor voorkeuraccounts
069 9792-7320
Customer Care voor grote accounts
069 9792-7320
Customer Care voor publiek accounts
069 9792-7320
Schakelbord
069 9792-7000
Ecuador Website: www.dell.com/ec
E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
(wanneer u belt vanuit Quito)
gratis: 999-119-877-655-3355
Algemene ondersteuning
(wanneer u belt vanuit Guayaquil)
gratis: 1800-999-119-877-655-
3355
El Salvador Website: www.dell.com/ec
E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
800-6132
Finland (Helsinki)
Internationale toegangscode:
990
Landcode: 358
Netnummer: 9
Website: support.euro.dell.com
E-mail: [email protected]
Technische ondersteuning
0207 533 555
Customer Care
0207 533 538
Schakelbord
0207 533 533
Verkopen bij minder dan 500 werknemers
0207 533 540
Fax
0207 533 530
Verkopen bij meer dan 500 werknemers
0207 533 533
Fax
0207 533 530
Land (Plaats)
Internationale toegangscode
Landcode
Netnummer
Afdeling of servicegebied,
Website en e-mailadres
Netnummers,
lokale nummers en
gratis nummers

Bijlage 137
Frankrijk (Parijs) (Montpellier)
Internationale toegangscode: 00
Landcode: 33
Netnummers: (1) (4)
Website: support.euro.dell.com
Consumenten en kleine ondernemingen
Technische ondersteuning voor XPS
0825 387 129
Technische ondersteuning
voor alle andere Dell-computers
0825 387 270
Customer Care
0825 823 833
Schakelbord
0825 004 700
Schakelbord (gesprekken van buiten Frankrijk)
04 99 75 40 00
Verkoop
0825 004 700
Fax
0825 004 701
Fax (gesprekken van buiten Frankrijk)
04 99 75 40 01
Ondernemingen
Technische ondersteuning
0825 004 719
Customer Care
0825 338 339
Schakelbord
01 55 94 71 00
Verkoop
01 55 94 71 00
Fax
01 55 94 71 01
Grenada E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
gratis: 1-866-540-3355
Griekenland
Internationale toegangscode: 00
Landcode: 30
Website: support.euro.dell.com
Technische ondersteuning
00800-44 14 95 18
Gold Service technische ondersteuning
00800-44 14 00 83
Schakelbord
2108129810
Gold Service schakelbord
2108129811
Verkoop
2108129800
Fax
2108129812
Guatemala E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
1-800-999-0136
Guyana E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
gratis: 1-877-270-4609
Land (Plaats)
Internationale toegangscode
Landcode
Netnummer
Afdeling of servicegebied,
Website en e-mailadres
Netnummers,
lokale nummers en
gratis nummers

138 Bijlage
Hong Kong
Internationale toegangscode:
001
Landcode: 852
Website: support.ap.dell.com
E-mailadres technische ondersteuning:
Technische ondersteuning (Dimension en Inspiron)
2969 3188
Technische ondersteuning (OptiPlex, Latitude en
Dell Precision)
2969 3191
Technische ondersteuning (PowerApp, PowerEdge,
PowerConnect, and PowerVault)
2969 3196
Customer Care
3416 0910
Grootzakelijke accounts
3416 0907
Wereldwijde klantenprogramma's
3416 0908
Afdeling middelgrote ondernemingen
3416 0912
Afdeling consumenten en kleine ondernemingen
2969 3105
Land (Plaats)
Internationale toegangscode
Landcode
Netnummer
Afdeling of servicegebied,
Website en e-mailadres
Netnummers,
lokale nummers en
gratis nummers

Bijlage 139
Ierland (Cherrywood)
Internationale toegangscode: 00
Landcode: 353
Netnummer: 1
Website: support.euro.dell.com
E-mail: [email protected]
Verkoop
Verkoop Ierland
01 204 4444
Dell Outlet
1850 200 778
HelpDesk online bestellen
1850 200 778
Customer Care
Customer Care voor thuisgebruiker
01 204 4014
Customer Care voor kleine ondernemingen
01 204 4014
Customer Care voor ondernemingen
1850 200 982
Technische ondersteuning
Technische ondersteuning
voor uitsluitend XPS-computers
1850 200 722
Technische ondersteuning
voor alle andere Dell-computers
1850 543 543
Algemeen
Fax/Verkoop Fax
01 204 0103
Schakelbord
01 204 4444
Customer Care voor het Verenigd Koninkrijk
(alleen gesprekken binnen het Verenigd Koninkrijk)
0870 906 0010
Customer Care voor ondernemingen (alleen
gesprekken binnen het Verenigd Koninkrijk)
0870 907 4499
Verkoop Verenigd Koninkrijk (alleen gesprekken
binnen het Verenigd Koninkrijk)
0870 907 4000
India E-mail: [email protected]
Technische ondersteuning
1600338045
en 1600448046
Verkoop (grootzakelijke accounts)
1600 33 8044
Verkoop (consumenten en kleine ondernemingen)
1600 33 8046
Land (Plaats)
Internationale toegangscode
Landcode
Netnummer
Afdeling of servicegebied,
Website en e-mailadres
Netnummers,
lokale nummers en
gratis nummers

140 Bijlage
Italië (Milaan)
Internationale toegangscode: 00
Landcode: 39
Netnummer: 02
Website: support.euro.dell.com
Consumenten en kleine ondernemingen
Technische ondersteuning
02 577 826 90
Customer Care
02 696 821 14
Fax
02 696 821 13
Schakelbord
02 696 821 12
Ondernemingen
Technische ondersteuning
02 577 826 90
Customer Care
02 577 825 55
Fax
02 575 035 30
Schakelbord
02 577 821
Jamaica E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
(alleen gesprekken binnen Jamaica)
1-800-440-9205
Land (Plaats)
Internationale toegangscode
Landcode
Netnummer
Afdeling of servicegebied,
Website en e-mailadres
Netnummers,
lokale nummers en
gratis nummers

Bijlage 141
Japan (Kawasaki)
Internationale toegangscode:
001
Landcode: 81
Netnummer: 44
Website: support.jp.dell.com
Technische ondersteuning (servers)
gratis: 0120-198-498
Technische ondersteuning buiten Japan (servers)
81-44-556-4162
Technische ondersteuning (Dimension en Inspiron)
gratis: 0120-198-226
Technische ondersteuning buiten Japan
(Dimension en Inspiron)
81-44-520-1435
Technische ondersteuning
(OptiPlex, Latitude en Dell Precision)
gratis:0120-198-433
Technische ondersteuning buiten Japan
(Dell Precision, OptiPlex en Latitude)
81-44-556-3894
Technische ondersteuning
(PDA's, projectors, printers, routers)
gratis: 0120-981-690
Technische ondersteuning buiten Japan
(PDA's, projectors, printers, routers)
81-44-556-3468
Faxboxservice
044-556-3490
24-uurs service voor status geautomatiseerde orders
044-556-3801
Customer Care
044-556-4240
Verkoop aan ondernemingen
(maximaal 400 werknemers)
044-556-1465
Verkoop aan voorkeuraccounts
(meer dan 400 werknemers)
044-556-3433
Verkoop aan publieke sector (overheidsinstellingen,
onderwijsinstellingen en medische instellingen)
044-556-5963
Global Segment Japan
044-556-3469
Individuele gebruiker
044-556-1760
Schakelbord
044-556-4300
Korea (Seoul)
Internationale toegangscode:
001
Landcode: 82
Netnummer: 2
E-mail: [email protected]
Ondersteuning
gratis: 080-200-3800
Ondersteuning (Dimension, PDA,
Electronics en accessoires)
gratis: 080-200-3801
Verkoop
gratis: 080-200-3600
Fax
2194-6202
Schakelbord
2194-6000
Land (Plaats)
Internationale toegangscode
Landcode
Netnummer
Afdeling of servicegebied,
Website en e-mailadres
Netnummers,
lokale nummers en
gratis nummers

142 Bijlage
Latijns-Amerika Technische klantenondersteuning
(Austin, Texas, V.S.)
512 728-4093
Klantenservice (Austin, Texas, V.S.)
512 728-3619
Fax (technische ondersteuning en klantenservice)
(Austin, Texas, V.S.)
512 728-3883
Verkoop (Austin, Texas, V.S.)
512 728-4397
Faxnummer verkoop (Austin, Texas, V.S.)
512 728-4600
of 512 728-3772
Luxemburg
Internationale toegangscode: 00
Landcode: 352
Website: support.euro.dell.com
Ondersteuning
3420808075
Verkoop consumenten/kleine ondernemingen
+32 (0)2 713 15 96
Verkoop ondernemingen
26 25 77 81
Customer Care
+32 (0)2 481 91 19
Fax
26 25 77 82
Macao
Landcode: 853
Technische ondersteuning
gratis: 0800 105
Klantenservice (Xiamen, China)
34 160 910
Verkooptransactie (Penang, Maleisië)
29 693 115
Maleisië (Penang)
Internationale toegangscode: 00
Landcode: 60
Netnummer: 4
Website: support.ap.dell.com
Technische ondersteuning (OptiPlex,
Latitude en Dell Precision)
gratis: 1 800 880 193
Technische ondersteuning (Dimension,
Inspiron, en Electronics en accessoires)
gratis: 1 800 881 306
Technische ondersteuning (PowerApp,
PowerEdge, PowerConnect en PowerVault)
gratis: 1800 881 386
Customer Care
gratis:
1800 881 306 (optie 6)
Verkooptransacties
gratis: 1 800 888 202
Verkoop ondernemingen
gratis: 1 800 888 213
Land (Plaats)
Internationale toegangscode
Landcode
Netnummer
Afdeling of servicegebied,
Website en e-mailadres
Netnummers,
lokale nummers en
gratis nummers

Bijlage 143
Mexico
Internationale toegangscode: 00
Landcode: 52
E-mail: [email protected]
Technische klantenondersteuning
001-877-384-8979
of 001-877-269-3383
Verkoop
50-81-8800
of 01-800-888-3355
Klantenservice
001-877-384-8979
of 001-877-269-3383
Algemeen
50-81-8800
of 01-800-888-3355
Montserrat E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
gratis: 1-866-278-6822
Nederlandse Antillen E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
001-800-882-1519
Nederland (Amsterdam)
Internationale toegangscode: 00
Landcode: 31
Netnummer: 20
Website: support.euro.dell.com
Technische ondersteuning voor XPS
020 674 45 94
Technische ondersteuning
voor alle andere Dell-computers
020 674 45 00
Faxnummer technische ondersteuning
020 674 47 66
Customer Care voor consumenten/kleine
ondernemingen
020 674 42 00
Customer Care (Relationeel)
020 674 4325
Verkoop consumenten/kleine ondernemingen
020 674 55 00
Relationele verkoop
020 674 50 00
Faxnummer verkoop consumenten/kleine
ondernemingen
020 674 47 75
Faxnummer relationele verkoop
020 674 47 50
Schakelbord
020 674 50 00
Faxnummer schakelbord
020 674 47 50
Nicaragua E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
001-800-220-1377
Land (Plaats)
Internationale toegangscode
Landcode
Netnummer
Afdeling of servicegebied,
Website en e-mailadres
Netnummers,
lokale nummers en
gratis nummers

144 Bijlage
Nieuw-Zeeland
Internationale toegangscode: 00
Landcode: 64
Website: support.ap.dell.com
E-mail: support.ap.dell.com/contactus
Algemene ondersteuning
0800 441 567
Noorwegen (Lysaker)
Internationale toegangscode: 00
Landcode: 47
Website: support.euro.dell.com
Technische ondersteuning voor XPS
815 35 043
Technische ondersteuning
voor alle andere Dell-producten
671 16882
Customer Care (Relationeel)
671 17575
Customer Care voor consumenten/kleine
ondernemingen
23162298
Schakelbord
671 16800
Faxnummer schakelbord
671 16865
Oostenrijk (Wenen)
Internationale toegangscode:
900
Landcode: 43
Netnummer: 1
Website: support.euro.dell.com
E-mail: [email protected]
Verkoop consumenten/kleine ondernemingen
0820 240 530 00
Faxnummer consumenten/kleine ondernemingen
0820 240 530 49
Customer Care voor consumenten/kleine
ondernemingen
0820 240 530 14
Customer Care voor
voorkeuraccounts/ondernemingen
0820 240 530 16
Ondersteuning voor XPS
0820 240 530 81
Ondersteuning consumenten/kleine
ondernemingen voor alle andere Dell-computers
0820 240 530 17
Ondersteuning voor
voorkeuraccounts/ondernemingen
0820 240 530 17
Schakelbord
0820 240 530 00
Panama E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
011-800-507-1264
Peru E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
0800-50-669
Land (Plaats)
Internationale toegangscode
Landcode
Netnummer
Afdeling of servicegebied,
Website en e-mailadres
Netnummers,
lokale nummers en
gratis nummers

Bijlage 145
Polen (Warschau)
Internationale toegangscode:
011
Landcode: 48
Netnummer: 22
Website: support.euro.dell.com
E-mail: [email protected]
Klantenservice
57 95 700
Customer Care
57 95 999
Verkoop
57 95 999
Faxnummer klantenservice
57 95 806
Faxnummer receptie
57 95 998
Schakelbord
57 95 999
Portugal
Internationale toegangscode: 00
Landcode: 351
Website: support.euro.dell.com
Technische ondersteuning
707200149
Customer Care
800 300 413
Verkoop
800 300 410 or 800 300 411 or
800 300 412 or 21 422 07 10
Fax
21 424 01 12
Puerto Rico E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
1-877-537-3355
Spanje (Madrid)
Internationale toegangscode: 00
Landcode: 34
Netnummer: 91
Website: support.euro.dell.com
Consumenten en kleine ondernemingen
Technische ondersteuning
902 100 130
Customer Care
902 118 540
Verkoop
902 118 541
Schakelbord
902 118 541
Fax
902 118 539
Ondernemingen
Technische ondersteuning
902 100 130
Customer Care
902 115 236
Schakelbord
91 722 92 00
Fax
91 722 95 83
St. Kitts en Nevis Website: www.dell.com/kn
E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
gratis: 1-866-540-3355
Land (Plaats)
Internationale toegangscode
Landcode
Netnummer
Afdeling of servicegebied,
Website en e-mailadres
Netnummers,
lokale nummers en
gratis nummers

146 Bijlage
St. Lucia Website: www.dell.com/lc
E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
1-800-882-1521
St. Vincent en de Grenadines Website: www.dell.com/vc
E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
gratis: 1-877-441-4740
Singapore (Singapore)
Internationale toegangscode:
005
Landcode: 65
OPMERKING: De telefoonnummers in dit gedeelte
ogen alleen worden gebeld vanuit Singapore of
Maleisië.
Website: support.ap.dell.com
Technische ondersteuning (Dimension,
Inspiron, en Electronics en accessoires)
gratis: 1 800 394 7430
Technische ondersteuning (OptiPlex,
Latitude en Dell Precision)
gratis: 1 800 394 7488
Technische ondersteuning (PowerApp,
PowerEdge, PowerConnect en PowerVault)
gratis: 1 800 394 7478
Customer Care
gratis:
1 800 394 7430 (optie 6)
Verkooptransacties
gratis: 1 800 394 7412
Verkoop ondernemingen
gratis: 1 800 394 7419
Slowakije (Praag)
Internationale toegangscode: 00
Landcode: 421
Website: support.euro.dell.com
E-mail: [email protected]
Technische ondersteuning
02 5441 5727
Customer Care
420 22537 2707
Fax
02 5441 8328
Faxnummer technische ondersteuning
02 5441 8328
Schakelbord (verkoop)
02 5441 7585
Land (Plaats)
Internationale toegangscode
Landcode
Netnummer
Afdeling of servicegebied,
Website en e-mailadres
Netnummers,
lokale nummers en
gratis nummers

Bijlage 147
Tsjechische Republiek (Praag)
Internationale toegangscode: 00
Landcode: 420
Website: support.euro.dell.com
E-mail: [email protected]
Technische ondersteuning
22537 2727
Customer Care
22537 2707
Fax
22537 2714
Faxnummer technische ondersteuning
22537 2728
Schakelbord
22537 2711
Tai wa n
Internationale toegangscode:
002
Landcode: 886
Website: support.ap.dell.com
E-mail: [email protected]
Technische ondersteuning (OptiPlex, Latitude,
Inspiron, Dimension en Electronics en accessoires)
gratis: 00801 86 1011
Technische ondersteuning (PowerApp,
PowerEdge, PowerConnect en PowerVault)
gratis: 00801 60 1256
Customer Care
gratis:
00801 60 1250
(optie 5)
Verkooptransacties
gratis: 00801 65 1228
Verkoop ondernemingen
gratis: 00801 651 227
Thailand
Internationale toegangscode:
001
Landcode: 66
Website: support.ap.dell.com
Technische ondersteuning
(OptiPlex, Latitude en Dell Precision)
gratis: 1800 0060 07
Technische ondersteuning (PowerApp,
PowerEdge, PowerConnect en PowerVault)
gratis: 1800 0600 09
Customer Care
gratis:
1800 006 007
(optie 7)
Verkoop ondernemingen
gratis: 1800 006 009
Verkooptransacties
gratis: 1800 006 006
Trinidad/Tobago Website: www.dell.com/tt
E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
1-800-805-8035
Turks- en Caicoseilanden Website: www.dell.com/tc
E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
gratis: 1-877-441-4735
Land (Plaats)
Internationale toegangscode
Landcode
Netnummer
Afdeling of servicegebied,
Website en e-mailadres
Netnummers,
lokale nummers en
gratis nummers

148 Bijlage
Uruguay Website: www.dell.com/uy
E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
gratis: 000-413-598-2521
Venezuela Website: www.dell.com/ve
E-mail: [email protected]
Algemene ondersteuning
0800-100-4752
V.K. (Bracknell)
Internationale toegangscode: 00
Landcode: 44
Netnummer: 1344
Website: support.euro.dell.com
E-mail: [email protected]
Customer Care-website:
support.euro.dell.com/uk/en/ECare/form/home.asp
Verkoop
Verkoop aan consumenten en kleine
ondernemingen
0870 907 4000
Verkoop voor ondernemingen/publiek sector
01344 860 456
Customer Care
Customer Care voor consumenten
en kleine ondernemingen
0870 906 0010
Customer Care voor ondernemingen
01344 373 185
Voorkeursaccounts (500–5000 werknemers)
0870 906 0010
Customer Care voor wereldwijd opererende
ondernemingen
01344 373 186
Customer Care voor centrale overheid
01344 373 193
Customer Care voor lokale overheid en onderwijs
01344 373 199
Customer Care voor gezondheidszorg
01344 373 194
Technische ondersteuning
Technische ondersteuning
voor uitsluitend XPS-computers
0870 366 4180
Technische ondersteuning
(ondernemingen/voorkeuraccounts/PAD [1000+
werknemers])
0870 908 0500
Land (Plaats)
Internationale toegangscode
Landcode
Netnummer
Afdeling of servicegebied,
Website en e-mailadres
Netnummers,
lokale nummers en
gratis nummers

Bijlage 149
V.K. (Bracknell)
(vervolg)
Technische ondersteuning voor alle andere producten
0870 353 0800
Algemeen
Faxnummer voor consumenten en kleine
ondernemingen
0870 907 4006
V.S. (Austin, Texas)
Internationale toegangscode:
011
Landcode: 1
Online order-Status bestelling
gratis: 1-800-433-9014
AutoTech (draagbare en desktopcomputers)
gratis: 1-800-247-9362
Hardware en garantie (Dell tv, printers en
projectoren
) voor relaties
gratis: 1-877-459-7298
XPS-ondersteuning consumenten in Noord-
en Zuid-Amerika
gratis: 1-800-232-8544
Consumenten (thuis en thuiskantoor)
Ondersteuning voor alle andere Dell-producten
gratis: 1-800-624-9896
Klantenservice
gratis: 1-800-624-9897
Klanten Employee Purchase Program (EPP)
gratis: 1-800-695-8133
Website met financiële services:
www.dellfinancialservices.com
Financiële services (lease/lening)
gratis: 1-877-577-3355
Financiële services (Dell Preferred Accounts [DPA])
gratis: 1-800-283-2210
Onderneming
Klantenservice en ondersteuning
gratis: 1-800-456-3355
Klanten Employee Purchase Program (EPP)
gratis: 1-800-695-8133
Ondersteuning voor printers, projectoren,
PDA's en MP3-spelers
gratis: 1-877-459-7298
Publieke sector (overheid, onderwijs en gezondheidszorg)
Klantenservice en ondersteuning
gratis: 1-800-456-3355
Klanten Employee Purchase Program (EPP)
gratis: 1-800-695-8133
Dell Sales
gratis: 1-800-289-3355
of gratis: 1-800-879-3355
Dell Outlet Store (Dell refurbished computers)
gratis: 1-888-798-7561
Verkoop van software en randapparatuur
gratis: 1-800-671-3355
Land (Plaats)
Internationale toegangscode
Landcode
Netnummer
Afdeling of servicegebied,
Website en e-mailadres
Netnummers,
lokale nummers en
gratis nummers

150 Bijlage
V.S. (Austin, Texas)
(vervolg)
Verkoop van onderdelen
gratis: 1-800-357-3355
Verkoop van serviceovereenkomsten en garanties
gratis: 1-800-247-4618
Fax
gratis: 1-800-727-8320
Dell-services voor doven, slechthorenden
en slechtsprekenden
gratis: 1-877-DELLTTY
(1-877-335-5889)
Zuid-Afrika (Johannesburg)
Internationale toegangscode:
09/091
Landcode: 27
Netnummer: 11
Website: support.euro.dell.com
E-mail: [email protected]
Gold Queue
011 709 7713
Technische ondersteuning
011 709 7710
Customer Care
011 709 7707
Verkoop
011 709 7700
Fax
011 706 0495
Schakelbord
011 709 7700
Zuidoost-Azië en de Pacific Technische ondersteuning, klantenservice
en verkoop (Penang, Maleisië)
604 633 4810
Zweden (Upplands Vasby)
Internationale toegangscode: 00
Landcode: 46
Netnummer: 8
Website: support.euro.dell.com
Technische ondersteuning voor XPS
0771 340 340
Technische ondersteuning
voor alle andere Dell-producten
08 590 05 199
Customer Care (Relationeel)
08 590 05 642
Customer Care voor consumenten/kleine
ondernemingen
08 587 70 527
Ondersteuning voor Employee Purchase
Program (EPP)
020 140 14 44
Faxnummer technische ondersteuning
08 590 05 594
Verkoop
08 590 05 185
Land (Plaats)
Internationale toegangscode
Landcode
Netnummer
Afdeling of servicegebied,
Website en e-mailadres
Netnummers,
lokale nummers en
gratis nummers

Bijlage 151
Zwitserland (Genève)
Internationale toegangscode: 00
Landcode: 41
Netnummer: 22
Website: support.euro.dell.com
E-mail: T[email protected]
Technische ondersteuning voor XPS
0848 33 88 57
Technische ondersteuning (consumenten en kleine
ondernemingen) voor alle andere Dell-producten
0844 811 411
Technische ondersteuning (ondernemingen)
0844 822 844
Customer Care (consumenten en kleinen
ondernemingen)
0848 802 202
Customer Care voor ondernemingen
0848 821 721
Fax
022 799 01 90
Schakelbord
022 799 01 01
Land (Plaats)
Internationale toegangscode
Landcode
Netnummer
Afdeling of servicegebied,
Website en e-mailadres
Netnummers,
lokale nummers en
gratis nummers

152 Bijlage

Verklarende woordenlijst 153
Verklarende woordenlijst
Begrippen in deze woordenlijst zijn alleen voor
informatieve doeleinden. De beschreven begrippen
hebben al dan niet betrekking op uw specifieke
computer.
A
AC — alternating current — The form of electricity that
powers your computer when you plug the AC adapter
power cable in to an electrical outlet.
ACPI — advanced configuration and power interface —
A power management specification that enables
Microsoft
®
Windows
®
operating systems to put a
computer in standby or hibernate mode to conserve the
amount of electrical power allocated to each device
attached to the computer.
AGP — accelerated graphics port — A dedicated graphics
port that allows system memory to be used for video-
related tasks. AGP levert vloeiende videobeelden met
zuivere kleuren, vanwege de snellere samenwerking tussen
het videoschakelsysteem en het computergeheugen.
AHCI — Advanced Host Controller Interface — An
interface for a SATA hard drive Host Controller which
allows the storage driver to enable technologies such as
Native Command Queuing (NCQ) and hot plug.
ALS — ambient light sensor — A feature that helps to
control display brightness.
antivirus software — A program designed to identify,
quarantine, and/or delete viruses from your computer.
ASF — alert standards format — A standard to define
a mechanism for reporting hardware and software alerts
to a management console. ASF is platform- en besturings-
systeemonafhankelijk.
B
battery life span — The length of time (years) during
which a portable computer battery is able to be depleted
and recharged.
battery operating time — The length of time (minutes
or hours) that a portable computer battery powers the
computer.
BIOS — basic input/output system — A program (or
utility) that serves as an interface between the computer
hardware and the operating system. Wijzig deze
instellingen niet, tenzij u op de hoogte bent van de
effecten ervan op uw computer. Dit wordt ook wel
systeeminstellingen genoemd.
bit — The smallest unit of data interpreted by your
computer.
Bluetooth
®
wireless technology — A wireless technology
standard for short-range (9 m [29 feet]) networking
devices that allows for enabled devices to automatically
recognize each other.
boot sequence — Specifies the order of the devices from
which the computer attempts to boot.
bootable CD — A CD that you can use to start your
computer. Zorg ervoor dat u altijd een opstart-cd of -
diskette bij de hand hebt in het geval uw harde schijf is
beschadigd of uw computer een virus bevat. Uw Drivers
and Utilities (Stuur- en hulpprogramma's) (of
ResourceCD) (Bron-cd) is een opstart-cd.
bootable disk — A disk that you can use to start your
computer. Zorg ervoor dat u altijd een opstart-cd of -
diskette bij de hand hebt in het geval uw harde schijf is
beschadigd of uw computer een virus bevat.
bps — bits per second — The standard unit for measuring
data transmission speed.
BTU — British thermal unit — A measurement of heat
output.

154 Verklarende woordenlijst
bus — A communication pathway between the
components in your computer.
bus speed — The speed, given in MHz, that indicates how
fast a bus can transfer information.
byte — The basic data unit used by your computer. Een
byte is gelijk aan 8 bits.
C
C — Celsius — A temperature measurement scale where
0° is the freezing point and 100° is the boiling point of water.
cache — A special high-speed storage mechanism which
can be either a reserved section of main memory or an
independent high-speed storage device. Het cache-
geheugen vergroot de efficiëntie van processor-
bewerkingen.
L1 cache — Primary cache stored inside the processor.
L2 cache — Secondary cache which can either be external
to the processor or incorporated into the processor
architecture.
carnet — An international customs document that
facilitates temporary imports into foreign countries. Dit
wordt ook wel een goederenpaspoort genoemd.
CD-R — CD recordable — A recordable version of a CD.
U kunt slechts één keer gegevens op een cd-r opnemen.
De gegevens kunnen niet worden gewist of overschreven.
CD-RW — CD rewritable — A rewritable version of a
CD. Op een cd-rw kunt u gegevens opnemen, deze wissen
en overschrijven (opnieuw opnemen).
CD-RW drive — A drive that can read CDs and write to
CD-RW (rewritable CDs) and CD-R (recordable CDs)
discs. U kunt meerdere keren naar cd-rw's schrijven, maar
slechts één keer naar cd-r's.
CD-RW/DVD drive — A drive, sometimes referred to as a
combo drive, that can read CDs and DVDs and write to
CD-RW (rewritable CDs) and CD-R (recordable CDs)
discs. U kunt meerdere keren naar cd-rw's schrijven, maar
slechts één keer naar cd-r's.
clock speed — The speed, given in MHz, that indicates
how fast computer components that are connected to the
system bus operate.
COA — Certificate of Authenticity — The Windows
alpha-numeric code located on a sticker on your computer.
Dit wordt ook wel de productcode, of product-id genoemd.
Control Panel — A Windows utility that allows you to
modify operating system and hardware settings, such as
display settings.
controller — A chip that controls the transfer of data
between the processor and memory or between the
processor and devices.
CRIMM — continuity rambus in-line memory module —
A special module that has no memory chips and is used to
fill unused RIMM slots.
cursor — The marker on a display or screen that shows
where the next keyboard, touch pad, or mouse action will
occur. Vaak is dit een knipperende rechte lijn, een liggend
streepje of een kleine pijl.
D
DDR SDRAM — double-data-rate SDRAM — A type of
SDRAM that doubles the data burst cycle, improving
system performance.
DDR2 SDRAM — double-data-rate 2 SDRAM — A type
of DDR SDRAM that uses a 4-bit prefetch and other
architectural changes to boost memory speed to over
400 MHz.
device — Hardware such as a disk drive, printer, or
keyboard that is installed in or connected to your computer.
device driver — See driver.
DIMM — dual in-line memory module — A circuit board
with memory chips that connects to a memory module on
the system board.
DIN connector — A round, six-pin connector that conforms
to DIN (Deutsche Industrie-Norm) standards; it is typically
used to connect PS/2 keyboard or mouse cable connectors.
disk striping — A technique for spreading data over
multiple disk drives. Disk striping kan de snelheid verhogen
van bewerkingen die gegevens van schijfopslag ophalen.
Computers die gebruikmaken van disk striping bieden de
gebruiker de mogelijkheid de grootte van de
gegevenseenheid of stripebreedte te kiezen.

Verklarende woordenlijst 155
DMA — direct memory access — A channel that allows
certain types of data transfer between RAM and a device
to bypass the processor.
DMTF — Distributed Management Task Force — A
consortium of hardware and software companies who
develop management standards for distributed desktop,
network, enterprise, and Internet environments.
domain — A group of computers, programs, and devices
on a network that are administered as a unit with common
rules and procedures for use by a specific group of users.
Een gebruiker meldt zich aan bij het domein om toegang
te krijgen tot de bronnen.
DRAM — dynamic random-access memory — Memory
that stores information in integrated circuits containing
capacitors.
driver — Software that allows the operating system to control
a device such as a printer. Veel apparaten werken niet goed
als het juiste stuurprogramma niet op de computer is
geïnstalleerd.
DSL — Digital Subscriber Line — A technology that
provides a constant, high-speed Internet connection
through an analog telephone line.
dual-core — An Intel
®
technology in which two physical
computational units exist inside a single processor
package, thereby increasing computing efficiency and
multi-tasking ability.
dual display mode — A display setting that allows you to
use a second monitor as an extension of your display. Dit
wordt ook wel dubbele schermmodus genoemd.
DVD-R — DVD recordable — A recordable version of a
DVD. U kunt slechts één keer gegevens op een dvd-r
opnemen. De gegevens kunnen niet worden gewist of
overschreven.
DVD+RW — DVD rewritable — A rewritable version of
a DVD. Op een dvd+rw kunt u gegevens opnemen, deze
wissen en overschrijven (opnieuw opnemen). (Dvd+rw
technologie verschilt van dvd-rw technologie.)
DVD+RW drive — drive that can read DVDs and most
CD media and write to DVD+RW (rewritable DVDs) discs.
DVI — digital video interface — A standard for digital
transmission between a computer and a digital video display.
E
ECC — error checking and correction — A type of
memory that includes special circuitry for testing the
accuracy of data as it passes in and out of memory.
ECP — extended capabilities port — A parallel connector
design that provides improved bidirectional data transmission.
ECP gebruikt, net als EPP, directe geheugentoegang voor
het overbrengen van gegevens en verbetert in veel gevallen
de prestaties.
EIDE — enhanced integrated device electronics — An
improved version of the IDE interface for hard drives and
CD drives.
EMI — electromagnetic interference — Electrical
interference caused by electromagnetic radiation.
ENERGY STAR
®
— Environmental Protection Agency
requirements that decrease the overall consumption of
electricity.
EPP — enhanced parallel port — A parallel connector
design that provides bidirectional data transmission.
ESD — electrostatic discharge — A rapid discharge of
static electricity. ESD kan geïntegreerde circuits in
computer- en communicatieapparatuur beschadigen.
expansion card — A circuit board that installs in an
expansion slot on the system board in some computers,
expanding the capabilities of the computer. Denk hierbij
aan video-, modem, en geluidskaarten.
expansion slot — A connector on the system board (in
some computers) where you insert an expansion card,
connecting it to the system bus.
ExpressCard — A removable I/O card adhering to the
PCMCIA standard. Modems en netwerkadapters zijn
gangbare types expresskaart. Expresskaarten ondersteunen
zowel de PCI Express als de USB 2.0 standaard.
Express Service Code — A numeric code located on a sticker
on your Dell™ computer. Gebruik de Express servicecode
als u voor ondersteuning contact opneemt met Dell. De
Express servicecode wordt in sommige landen niet gebruikt.

156 Verklarende woordenlijst
extended display mode — A display setting that allows
you to use a second monitor as an extension of your
display. Dit wordt ook wel Dual Display-modus genoemd.
extended PC Card — A PC Card that extends beyond the
edge of the PC Card slot when installed.
F
Fahrenheit — A temperature measurement scale where
32° is the freezing point and 212° is the boiling point of
water.
FBD — fully-buffered DIMM — A DIMM with DDR2
DRAM chips and an Advanced Memory Buffer (AMB)
that speeds communication between the DDR2 SDRAM
chips and the system.
FCC — Federal Communications Commission — A U.S.
agency responsible for enforcing communications-related
regulations that state how much radiation computers and
other electronic equipment can emit.
fingerprint reader — A strip sensor that uses your unique
fingerprint to authenticate your user identity to help
secure your computer.
folder — A term used to describe space on a disk or drive
where files are organized and grouped. Bestanden in een
map kunnen worden weergegeven en geordend op
verschillende manieren, bijvoorbeeld alfabetisch, op
datum of op grootte.
format — The process that prepares a drive or disk for
file storage. Wanneer een schijf of station wordt
geformatteerd, wordt de aanwezige informatie gewist.
FSB — front side bus — The data path and physical
interface between the processor and RAM.
FTP — file transfer protocol — A standard Internet
protocol used to exchange files between computers
connected to the Internet.
G
G — gravity — A measurement of weight and force.
GB — gigabyte — A measurement of data storage that
equals 1024 MB (1,073,741,824 bytes). Bij verwijzing naar
opslag op een harde schijf wordt dit vaak afgerond naar
1.000.000.000 bytes.
GHz — gigahertz — A measurement of frequency that
equals one thousand million Hz, or one thousand MHz.
De snelheid voor computerprocessoren. bussen en
interfaces wordt vaak vermeld in GHz.
graphics mode — A video mode that can be defined as x
horizontal pixels by y vertical pixels by z colors. Grafische
modi kunnen oneindig veel verschillende vormen en
lettertypen weergeven.
GUI — graphical user interface — Software that interacts
with the user by means of menus, windows, and icons. De
meeste programma's die werken onder de
besturingssystemen van Windows zijn GUI's.
H
hard drive — A drive that reads and writes data on a hard
disk. De termen harde schijf en vaste schijf worden door
elkaar gebruikt.
heat sink — A metal plate on some processors that helps
dissipate heat.
hibernate mode — A power management mode that saves
everything in memory to a reserved space on the hard
drive and then turns off the computer. Als u de computer
opnieuw opstart wordt de informatie die was opgeslagen
op de harde schijf automatisch teruggezet.
HTTP — hypertext transfer protocol — A protocol for
exchanging files between computers connected to the
Internet.
Hyper-Threading — Hyper-Threading is an Intel
technology that can enhance overall computer
performance by allowing one physical processor to
function as two logical processors, capable of performing
certain tasks simultaneously.
Hz — hertz — A unit of frequency measurement that
equals 1 cycle per second. Metingen voor computers en
elektronische apparaten worden vaak weergegeven in
kilohertz (kHz), megahertz (MHz), gigahertz (GHz),
of terahertz (THz).

Verklarende woordenlijst 157
I
IC — integrated circuit — A semiconductor wafer, or
chip, on which thousands or millions of tiny electronic
components are fabricated for use in computer, audio, and
video equipment.
IDE — integrated device electronics — An interface for
mass storage devices in which the controller is integrated
into the hard drive or CD drive.
IEEE 1394 — Institute of Electrical and Electronics
Engineers, Inc. — A high-performance serial bus used to
connect IEEE 1394-compatible devices, such as digital
cameras and DVD players, to the computer.
infrared sensor — A port that allows you to transfer data
between the computer and infrared-compatible devices
without using a cable connection.
integrated — Usually refers to components that are
physically located on the computer’s system board. Dit
wordt ook wel ingebouwd genoemd.
I/O — input/output — An operation or device that enters
and extracts data from your computer. Toetsenborden en
printers zijn I/O-apparaten.
I/O address — An address in RAM that is associated with
a specific device (such as a serial connector, parallel
connector, or expansion slot) and allows the processor to
communicate with that device.
IrDA — Infrared Data Association — The organization
that creates international standards for infrared
communications.
IRQ — interrupt request — An electronic pathway
assigned to a specific device so that the device can
communicate with the processor. Aan elke
apparaatverbinding moet een IRQ worden toegewezen.
Hoewel dezelfde IRQ aan twee apparaten kan worden
toegewezen, kunt u niet op hetzelfde moment met beide
apparaten werken.
ISP — Internet service provider — A company that allows
you to access its host server to connect directly to the
Internet, send and receive e-mail, and access websites. De
internet-provider voorziet u tegen een vergoeding van een
softwarepakket, een gebruikersnaam en inbelnummers.
K
Kb — kilobit — A unit of data that equals 1024 bits. Een
maatstelsel voor de capaciteit van in het geheugen
geïntegreerde circuits.
KB — kilobyte — A unit of data that equals 1024 bytes
but is often referred to as 1000 bytes.
key combination — A command requiring you to press
multiple keys at the same time.
kHz — kilohertz — A measurement of frequency that
equals 1000 Hz.
L
LAN — local area network — A computer network
covering a small area. Een LAN is meestal beperkt tot een
gebouw of een aantal nabijgelegen gebouwen. Een LAN
kan over elke afstand worden verbonden met een andere
LAN via telefoonlijnen en radiogolven en zo een WAN
(Wide Area Network) vormen.
LCD — liquid crystal display — The technology used by
portable computer and flat-panel displays.
LED — light-emitting diode — An electronic component
that emits light to indicate the status of the computer.
local bus — A data bus that provides a fast throughput for
devices to the processor.
LPT — line print terminal — The designation for a
parallel connection to a printer or other parallel device.
M
Mb — megabit — A measurement of memory chip
capacity that equals 1024 Kb.
Mbps — megabits per second — One million bits per
second. Dit maatstelsel wordt gebruikt bij
transmissiesnelheden voor netwerken en modems.
MB — megabyte — A measurement of data storage that
equals 1,048,576 bytes. 1 MB is gelijk aan 1024 KB. Bij
verwijzing naar opslag op een harde schijf wordt dit vaak
afgerond naar 1.000.000 bytes.

158 Verklarende woordenlijst
MB/sec — megabytes per second — One million bytes
per second. Dit maatstelsel wordt gebruikt voor de
classificatie van gegevensoverdracht.
media bay — A bay that supports devices such as optical
drives, a second battery, or a Dell TravelLite™ module.
memory — A temporary data storage area inside your
computer. Omdat de gegevens in het geheugen niet
blijvend zijn, wordt aanbevolen om uw bestanden
regelmatig op te slaan terwijl u er aan werkt, en deze altijd
op te slaan voordat u de computer uitschakelt. Uw
computer kan verschillende soorten geheugen bevatten,
zoals RAM, ROM en videogeheugen. Vaak wordt het
woord geheugen gebruikt als synoniem voor RAM.
memory address — A specific location where data is
temporarily stored in RAM.
memory mapping — The process by which the computer
assigns memory addresses to physical locations at start-up.
Apparaten en software kunnen vervolgens informatie
identificeren die voor de processor toegankelijk is.
memory module — A small circuit board containing
memory chips, which connects to the system board.
MHz — megahertz — A measure of frequency that equals
1 million cycles per second. De snelheid voor
computerprocessoren, bussen en interfaces wordt vaak
vermeld in MHz.
Mini PCI — A standard for integrated peripheral devices
with an emphasis on communications such as modems
and NICs. Een Mini PCI-kaart is een kleine externe kaart
die wat betreft functionaliteit gelijk is aan een standaard
PCI-uitbreidingskaart.
Mini-Card — A small card designed for integrated
peripherals, such as communication NICs. De Minikaart
is wat betreft functionaliteit gelijk aan een standaard PCI-
uitbreidingskaart.
modem — A device that allows your computer to
communicate with other computers over analog telephone
lines. Er zijn drie types modem: extern, pc-kaart en intern.
Modems worden doorgaans gebruikt voor verbinding met
internet en het verzenden en ontvangen van e-mail.
module bay — See media bay.
MP — megapixel — A measure of image resolution used
for digital cameras.
ms — millisecond — A measure of time that equals one
thousandth of a second. Toegangstijden van
opslagapparaten worden vaak gemeten in ms.
N
network adapter — A chip that provides network capabilities.
Een computer heeft mogelijk een netwerkadapter op de
systeemkaart, of heeft een pc-kaart met een adapter. Een
netwerkadapter wordt ook wel een NIC (Network
Interface Controller, netwerkinterfacekaart) genoemd.
NIC — See network adapter.
notification area — The section of the Windows taskbar
that contains icons for providing quick access to programs
and computer functions, such as the clock, volume
control, and print status. Dit wordt ook wel het systeemvak
genoemd
ns — nanosecond — A measure of time that equals one
billionth of a second.
NVRAM — nonvolatile random access memory — A type
of memory that stores data when the computer is turned off
or loses its external power source. NVRAM wordt gebruikt
voor het behoud van configuratie-informatie, zoals datum,
tijd en andere systeemopties die u kunt instellen.
O
optical drive — A drive that uses optical technology to
read or write data from CDs, DVDs, or DVD+RWs.
Voorbeelden van optische stations zijn cd-stations, dvd-
stations, cd-rw-stations en cd-rw/dvd-combostations.
P
parallel connector — An I/O port often used to connect a
parallel printer to your computer. Ook bekend als LPT-poort.
partition — A physical storage area on a hard drive that is
assigned to one or more logical storage areas known as
logical drives. Elke partitie kan meerdere logische stations
bevatten.

Verklarende woordenlijst 159
PC Card — A removable I/O card adhering to the PCMCIA
standard. Modems en netwerkadapters zijn gangbare
types pc-kaart.
PCI — peripheral component interconnect — PCI is a
local bus that supports 32-and 64-bit data paths, providing
a high-speed data path between the processor and devices
such as video, drives, and networks.
PCI Express — A modification to the PCI interface that
boosts the data transfer rate between the processor and
the devices attached to it. PCI Express kan gegevens
overdragen met snelheden van 250 MB per seconde tot
4 GB per seconde. Indien de PCI Express chipset en het
apparaat verschillende snelheden aankunnen,
functioneren ze minder snel.
PCMCIA — Personal Computer Memory Card
International Association — The organization that
establishes standards for PC Cards.
PIO — programmed input/output — A method of
transferring data between two devices through the
processor as part of the data path.
pixel — A single point on a display screen. Pixels worden
gerangschikt in rijen en kolommen om een beeld te vormen.
Een videoresolutie, zoals 800 x 600, wordt uitgedrukt als
het aantal horizontale pixels bij het aantal verticale pixels.
Plug-and-Play — The ability of the computer to automatically
configure devices. Plug en Play levert automatische
installatie, configuratie en compatibiliteit met bestaande
hardware, wanneer de BIOS, het besturingssysteem en alle
apparaten geschikt zijn voor Plug en Play.
POST — power-on self-test — Diagnostics programs,
loaded automatically by the BIOS, that perform basic tests
on the major computer components, such as memory, hard
drives, and video. Als er tijdens POST geen problemen
worden gevonden, voltooit de computer het opstartproces.
processor — A computer chip that interprets and executes
program instructions. Soms wordt de term CPU (Central
Processing Unit) voor processor gebruikt.
PS/2 — personal system/2 — A type of connector for
attaching a PS/2-compatible keyboard, mouse, or keypad.
PXE — pre-boot execution environment — A WfM
(Wired for Management) standard that allows networked
computers that do not have an operating system to be
configured and started remotely.
R
RAID — redundant array of independent disks — A
method of providing data redundancy. Enkele algemene
implementaties van RAID zijn RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5,
RAID 10 en RAID 50.
RAM — random-access memory — The primary
temporary storage area for program instructions and data.
De informatie die in RAM is opgeslagen wordt gewist
zodra u de computer uitschakelt.
readme file — A text file included with a software package
or hardware product. Readme-bestanden bevatten
normaliter informatie over de installatie en beschrijven
productverbeteringen of -correcties, die nog niet eerder
zijn gedocumenteerd.
read-only — Data and/or files you can view but cannot
edit or delete. Een bestand kan de status alleen-lezen
hebben, wanneer:
• het zich bevindt op een fysieke, tegen schrijven
beveiligde diskette, cd of dvd;
• het zich bevindt op een netwerk in een directory en
de systeembeheerder alleen rechten heeft toegekend
aan bepaalde personen.
refresh rate — The frequency, measured in Hz, at which
your screen's horizontal lines are recharged (sometimes
also referred to as its vertical frequency). Hoe hoger de
vernieuwingsfrequentie, des te minder flikkeringen in het
beeld het menselijk oog kan waarnemen.
resolution — The sharpness and clarity of an image
produced by a printer or displayed on a monitor. Hoe
hoger de resolutie, des te scherper de afbeelding.
RFI — radio frequency interference — Interference that
is generated at typical radio frequencies, in the range of
10 kHz to 100,000 MHz. Radiofrequenties bevinden zich
onder aan het elektromagnetische frequentiespectrum en
ondervinden eerder storingen dan de hogere
frequentiestralingen, zoals infrarood en licht.

160 Verklarende woordenlijst
ROM — read-only memory — Memory that stores data
and programs that cannot be deleted or written to by the
computer. ROM, in tegenstelling tot RAM, behoudt zijn
inhoud als u de computer uitschakelt. Sommige
programma's die essentieel zijn voor de besturing van uw
computer bevinden zich op ROM.
RPM — revolutions per minute — The number of
rotations that occur per minute. De snelheid van de harde
schijf wordt vaak gemeten in RPM.
RTC — real time clock — Battery-powered clock on the
system board that keeps the date and time after you shut
down the computer.
RTCRST — real-time clock reset — A jumper on the
system board of some computers that can often be used
for troubleshooting problems.
S
SAS — serial attached SCSI — A faster, serial version of
the SCSI interface (as opposed to the original SCSI
parallel architecture).
SATA — serial ATA — A faster, serial version of the ATA
(IDE) interface.
ScanDisk — A Microsoft utility that checks files, folders,
and the hard disk’s surface for errors. ScanDisk wordt vaak
uitgevoerd wanneer u de computer opnieuw opstart als
deze niet meer reageert.
SCSI — small computer system interface — A high-speed
interface used to connect devices to a computer, such as
hard drives, CD drives, printers, and scanners. De SCSI
kan met een enkele controller meerdere apparaten
aansluiten. Elk apparaat is beschikbaar via een individueel
identificatienummer op de SCSI-controllerbus.
SDRAM — synchronous dynamic random-access memory —
A type of DRAM that is synchronized with the optimal
clock speed of the processor.
serial connector — An I/O port often used to connect devices
such as a handheld digital device or digital camera to your
computer.
Service Tag — A bar code label on your computer that
identifies your computer when you access Dell Support at
support.dell.com or when you call Dell for customer
service or technical support.
setup program — A program that is used to install and
configure hardware and software. Het programma setup.exe
of install.exe wordt bij de meeste softwarepakketten van
Windows geleverd. Installatieprogramma is iets anders
dan systeeminstellingen.
shortcut — An icon that provides quick access to frequently
used programs, files, folders, and drives. Wanneer u een
snelkoppeling op het bureaublad van Windows maakt en
op het pictogram dubbelklikt, opent u het corresponderende
item zonder het eerst te hoeven zoeken. Pictogrammen
voor snelkoppelingen veranderen de locatie van bestanden
niet. Wanneer u een snelkoppeling verwijdert, heeft dit
geen invloed op het oorspronkelijke bestand. U kunt tevens
de naam van een snelkoppelingspictogram aanpassen.
SIM — Subscriber Identity Module — A SIM card
contains a microchip that encrypts voice and data
transmissions. Simkaarten kunnen worden gebruikt in
telefoons of draagbare computers.
smart card — A card that is embedded with a processor
and a memory chip. Smart cards kunnen worden gebruikt
voor het verifiëren van een gebruiker op computers die
zijn uitgerust voor smart cards.
S/PDIF — Sony/Philips Digital Interface — An audio
transfer file format that allows the transfer of audio from
one file to another without converting it to and from an
analog format, which could degrade the quality of the file.
standby mode — A power management mode that shuts
down all unnecessary computer operations to save energy.
Strike Zone™ — Reinforced area of the platform base
that protects the hard drive by acting as a dampening
device when a computer experiences resonating shock or
is dropped (whether the computer is on or off).
surge protectors — Prevent voltage spikes, such as those
that may occur during an electrical storm, from entering
the computer through the electrical outlet. Stroombeveiligers
beschermen niet tegen blikseminslag of stroomstoringen,
die voorkomen wanneer het voltage meer dan 20 procent
onder het normale voltageniveau voor wisselstroom zakt.

Verklarende woordenlijst 161
Netwerkverbindingen worden niet beschermd door
stroomstootbeveiliging. Ontkoppel de netwerkkabel
tijdens onweer altijd van de netwerkconnector.
SVGA — super-video graphics array — A video standard
for video cards and controllers. Veel voorkomende SVGA-
resoluties zijn 800 x 600 en 1024 x 768.
Het aantal kleuren en de resolutie die een programma
weergeven is afhankelijk van de mogelijkheden van de
monitor, de videocontroller en de bijbehorende
stuurprogramma’s en de hoeveelheid videogeheugen dat
op de computer is geïnstalleerd.
S-video TV-out — A connector used to attach a TV or
digital audio device to the computer.
SXGA — super-extended graphics array — A video
standard for video cards and controllers that supports
resolutions up to 1280 x 1024.
SXGA+ — super-extended graphics array plus — A video
standard for video cards and controllers that supports
resolutions up to 1400 x 1050.
system board — The main circuit board in your computer.
Dit wordt ook wel moederbord genoemd.
system setup — A utility that serves as an interface
between the computer hardware and the operating
system. Met systeeminstellingen kunt u door de gebruiker
te selecteren opties, zoals datum en tijd of het
wachtwoord van het systeem, configureren in de BIOS.
Wijzig de instellingen voor dit programma niet, tenzij u
op de hoogte bent van de effecten ervan op de computer.
T
TAPI — telephony application programming interface —
Enables Windows programs to operate with a wide variety
of telephony devices, including voice, data, fax, and video.
text editor — A program used to create and edit files that
contain only text; for example, Windows Notepad uses a
text editor. Teksteditors bieden meestal geen mogelijkheden
voor automatische terugloop of opmaak (onderstrepen,
lettertypes wijzigen et cetera).
TPM — trusted platform module — A hardware-based
security feature that when combined with security
software enhances network and computer security by
enabling features such as file and e-mail protection.
travel module — A plastic device designed to fit inside
the module bay of a portable computer to reduce the
weight of the computer.
U
UMA — unified memory allocation — System memory
dynamically allocated to video.
UPS — uninterruptible power supply — A backup power
source used when the electrical power fails or drops to an
unacceptable voltage level. Een UPS zorgt ervoor dat een
computer voor een beperkte tijdsduur blijft functioneren
wanneer er geen stroomtoevoer is. UPS-systemen bieden
stroomstootonderdrukking en mogelijk ook voltageregulatie.
Kleine UPS-systemen leveren batterijvoeding voor een
aantal minuten, zodat u uw computer kunt afsluiten.
USB — universal serial bus — A hardware interface for a
low-speed device such as a USB-compatible keyboard,
mouse, joystick, scanner, set of speakers, printer,
broadband devices (DSL and cable modems), imaging
devices, or storage devices. Apparaten worden rechtstreeks
op een 4 pins socket op uw computer aangesloten, of op
een hub met meerdere poorten die op uw computer is
aangesloten. USB-apparaten kunnen worden aangesloten
en ontkoppeld terwijl de computer aanstaat. Tevens
kunnen ze aaneengeschakeld worden.
UTP — unshielded twisted pair — Describes a type of
cable used in most telephone networks and some
computer networks. Paren niet-afgeschermde draden
worden gevlochten voor bescherming tegen
elektromagnetische storing, in plaats van deze te
omhullen met een metalen mantel.
UXGA — ultra extended graphics array — A video
standard for video cards and controllers that supports
resolutions up to 1600 x 1200.

162 Verklarende woordenlijst
V
video controller — The circuitry on a video card or on the
system board (in computers with an integrated video
controller) that provides the video capabilities—in
combination with the monitor—for your computer.
video memory — Memory that consists of memory chips
dedicated to video functions. Videogeheugen is doorgaans
sneller dan systeemgeheugen. De grootte van het
geïnstalleerde videogeheugen beïnvloedt in de eerste plaats
het aantal kleuren dat een programma kan weergeven.
video mode — A mode that describes how text and graphics
are displayed on a monitor. Op beelden gebaseerde software,
zoals de besturingssystemen van Windows, werkt in
videomodi die kunnen worden gedefinieerd als x horizontale
pixels bij y verticale pixels bij z kleuren. Op tekens gebaseerde
software, zoals teksteditors, werkt in videomodi die kunnen
worden gedefinieerd als x kolommen bij y rijen tekens.
video resolution — See resolution.
virus — A program that is designed to inconvenience you
or to destroy data stored on your computer. Een
virusprogramma kan van de ene computer op een andere
overgaan via een geïnfecteerde diskette, van internet
gedownloade software, of e-mailbijlagen. Wanneer een
geïnfecteerd programma wordt gestart, wordt het
aangehechte virus ook gestart.
Een veel voorkomend virus is een opstartvirus, dat is
opgeslagen in de opstartsectoren van een diskette. Als de
diskette in het station zit op het moment dat de computer
wordt uitgeschakeld en deze wordt vervolgens weer
aangezet, wordt de computer geïnfecteerd tijdens het
lezen van de opstartsectoren van de diskette. Als de
computer eenmaal is geïnfecteerd, kopieert het
opstartvirus zichzelf op alle diskettes die worden gelezen
of geschreven in die computer, totdat het virus is
verwijderd.
V — volt — The measurement of electric potential or
electromotive force. Eén volt ontstaat bij een weerstand
van 1 ohm, wanneer een stroom van 1 ampère door die
weerstand gaat.
W
W — watt — The measurement of electrical power. Eén
watt is 1 ampère stroom bij 1 volt.
WHr — watt-hour — A unit of measure commonly used
to indicate the approximate capacity of a battery. Een
batterij van 66 WHr levert bijvoorbeeld één uur lang 66
watt, of twee uur lang 33 watt.
wallpaper — The background pattern or picture on the
Windows desktop. Verander uw achtergrond via het
Configuratiescherm in Windows. U kunt ook een
afbeelding inscannen en deze instellen als achtergrond.
WLAN — wireless local area network. Een aantal
onderling aangesloten computers dat via luchtgolven met
elkaar communiceert en toegangspunten of draadloze
routers gebruikt voor toegang tot internet.
write-protected — Files or media that cannot be changed.
Wanneer u gegevens wilt beschermen tegen wijzigingen of
vernietiging, kunt u deze tegen schrijven beveiligen. Om
een diskette tegen schrijven te beveiligen, schuift u het
tegen-schrijven-beveiligen-palletje op de 3,5 inch diskette
naar de open-positie.
WWAN — wireless wide area network. Een draadloos
gegevensnetwerk met hoge snelheid dat gebruikmaakt van
cellulaire technologie en die een veel groter geografisch
gebied bestrijkt dan WLAN.
WXGA — wide-aspect extended graphics array — A video
standard for video cards and controllers that supports
resolutions up to 1280 x 800.
X
XGA — extended graphics array — A video standard for
video cards and controllers that supports resolutions up to
1024 x 768.

Verklarende woordenlijst 163
Z
ZIF — zero insertion force — A type of socket or connector
that allows a computer chip to be installed or removed
with no stress applied to either the chip or its socket.
Zip — A popular data compression format. Bestanden die
zijn gecomprimeerd met de zip-indeling worden zip-
bestanden genoemd en hebben normaliter de extensie
.zip. Een speciaal soort zip-bestand is een zelfuitpakkkend
bestand, die de extensie .exe heeft. U kunt een
zelfuitpakkend bestand uitpakken door erop te dubbelklikken.
Zip drive — A high-capacity floppy drive developed by
Iomega Corporation that uses 3.5-inch removable disks
called Zip disks. Zip-diskettes zijn iets groter dan gewone
diskettes, ongeveer twee keer zo dik en kunnen 100 MB
aan gegevens opslaan.

164 Verklarende woordenlijst

Index 165
Index
A
aan/uit-lampje
indicaties, 43
audio. Zie geluid
B
batterij
problemen, 33
terugplaatsen, 109
behuizing
terugplaatsen, 111
verwijderen, 69
berichten
fout, 37
besturingssysteem
Windows XP opnieuw
installeren, 57
BIOS, 117
C
Cd's, 18
afspelen, 16
cd's en dvd's afspelen, 16
cd's kopiëren
algemene informatie, 18
hoe kan ik, 18
nuttige tips, 19
cd/dvd-station
ejectknop, 65
installeren, 107
lampje, 65
problemen, 34
verwijderen, 105
cd-rw-station
problemen, 35
CMOS-instellingen
wissen, 127
computer
binnenkant, 71
componenten binnenin, 71
reageert niet, 38
terugzetten in een eerdere
status, 57
vastlopen, 38-39
connectoren
hoofdtelefoon, 66
microfoon, 66
USB, 66
controlelampjes, 49
D
De wizard Netwerk
instellen, 25
De wizard Programma-
compatibiliteit, 39
Dell
contact opnemen, 130
Dell Diagnostics, 53
ondersteuningsbeleid, 129
Support-website, 10
diagnoseprogramma
Dell, 53
lampjes, 49, 66
diskettestation
installeren, 99
verwijderen, 97
documentatie
ergonomie, 9
garantie, 9
Informatie vinden, 9
Installatiediagram, 9
Licentieovereenkomst
voor eindgebruikers, 9
on line, 10
Productinformatie-
handleiding, 9
veiligheid, 9
wet- en regelgeving, 9
dvd's, 18
afspelen, 16
dvd's kopiëren
algemene informatie, 18
hoe kan ik, 18
nuttige tips, 19
dvd-station
problemen, 34

166 Index
166 Index
E
Eigenschappen voor
energiebeheer, 26
e-mail
problemen, 35
F
FlexBay-station
Mediakaartlezer, 65
foutmeldingen
controlelampjes, 49
problemen oplossen, 37
G
geheugen
4-GB-configuraties, 74
DDR2 overzicht, 73
installeren, 74
ondersteund type, 73
problemen, 41
richtlijnen voor installatie, 73
verwijderen, 76
geluid
problemen, 46
volume, 46
H
hardware
Dell Diagnostics, 53
Help en ondersteuning, 11
help-bestand
Help en ondersteuning
van Windows, 11
het overbrengen van
informatie naar een
nieuwe computer, 28
hoofdtelefoon
connector, 66
Hyper-Threading, 28
I
informatie omtrent
ergonomie, 9
informatie omtrent
garantie, 9
informatie omtrent wet-
en regelgeving, 9
Informatie vinden, 9
Installatiediagram, 9
instellingen
system setup, 117
internet
problemen, 35
verbinding, opties, 14
verbinding, over, 14
Internetverbinding
instellen, 15
inzetstuk stationspaneel
terugplaatsen, 88
verwijderen, 88
K
kaarten
ondersteunde types, 77
PCI, 77
PCI Express installeren, 82
PCI Express verwijderen, 86
PCI Express:, 81
PCI installeren, 78
PCI verwijderen, 81
sleuven, 77
L
labels
Productcode voor, 10
Servicelabel, 10, 65
lampjes
achterkant computer, 49
controle-, 49, 66
vaste schijf, 66
Licentieovereenkomst
voor eindgebruikers, 9
luidspreker
problemen, 46
volume, 46
M
Mediakaartlezer
gebruik, 20
installeren, 101, 103
problemen, 40
verwijderen, 101
microfoon
connector, 66

Index 167
modem
problemen, 35
moederbord, 72
moederbord. Zie systeemkaart
monitor
beelscherminstelingen, 24
clone-modus, 24
dubbel-bureaubladmodus, 24
DVI aansluiten, 22-23
leeg, 47
moeilijk leesbaar, 48
TV aansluiten, 22-23
twee aansluiten, 22-23
VGA aansluiten, 22-23
muis
problemen, 41
N
netwerk
De wizard Netwerk
instellen, 25
instellen, 24
problemen, 42
O
onderdelen installeren
aanbevolen hulpmiddelen, 63
uw computer uitschakelen, 63
voordat u begint, 63
ondersteuning
beleid, 129
contact opnemen
met Dell, 130
opnieuw installeren
Windows XP, 57
opstarten
vanaf een USB-apparaat, 124
opstartvolgorde
info, 123
opties, 124
wijzigen, 124-125
P
PC Restore, 59
PCI Express-kaarten
installeren, 82
verwijderen, 86
PCI-kaarten
installeren, 78
verwijderen, 81
printer
aansluiten, 13
instellen, 13
kabel, 13
problemen, 44
USB, 13
Probleemoplosser
voor hardware, 57
problemen
algemeen, 38
batterij, 33
beleid technische
ondersteuning, 129
blauw scherm, 39
cd-rw-station, 35
cd-station, 34
computer loopt vast, 38-39
computer reageert niet, 38
problemen (vervolg)
controlelampjes, 49
Dell Diagnostics, 53
dvd-station, 34
e-mail, 35
foutmeldingen, 37
geheugen, 41
geluid en luidsprekers, 46
indicaties aan/uit-lampje, 43
internet, 35
leeg scherm, 47
Mediakaartlezer, 40
modem, 35
monitor is leeg, 47
monitor is moeilijk te lezen, 48
muis, 41
netwerk, 42
printer, 44
programma loopt vast, 39
programma reageert
niet meer, 39
programma's en
compatibiliteit met
Windows, 39
scanner, 45
scherm is moeilijk te lezen, 48
software, 39-40
terugzetten in een eerdere
status, 57
tips voor het oplossen
van problemen, 33
toetsenbord, 38
vaste schijf, 35
vaste schijven, 34
voeding, 43
volume aanpassen, 46
problemen oplossen
controlelampjes, 49
Dell Diagnostics, 53

168 Index
168 Index
problemen (vervolg)
Help en ondersteuning, 11
Probleemoplosser voor
hardware, 57
terugzetten in een eerdere
status, 57
tips, 33
Productinformatie-
handleiding, 9
S
SATA. Zie seriële ATA
scanner
problemen, 45
Schijf controleren, 35
seriële ATA, 92
Servicelabel, 10, 65
slaapstand, 26-27
software
Hyper-Threading, 28
problemen, 39-40
specificaties
audio, 114
computergegevens, 113
connectoren, 115
fysieke, 116
geheugen, 113
knoppen en lampjes, 115
omgeving, 116
processor, 113
technische, 113
uitbreidingsbus, 114
vaste schijven, 115
video, 114
voeding, 116
stand-bymodus, 25
stationspaneel, 66, 86
terugplaatsen, 89
verwijderen, 87
stuurprogramma's
controleren, 55
info, 55
Support-website, 10
Systeemherstel, 57
system setup
info, 117
openen, 117
opties, 118
schermen, 117
T
technische ondersteuning
beleid, 129
toetsenbord
problemen, 38
tv
aansluiten
op computer, 22-23
U
USB
connectoren, 66
opstarten vanaf
apparaten, 124
V
vaste schijf
installeren, 94
lampje, 66
problemen, 35
tweede installeren, 95
verwijderen, 92
vaste schijven, 90
cd/dvd installeren, 107
cd/dvd verwijderen, 105
diskette verwijderen, 97
diskettestation installeren, 99
problemen, 34
seriële ATA, 92
tweede harde schijf, 95
vast schijven verwijderen, 92
vaste schijf, 92
vaste schijf installeren, 94
veiligheidsinstructies, 9
ventilatieopeningen, 66
voorpaneel, 66
vergrendeling
behuizing, 65
voeding
beheer, geavanceerd, 27
beheer, schema's, 26
beheer, slaap, 27
beheren, 25
besparen, 25
knop, 66
opties, 26
problemen, 43
slaapstand, 26-27
stand-bymodus, 25
volume
aanpassen, 46

Index 169
W
wachtwoord
jumper, 126
wissen, 126
Windows XP
De wizard Netwerk
instellen, 25
De wizard Programma-
compatibiliteit, 39
Help en ondersteuning, 11
Hyper-Threading, 28
opnieuw installeren, 57
Probleemoplosser voor
hardware, 57
scanner, 45
Systeemherstel, 57
Vorig stuurprogramma, 56
Wizard Bestanden en
Instellingen
overbrengen, 28
Wizard Bestanden en
Instellingen
overbrengen, 28
wizards
De wizard Netwerk
instellen, 25
De wizard Programma-
compatibiliteit, 39
Wizard Bestanden
en Instellingen
overbrengen, 28

170 Index
170 Index
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
 30
30
-
 31
31
-
 32
32
-
 33
33
-
 34
34
-
 35
35
-
 36
36
-
 37
37
-
 38
38
-
 39
39
-
 40
40
-
 41
41
-
 42
42
-
 43
43
-
 44
44
-
 45
45
-
 46
46
-
 47
47
-
 48
48
-
 49
49
-
 50
50
-
 51
51
-
 52
52
-
 53
53
-
 54
54
-
 55
55
-
 56
56
-
 57
57
-
 58
58
-
 59
59
-
 60
60
-
 61
61
-
 62
62
-
 63
63
-
 64
64
-
 65
65
-
 66
66
-
 67
67
-
 68
68
-
 69
69
-
 70
70
-
 71
71
-
 72
72
-
 73
73
-
 74
74
-
 75
75
-
 76
76
-
 77
77
-
 78
78
-
 79
79
-
 80
80
-
 81
81
-
 82
82
-
 83
83
-
 84
84
-
 85
85
-
 86
86
-
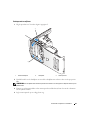 87
87
-
 88
88
-
 89
89
-
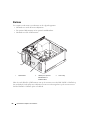 90
90
-
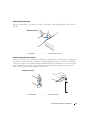 91
91
-
 92
92
-
 93
93
-
 94
94
-
 95
95
-
 96
96
-
 97
97
-
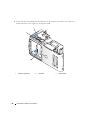 98
98
-
 99
99
-
 100
100
-
 101
101
-
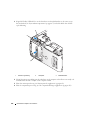 102
102
-
 103
103
-
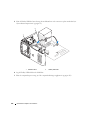 104
104
-
 105
105
-
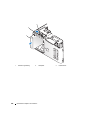 106
106
-
 107
107
-
 108
108
-
 109
109
-
 110
110
-
 111
111
-
 112
112
-
 113
113
-
 114
114
-
 115
115
-
 116
116
-
 117
117
-
 118
118
-
 119
119
-
 120
120
-
 121
121
-
 122
122
-
 123
123
-
 124
124
-
 125
125
-
 126
126
-
 127
127
-
 128
128
-
 129
129
-
 130
130
-
 131
131
-
 132
132
-
 133
133
-
 134
134
-
 135
135
-
 136
136
-
 137
137
-
 138
138
-
 139
139
-
 140
140
-
 141
141
-
 142
142
-
 143
143
-
 144
144
-
 145
145
-
 146
146
-
 147
147
-
 148
148
-
 149
149
-
 150
150
-
 151
151
-
 152
152
-
 153
153
-
 154
154
-
 155
155
-
 156
156
-
 157
157
-
 158
158
-
 159
159
-
 160
160
-
 161
161
-
 162
162
-
 163
163
-
 164
164
-
 165
165
-
 166
166
-
 167
167
-
 168
168
-
 169
169
-
 170
170
Gerelateerde papieren
-
Dell Inspiron 530 de handleiding
-
Dell Inspiron 530S de handleiding
-
Dell Dimension C521 de handleiding
-
Dell Vostro 200 de handleiding
-
Dell Vostro 200 de handleiding
-
Dell Vostro 200 de handleiding
-
Dell XPS 210 de handleiding
-
Dell Dimension 9200C de handleiding
-
Dell Inspiron 531S de handleiding
-
Dell XPS 430 Handleiding